Kiran Menachery
Benchmarking real-time algorithms for in-phase auditory stimulation of low amplitude slow waves with wearable EEG devices during sleep
Mar 04, 2022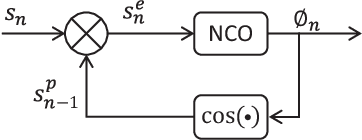
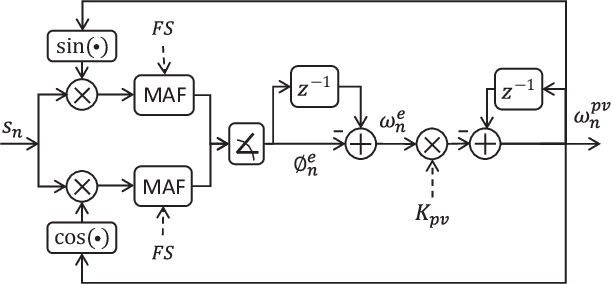
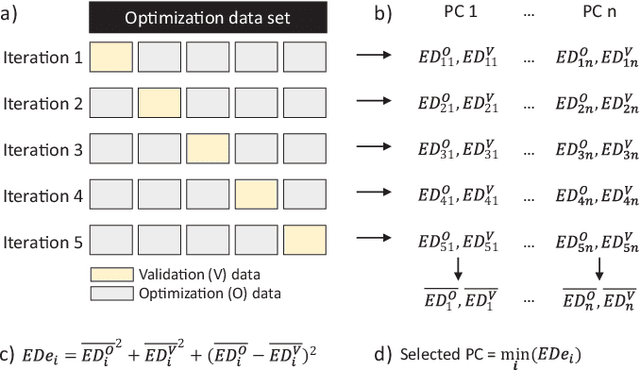
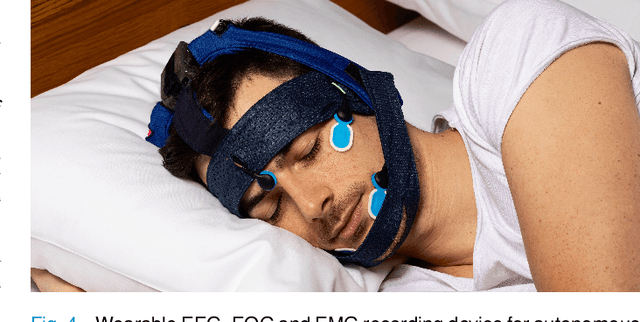
Abstract:Auditory stimulation of EEG slow waves (SW) during non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep has shown to improve cognitive function when it is delivered at the up-phase of SW. SW enhancement is particularly desirable in subjects with low-amplitude SW such as older adults or patients suffering from neurodegeneration such as Parkinson disease (PD). However, existing algorithms to estimate the up-phase suffer from a poor phase accuracy at low EEG amplitudes and when SW frequencies are not constant. We introduce two novel algorithms for real-time EEG phase estimation on autonomous wearable devices. The algorithms were based on a phase-locked loop (PLL) and, for the first time, a phase vocoder (PV). We compared these phase tracking algorithms with a simple amplitude threshold approach. The optimized algorithms were benchmarked for phase accuracy, the capacity to estimate phase at SW amplitudes between 20 and 60 microV, and SW frequencies above 1 Hz on 324 recordings from healthy older adults and PD patients. Furthermore, the algorithms were implemented on a wearable device and the computational efficiency and the performance was evaluated on simulated sleep EEG, as well as prospectively during a recording with a PD patient. All three algorithms delivered more than 70% of the stimulation triggers during the SW up-phase. The PV showed the highest capacity on targeting low-amplitude SW and SW with frequencies above 1 Hz. The testing on real-time hardware revealed that both PV and PLL have marginal impact on microcontroller load, while the efficiency of the PV was 4% lower than the PLL. Active auditory stimulation did not influence the phase tracking. This work demonstrated that phase-accurate auditory stimulation can be delivered during home-based sleep interventions with a wearable device also in populations with low-amplitude SW.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge