Kazufumi Kobashi
Multimodal Machine Learning for Integrating Heterogeneous Analytical Systems
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Understanding structure-property relationships in complex materials requires integrating complementary measurements across multiple length scales. Here we propose an interpretable "multimodal" machine learning framework that unifies heterogeneous analytical systems for end-to-end characterization, demonstrated on carbon nanotube (CNT) films whose properties are highly sensitive to microstructural variations. Quantitative morphology descriptors are extracted from SEM images via binarization, skeletonization, and network analysis, capturing curvature, orientation, intersection density, and void geometry. These SEM-derived features are fused with Raman indicators of crystallinity/defect states, specific surface area from gas adsorption, and electrical surface resistivity. Multi-dimensional visualization using radar plots and UMAP reveals clear clustering of CNT films according to crystallinity and entanglements. Regression models trained on the multimodal feature set show that nonlinear approaches, particularly XGBoost, achieve the best predictive accuracy under leave-one-out cross-validation. Feature-importance analysis further provides physically meaningful interpretations: surface resistivity is primarily governed by junction-to-junction transport length scales, crystallinity/defect-related metrics, and network connectivity, whereas specific surface area is dominated by intersection density and void size. The proposed multimodal machine learning framework offers a general strategy for data-driven, explainable characterization of complex materials.
Tabular Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis for Multifaceted Characterization Data
Nov 27, 2023

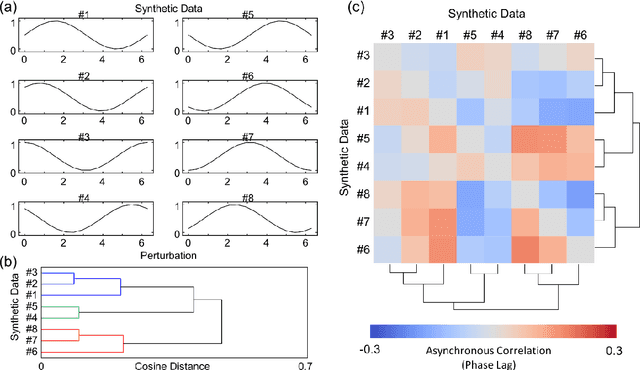
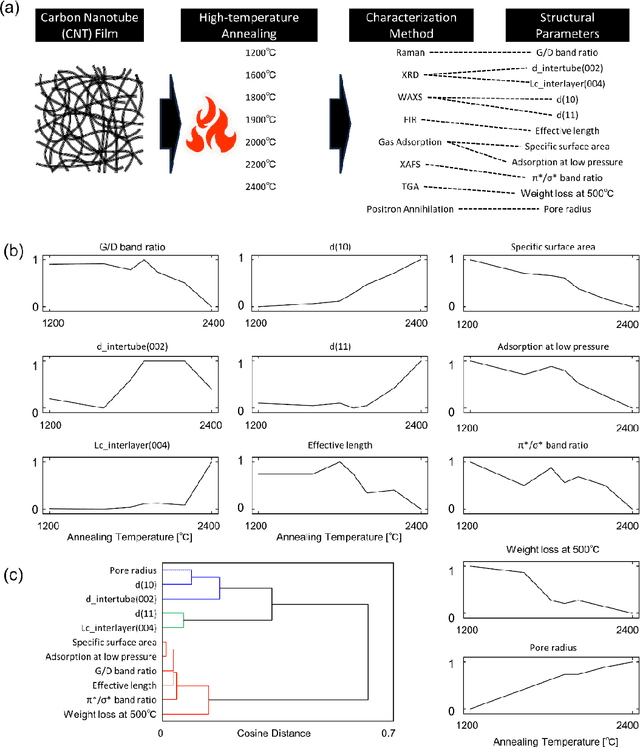
Abstract:We propose tabular two-dimensional correlation analysis for extracting features from multifaceted characterization data, essential for understanding material properties. This method visualizes similarities and phase lags in structural parameter changes through heatmaps, combining hierarchical clustering and asynchronous correlations. We applied the proposed method to datasets of carbon nanotube (CNTs) films annealed at various temperatures and revealed the complexity of their hierarchical structures, which include elements like voids, bundles, and amorphous carbon. Our analysis addresses the challenge of attempting to understand the sequence of structural changes, especially in multifaceted characterization data where 11 structural parameters derived from 8 characterization methods interact with complex behavior. The results show how phase lags (asynchronous changes from stimuli) and parameter similarities can illuminate the sequence of structural changes in materials, providing insights into phenomena like the removal of amorphous carbon and graphitization in annealed CNTs. This approach is beneficial even with limited data and holds promise for a wide range of material analyses, demonstrating its potential in elucidating complex material behaviors and properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge