Kerstin Fischer
Making Sense of Robots in Public Spaces: A Study of Trash Barrel Robots
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:In this work, we analyze video data and interviews from a public deployment of two trash barrel robots in a large public space to better understand the sensemaking activities people perform when they encounter robots in public spaces. Based on an analysis of 274 human-robot interactions and interviews with N=65 individuals or groups, we discovered that people were responding not only to the robots or their behavior, but also to the general idea of deploying robots as trashcans, and the larger social implications of that idea. They wanted to understand details about the deployment because having that knowledge would change how they interact with the robot. Based on our data and analysis, we have provided implications for design that may be topics for future human-robot design researchers who are exploring robots for public space deployment. Furthermore, our work offers a practical example of analyzing field data to make sense of robots in public spaces.
Trust regulation in Social Robotics: From Violation to Repair
Apr 20, 2023
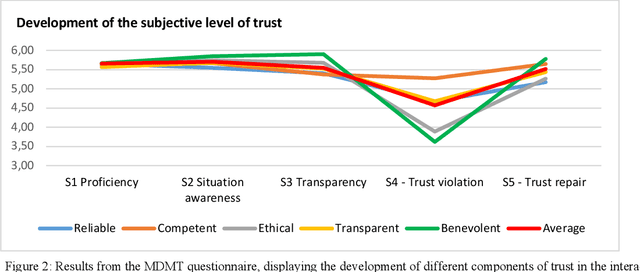
Abstract:While trust in human-robot interaction is increasingly recognized as necessary for the implementation of social robots, our understanding of regulating trust in human-robot interaction is yet limited. In the current experiment, we evaluated different approaches to trust calibration in human-robot interaction. The within-subject experimental approach utilized five different strategies for trust calibration: proficiency, situation awareness, transparency, trust violation, and trust repair. We implemented these interventions into a within-subject experiment where participants (N=24) teamed up with a social robot and played a collaborative game. The level of trust was measured after each section using the Multi-Dimensional Measure of Trust (MDMT) scale. As expected, the interventions have a significant effect on i) violating and ii) repairing the level of trust throughout the interaction. Consequently, the robot demonstrating situation awareness was perceived as significantly more benevolent than the baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge