Kevin Tee
Practical Bayesian optimization in the presence of outliers
Dec 12, 2017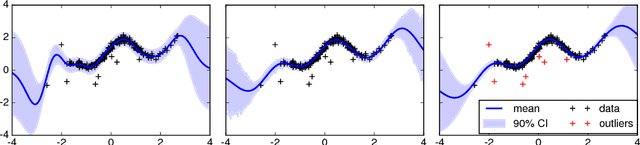
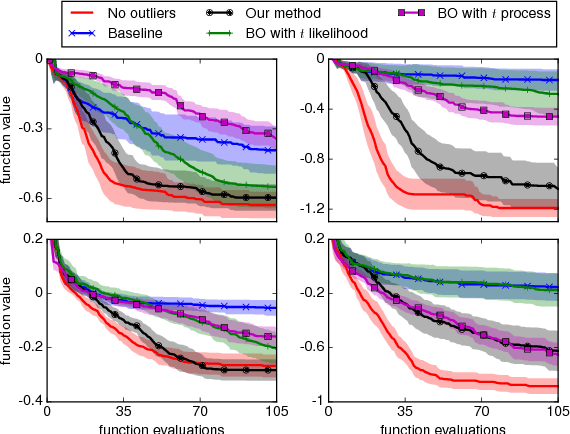
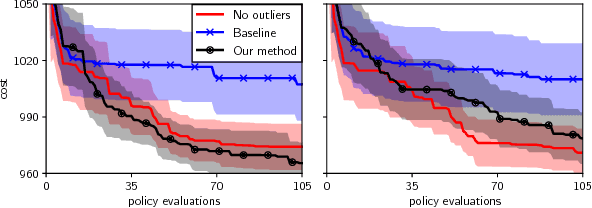
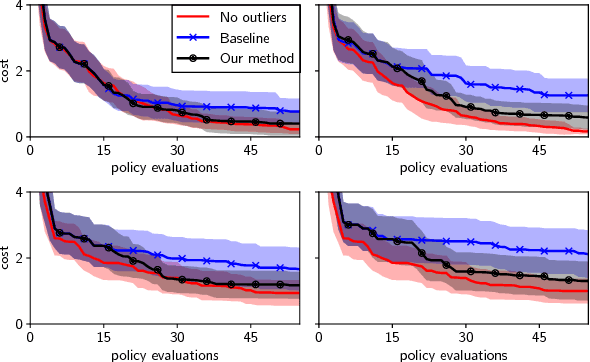
Abstract:Inference in the presence of outliers is an important field of research as outliers are ubiquitous and may arise across a variety of problems and domains. Bayesian optimization is method that heavily relies on probabilistic inference. This allows outstanding sample efficiency because the probabilistic machinery provides a memory of the whole optimization process. However, that virtue becomes a disadvantage when the memory is populated with outliers, inducing bias in the estimation. In this paper, we present an empirical evaluation of Bayesian optimization methods in the presence of outliers. The empirical evidence shows that Bayesian optimization with robust regression often produces suboptimal results. We then propose a new algorithm which combines robust regression (a Gaussian process with Student-t likelihood) with outlier diagnostics to classify data points as outliers or inliers. By using an scheduler for the classification of outliers, our method is more efficient and has better convergence over the standard robust regression. Furthermore, we show that even in controlled situations with no expected outliers, our method is able to produce better results.
Robust Bayesian Optimization with Student-t Likelihood
Jul 18, 2017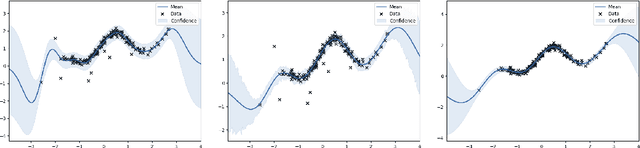
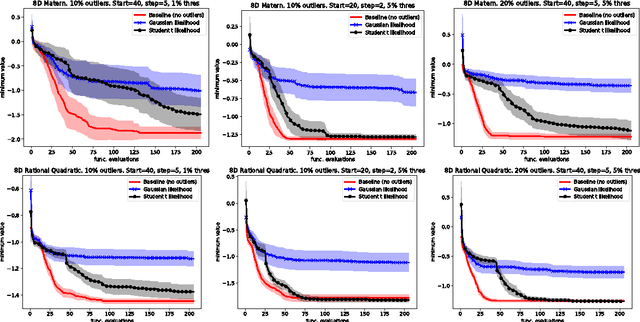
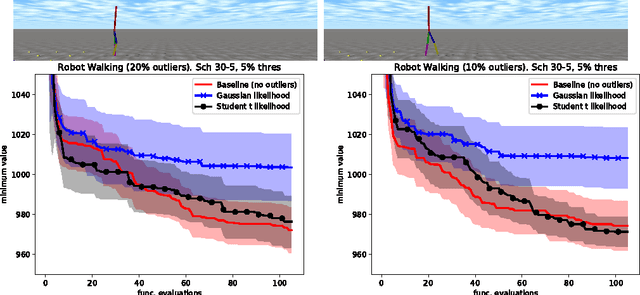
Abstract:Bayesian optimization has recently attracted the attention of the automatic machine learning community for its excellent results in hyperparameter tuning. BO is characterized by the sample efficiency with which it can optimize expensive black-box functions. The efficiency is achieved in a similar fashion to the learning to learn methods: surrogate models (typically in the form of Gaussian processes) learn the target function and perform intelligent sampling. This surrogate model can be applied even in the presence of noise; however, as with most regression methods, it is very sensitive to outlier data. This can result in erroneous predictions and, in the case of BO, biased and inefficient exploration. In this work, we present a GP model that is robust to outliers which uses a Student-t likelihood to segregate outliers and robustly conduct Bayesian optimization. We present numerical results evaluating the proposed method in both artificial functions and real problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge