Keval Morabia
CoVA: Context-aware Visual Attention for Webpage Information Extraction
Oct 24, 2021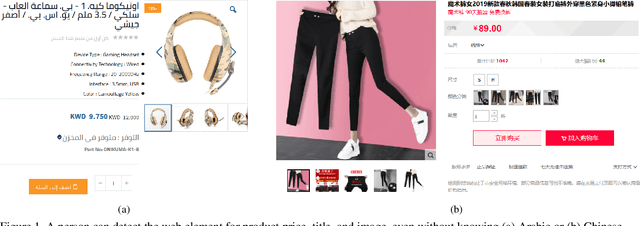
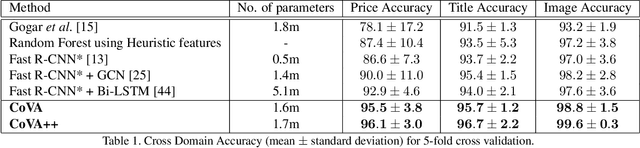
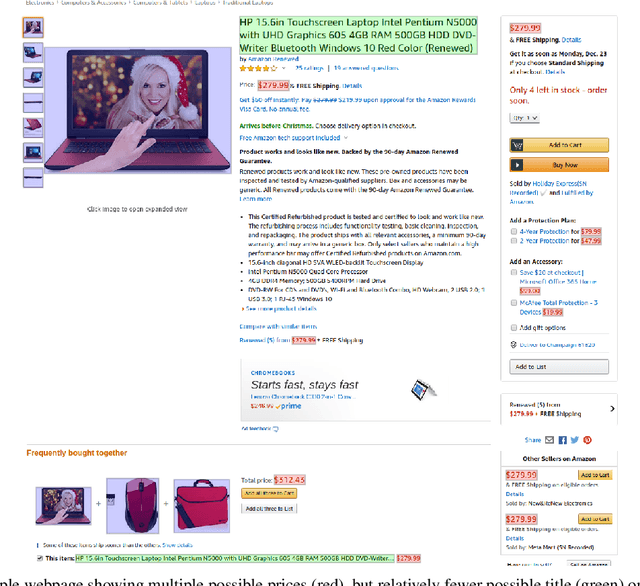
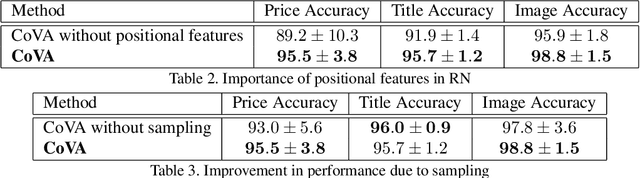
Abstract:Webpage information extraction (WIE) is an important step to create knowledge bases. For this, classical WIE methods leverage the Document Object Model (DOM) tree of a website. However, use of the DOM tree poses significant challenges as context and appearance are encoded in an abstract manner. To address this challenge we propose to reformulate WIE as a context-aware Webpage Object Detection task. Specifically, we develop a Context-aware Visual Attention-based (CoVA) detection pipeline which combines appearance features with syntactical structure from the DOM tree. To study the approach we collect a new large-scale dataset of e-commerce websites for which we manually annotate every web element with four labels: product price, product title, product image and background. On this dataset we show that the proposed CoVA approach is a new challenging baseline which improves upon prior state-of-the-art methods.
Attention-based Joint Detection of Object and Semantic Part
Jul 05, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of joint detection of objects like dog and its semantic parts like face, leg, etc. Our model is created on top of two Faster-RCNN models that share their features to perform a novel Attention-based feature fusion of related Object and Part features to get enhanced representations of both. These representations are used for final classification and bounding box regression separately for both models. Our experiments on the PASCAL-Part 2010 dataset show that joint detection can simultaneously improve both object detection and part detection in terms of mean Average Precision (mAP) at IoU=0.5.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge