Khalid N. Elmadani
A Large and Balanced Corpus for Fine-grained Arabic Readability Assessment
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces the Balanced Arabic Readability Evaluation Corpus BAREC, a large-scale, fine-grained dataset for Arabic readability assessment. BAREC consists of 68,182 sentences spanning 1+ million words, carefully curated to cover 19 readability levels, from kindergarten to postgraduate comprehension. The corpus balances genre diversity, topical coverage, and target audiences, offering a comprehensive resource for evaluating Arabic text complexity. The corpus was fully manually annotated by a large team of annotators. The average pairwise inter-annotator agreement, measured by Quadratic Weighted Kappa, is 81.3%, reflecting a high level of substantial agreement. Beyond presenting the corpus, we benchmark automatic readability assessment across different granularity levels, comparing a range of techniques. Our results highlight the challenges and opportunities in Arabic readability modeling, demonstrating competitive performance across various methods. To support research and education, we will make BAREC openly available, along with detailed annotation guidelines and benchmark results.
Guidelines for Fine-grained Sentence-level Arabic Readability Annotation
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:This paper presents the foundational framework and initial findings of the Balanced Arabic Readability Evaluation Corpus (BAREC) project, designed to address the need for comprehensive Arabic language resources aligned with diverse readability levels. Inspired by the Taha/Arabi21 readability reference, BAREC aims to provide a standardized reference for assessing sentence-level Arabic text readability across 19 distinct levels, ranging in targets from kindergarten to postgraduate comprehension. Our ultimate goal with BAREC is to create a comprehensive and balanced corpus that represents a wide range of genres, topics, and regional variations through a multifaceted approach combining manual annotation with AI-driven tools. This paper focuses on our meticulous annotation guidelines, demonstrated through the analysis of 10,631 sentences/phrases (113,651 words). The average pairwise inter-annotator agreement, measured by Quadratic Weighted Kappa, is 79.9%, reflecting a high level of substantial agreement. We also report competitive results for benchmarking automatic readability assessment. We will make the BAREC corpus and guidelines openly accessible to support Arabic language research and education.
Masader Plus: A New Interface for Exploring +500 Arabic NLP Datasets
Aug 01, 2022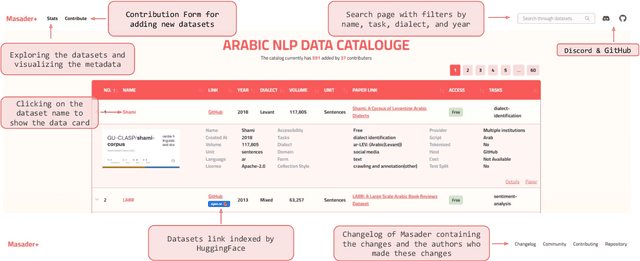
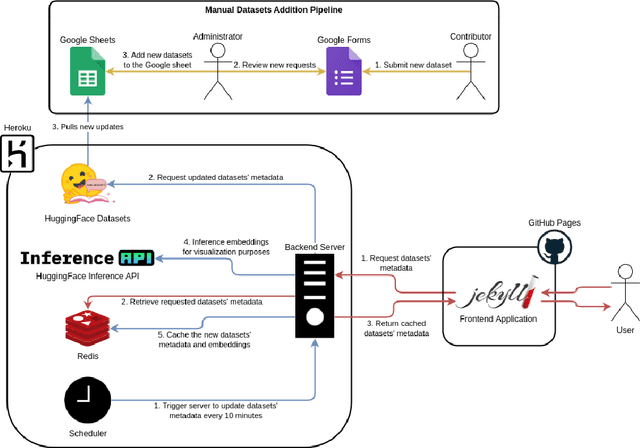
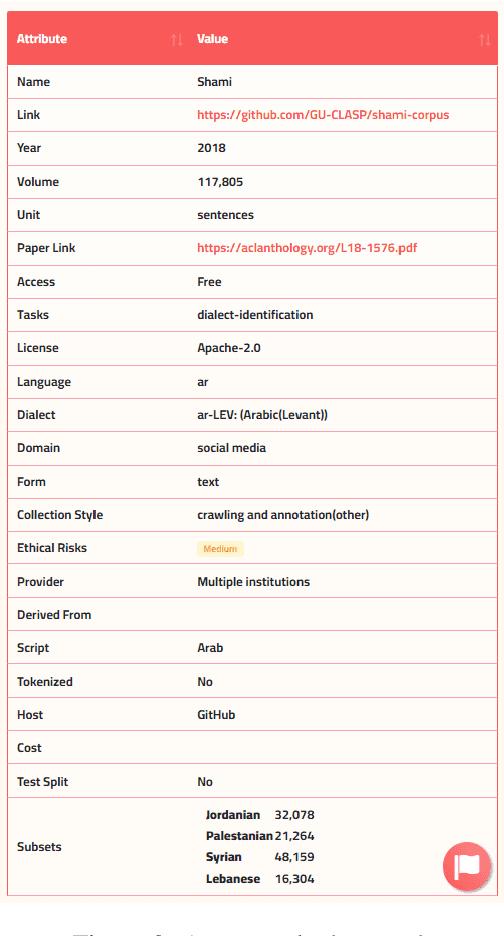
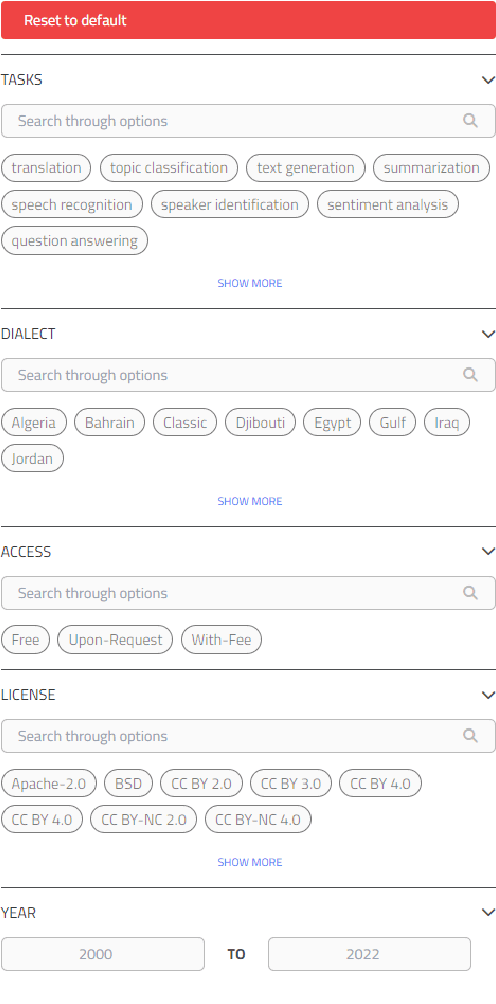
Abstract:Masader (Alyafeai et al., 2021) created a metadata structure to be used for cataloguing Arabic NLP datasets. However, developing an easy way to explore such a catalogue is a challenging task. In order to give the optimal experience for users and researchers exploring the catalogue, several design and user experience challenges must be resolved. Furthermore, user interactions with the website may provide an easy approach to improve the catalogue. In this paper, we introduce Masader Plus, a web interface for users to browse Masader. We demonstrate data exploration, filtration, and a simple API that allows users to examine datasets from the backend. Masader Plus can be explored using this link https://arbml.github.io/masader. A video recording explaining the interface can be found here https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SEtdlSeqchk.
BERT Fine-tuning For Arabic Text Summarization
Mar 29, 2020
Abstract:Fine-tuning a pretrained BERT model is the state of the art method for extractive/abstractive text summarization, in this paper we showcase how this fine-tuning method can be applied to the Arabic language to both construct the first documented model for abstractive Arabic text summarization and show its performance in Arabic extractive summarization. Our model works with multilingual BERT (as Arabic language does not have a pretrained BERT of its own). We show its performance in English corpus first before applying it to Arabic corpora in both extractive and abstractive tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge