Kong Wah Wan
Piecewise Linear De-skewing for LiDAR Inertial Odometry
Aug 13, 2021

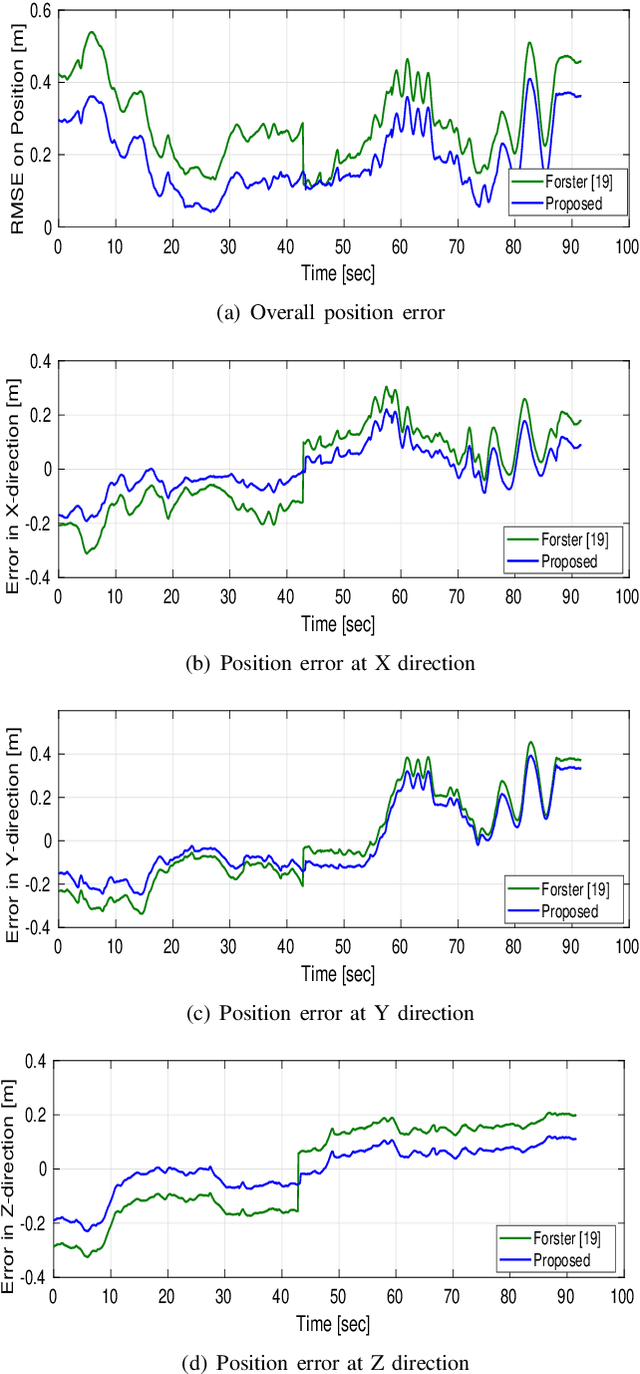
Abstract:Light detection and ranging (LiDAR) on a moving agent could suffer from motion distortion due to simultaneous rotation of the LiDAR and fast movement of the agent. An accurate piecewise linear de skewing algorithm is proposed to correct the motion distortions for LiDAR inertial odometry (LIO) using high frequency motion information provided by an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU). Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can be adopted to improve the performance of existing LIO algorithms especially in cases of fast movement.
Accurate IMU Preintegration Using Switched Linear Systems For Autonomous Systems
Jul 19, 2019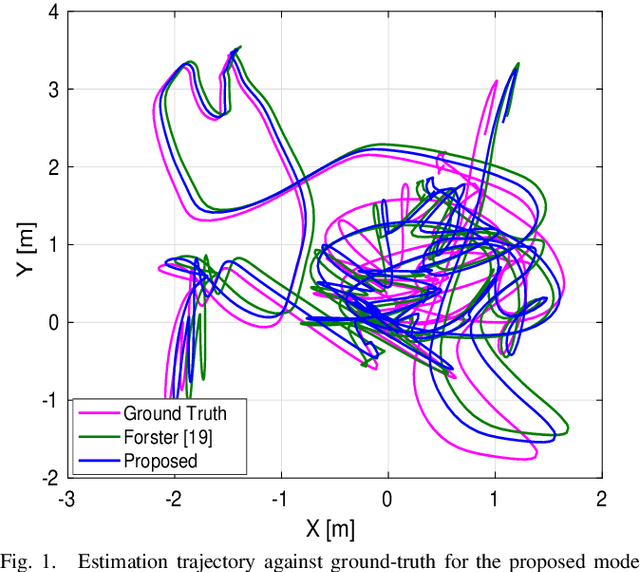
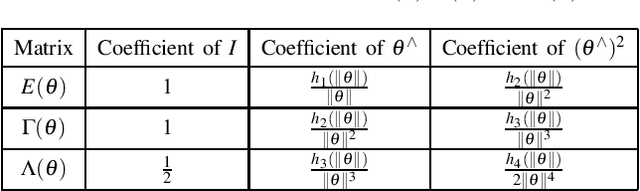
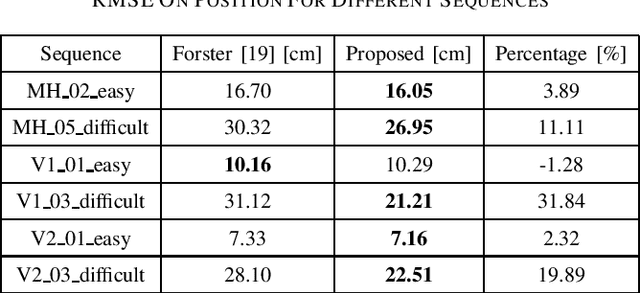
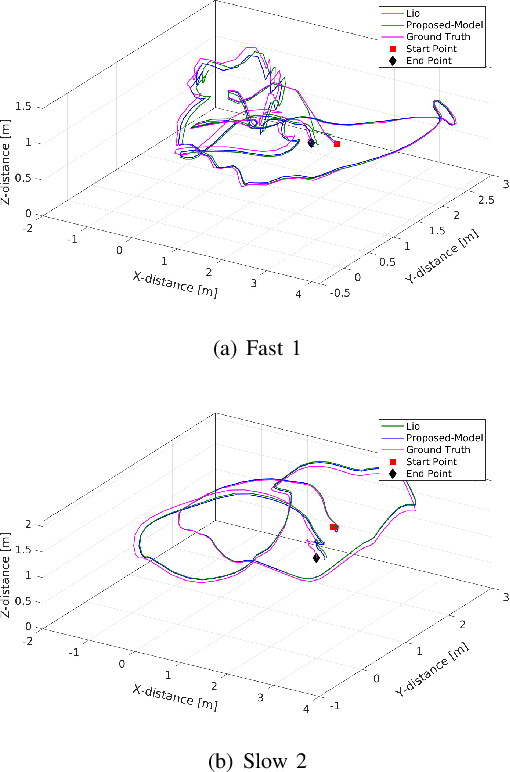
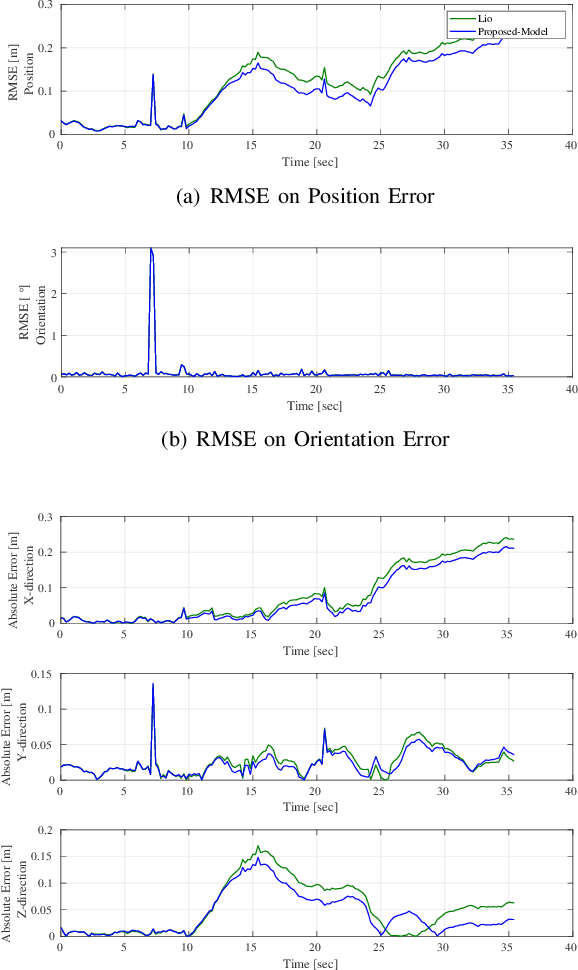
Abstract:Employing an inertial measurement unit (IMU) as an additional sensor can dramatically improve both reliability and accuracy of visual/Lidar odometry (VO/LO). Different IMU integration models are introduced using different assumptions on the linear acceleration from the IMU. In this paper, a novel IMU integration model is proposed by using switched linear systems. The proposed approach assumes that both the linear acceleration and the angular velocity in the body frame are constant between two consecutive IMU measurements. This is more realistic in real world situation compared to existing approaches which assume that linear acceleration is constant in the world frame while angular velocity is constant in the body frame between two successive IMU measurements. Experimental results show that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art IMU integration model. The proposed model is thus important for localization of high speed autonomous vehicles in GPS denied environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge