Kollipara Rithwik
Image Denoising using Optimally Weighted Bilateral Filters: A Sure and Fast Approach
May 25, 2015



Abstract:The bilateral filter is known to be quite effective in denoising images corrupted with small dosages of additive Gaussian noise. The denoising performance of the filter, however, is known to degrade quickly with the increase in noise level. Several adaptations of the filter have been proposed in the literature to address this shortcoming, but often at a substantial computational overhead. In this paper, we report a simple pre-processing step that can substantially improve the denoising performance of the bilateral filter, at almost no additional cost. The modified filter is designed to be robust at large noise levels, and often tends to perform poorly below a certain noise threshold. To get the best of the original and the modified filter, we propose to combine them in a weighted fashion, where the weights are chosen to minimize (a surrogate of) the oracle mean-squared-error (MSE). The optimally-weighted filter is thus guaranteed to perform better than either of the component filters in terms of the MSE, at all noise levels. We also provide a fast algorithm for the weighted filtering. Visual and quantitative denoising results on standard test images are reported which demonstrate that the improvement over the original filter is significant both visually and in terms of PSNR. Moreover, the denoising performance of the optimally-weighted bilateral filter is competitive with the computation-intensive non-local means filter.
A Simple Yet Effective Improvement to the Bilateral Filter for Image Denoising
May 25, 2015
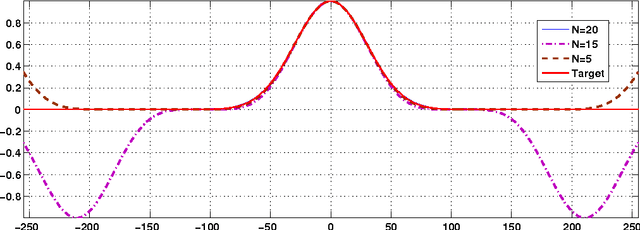
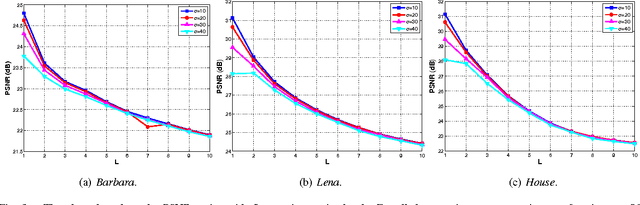
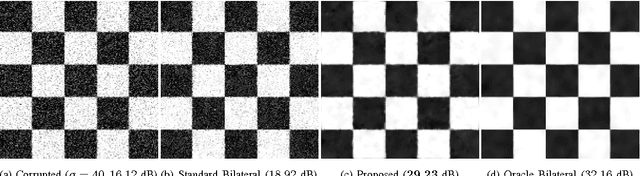
Abstract:The bilateral filter has diverse applications in image processing, computer vision, and computational photography. In particular, this non-linear filter is quite effective in denoising images corrupted with additive Gaussian noise. The filter, however, is known to perform poorly at large noise levels. Several adaptations of the filter have been proposed in the literature to address this shortcoming, but often at an added computational cost. In this paper, we report a simple yet effective modification that improves the denoising performance of the bilateral filter at almost no additional cost. We provide visual and quantitative results on standard test images which show that this improvement is significant both visually and in terms of PSNR and SSIM (often as large as 5 dB). We also demonstrate how the proposed filtering can be implemented at reduced complexity by adapting a recent idea for fast bilateral filtering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge