Kostas Margellos
Bridging conformal prediction and scenario optimization
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Conformal prediction and scenario optimization constitute two important classes of statistical learning frameworks to certify decisions made using data. They have found numerous applications in control theory, machine learning and robotics. Despite intense research in both areas, and apparently similar results, a clear connection between these two frameworks has not been established. By focusing on the so-called vanilla conformal prediction, we show rigorously how to choose appropriate score functions and set predictor map to recover well-known bounds on the probability of constraint violation associated with scenario programs. We also show how to treat ranking of nonconformity scores as a one-dimensional scenario program with discarded constraints, and use such connection to recover vanilla conformal prediction guarantees on the validity of the set predictor. We also capitalize on the main developments of the scenario approach, and show how we could analyze calibration conditional conformal prediction under this lens. Our results establish a theoretical bridge between conformal prediction and scenario optimization.
Finite sample learning of moving targets
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:We consider a moving target that we seek to learn from samples. Our results extend randomized techniques developed in control and optimization for a constant target to the case where the target is changing. We derive a novel bound on the number of samples that are required to construct a probably approximately correct (PAC) estimate of the target. Furthermore, when the moving target is a convex polytope, we provide a constructive method of generating the PAC estimate using a mixed integer linear program (MILP). The proposed method is demonstrated on an application to autonomous emergency braking.
Robust optimization for adversarial learning with finite sample complexity guarantees
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:Decision making and learning in the presence of uncertainty has attracted significant attention in view of the increasing need to achieve robust and reliable operations. In the case where uncertainty stems from the presence of adversarial attacks this need is becoming more prominent. In this paper we focus on linear and nonlinear classification problems and propose a novel adversarial training method for robust classifiers, inspired by Support Vector Machine (SVM) margins. We view robustness under a data driven lens, and derive finite sample complexity bounds for both linear and non-linear classifiers in binary and multi-class scenarios. Notably, our bounds match natural classifiers' complexity. Our algorithm minimizes a worst-case surrogate loss using Linear Programming (LP) and Second Order Cone Programming (SOCP) for linear and non-linear models. Numerical experiments on the benchmark MNIST and CIFAR10 datasets show our approach's comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods, without needing adversarial examples during training. Our work offers a comprehensive framework for enhancing binary linear and non-linear classifier robustness, embedding robustness in learning under the presence of adversaries.
Verification of safety critical control policies using kernel methods
Mar 23, 2022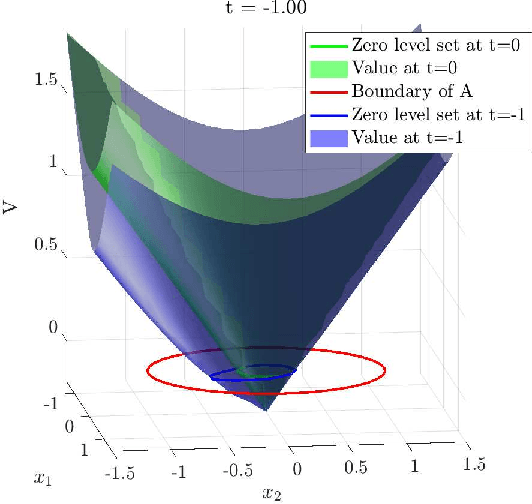
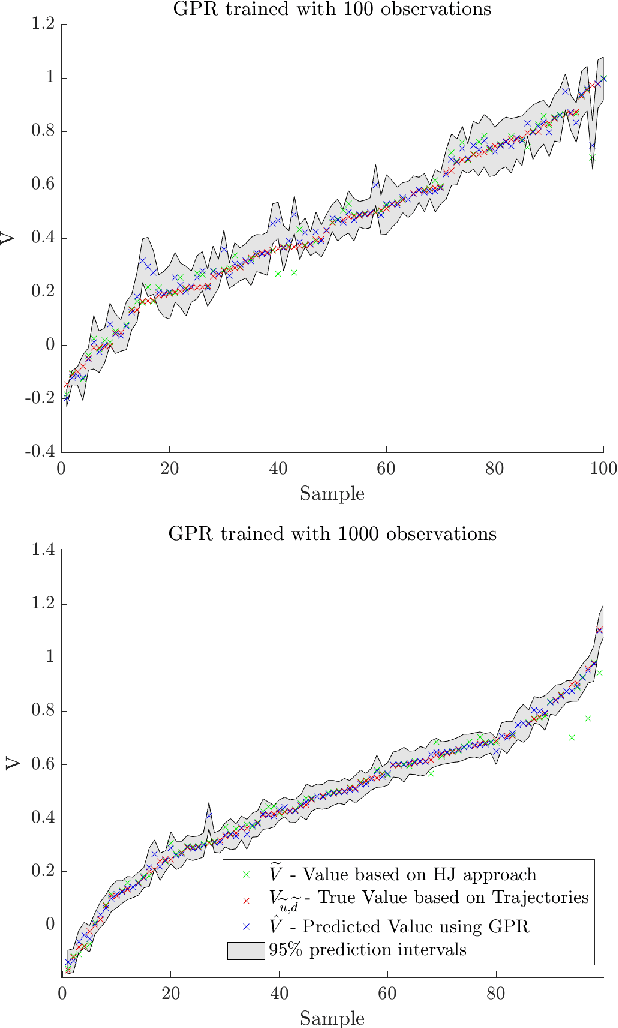
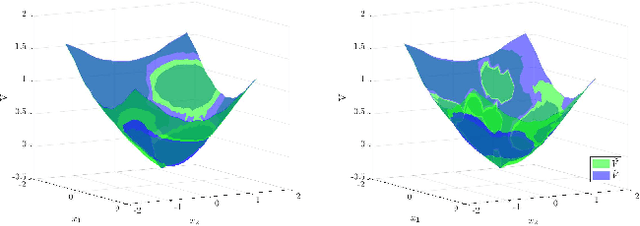
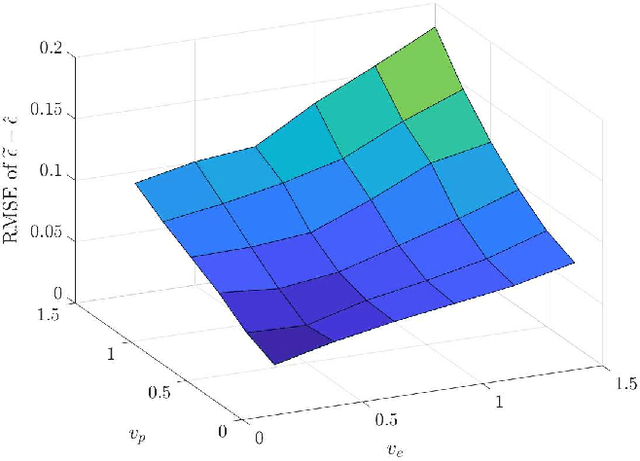
Abstract:Hamilton-Jacobi reachability methods for safety-critical control have been well studied, but the safety guarantees derived rely on the accuracy of the numerical computation. Thus, it is crucial to understand and account for any inaccuracies that occur due to uncertainty in the underlying dynamics and environment as well as the induced numerical errors. To this end, we propose a framework for modeling the error of the value function inherent in Hamilton-Jacobi reachability using a Gaussian process. The derived safety controller can be used in conjuncture with arbitrary controllers to provide a safe hybrid control law. The marginal likelihood of the Gaussian process then provides a confidence metric used to determine switches between a least restrictive controller and a safety controller. We test both the prediction as well as the correction capabilities of the presented method in a classical pursuit-evasion example.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge