Kevin Tomsovic
Towards Adversarial-Resilient Deep Neural Networks for False Data Injection Attack Detection in Power Grids
Feb 17, 2021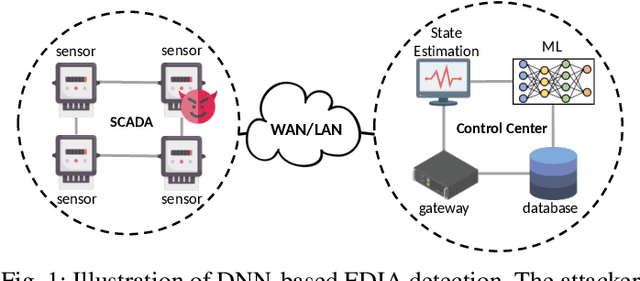
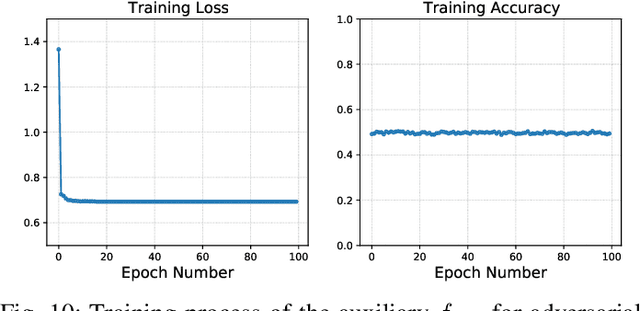
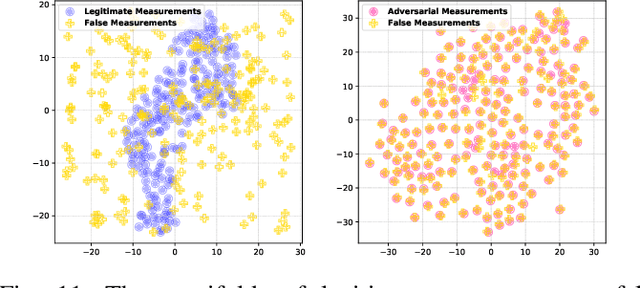
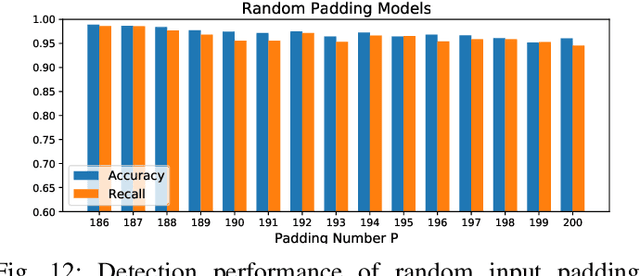
Abstract:False data injection attack (FDIA) is a critical security issue in power system state estimation. In recent years, machine learning (ML) techniques, especially deep neural networks (DNNs), have been proposed in the literature for FDIA detection. However, they have not considered the risk of adversarial attacks, which were shown to be threatening to DNN's reliability in different ML applications. In this paper, we evaluate the vulnerability of DNNs used for FDIA detection through adversarial attacks and study the defensive approaches. We analyze several representative adversarial defense mechanisms and demonstrate that they have intrinsic limitations in FDIA detection. We then design an adversarial-resilient DNN detection framework for FDIA by introducing random input padding in both the training and inference phases. Extensive simulations based on an IEEE standard power system show that our framework greatly reduces the effectiveness of adversarial attacks while having little impact on the detection performance of the DNNs.
ConAML: Constrained Adversarial Machine Learning for Cyber-Physical Systems
Mar 12, 2020
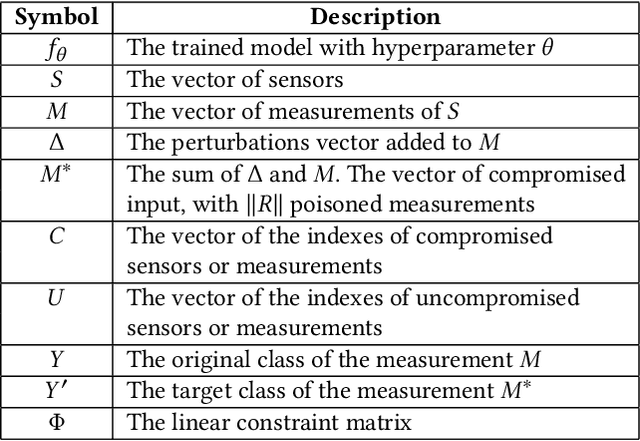
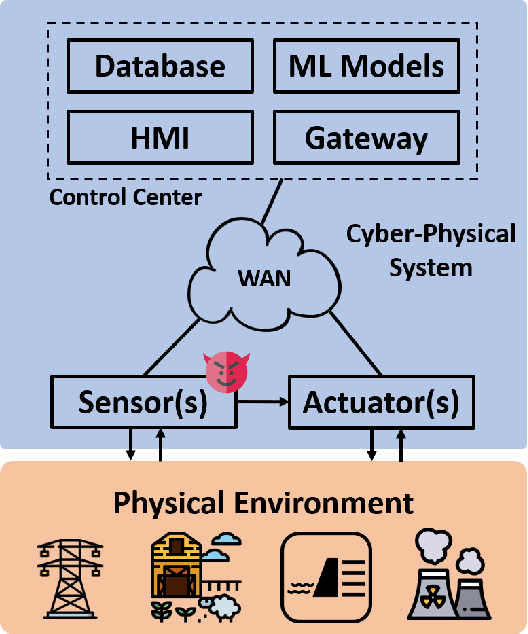

Abstract:Recent research demonstrated that the superficially well-trained machine learning (ML) models are highly vulnerable to adversarial examples. As ML techniques are rapidly employed in cyber-physical systems (CPSs), the security of these applications is of concern. However, current studies on adversarial machine learning (AML) mainly focus on computer vision and related fields. The risks the adversarial examples can bring to the CPS applications have not been well investigated. In particular, due to the distributed property of data sources and the inherent physical constraints imposed by CPSs, the widely-used threat models in previous research and the state-of-the-art AML algorithms are no longer practical when applied to CPS applications. We study the vulnerabilities of ML applied in CPSs by proposing Constrained Adversarial Machine Learning (ConAML), which generates adversarial examples used as ML model input that meet the intrinsic constraints of the physical systems. We first summarize the difference between AML in CPSs and AML in existing cyber systems and propose a general threat model for ConAML. We then design a best-effort search algorithm to iteratively generate adversarial examples with linear physical constraints. As proofs of concept, we evaluate the vulnerabilities of ML models used in the electric power grid and water treatment systems. The results show that our ConAML algorithms can effectively generate adversarial examples which significantly decrease the performance of the ML models even under practical physical constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge