Katja Kossira
Towards Object Segmentation Mask Selection Using Specular Reflections
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:Specular reflections pose a significant challenge for object segmentation, as their sharp intensity transitions often mislead both conventional algorithms and deep learning based methods. However, as the specular reflection must lie on the surface of the object, this fact can be exploited to improve the segmentation masks. By identifying the largest region containing the reflection as the object, we derive a more accurate object mask without requiring specialized training data or model adaption. We evaluate our method on both synthetic and real world images and compare it against established and state-of-the-art techniques including Otsu thresholding, YOLO, and SAM2. Compared to the best performing baseline SAM2, our approach achieves up to 26.7% improvement in IoU, 22.3% in DSC, and 9.7% in pixel accuracy. Qualitative evaluations on real world images further confirm the robustness and generalizability of the proposed approach.
Inter-Camera Color Correction for Multispectral Imaging with Camera Arrays Using a Consensus Image
Oct 30, 2024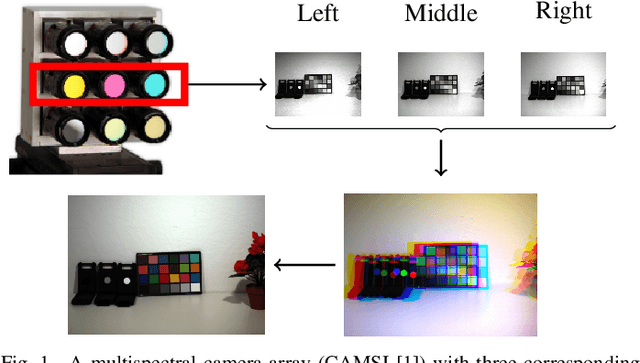
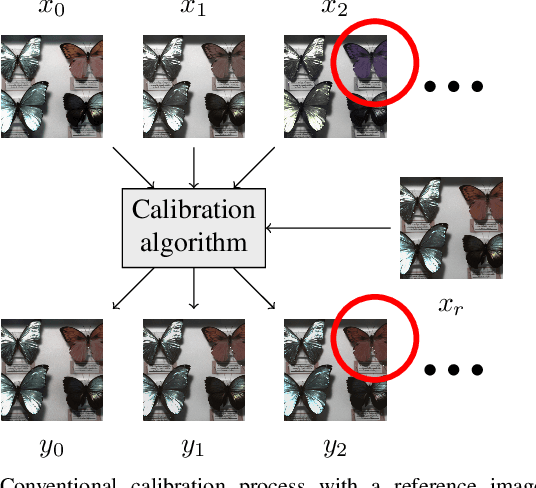
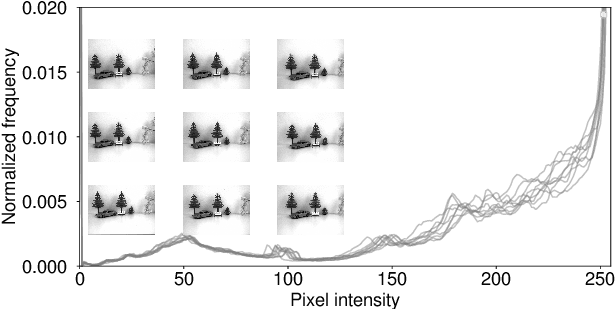

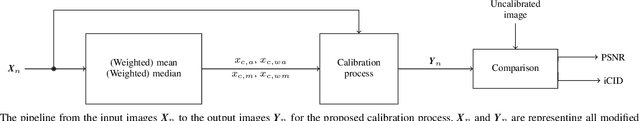
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel method for inter-camera color calibration for multispectral imaging with camera arrays using a consensus image. Capturing images using multispectral camera arrays has gained importance in medical, agricultural, and environmental processes. Due to fabrication differences, noise, or device altering, varying pixel sensitivities occur, influencing classification processes. Therefore, color calibration between the cameras is necessary. In existing methods, one of the camera images is chosen and considered as a reference, ignoring the color information of all other recordings. Our new approach does not just take one image as reference, but uses statistical information such as the location parameter to generate a consensus image as basis for calibration. This way, we managed to improve the PSNR values for the linear regression color correction algorithm by 1.15 dB and the improved color difference (iCID) values by 2.81.
Conditional Optimal Filter Selection for Multispectral Object Classification
Oct 02, 2024
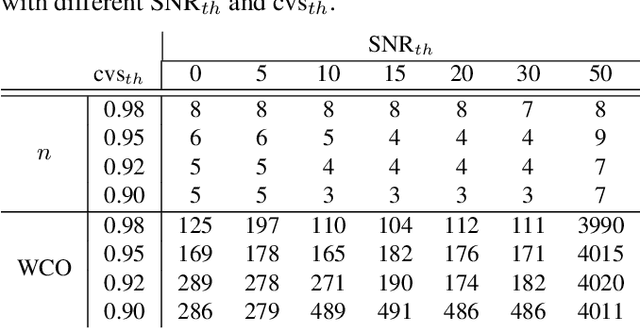
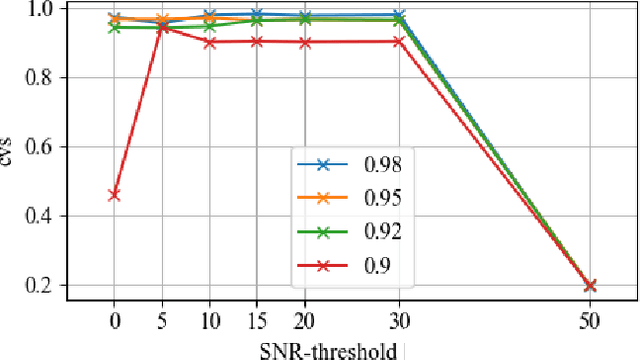
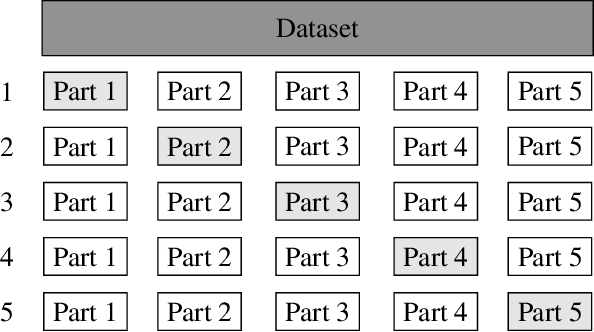
Abstract:Capturing images using multispectral camera arrays has gained importance in medical, agricultural and environmental processes. However, using all available spectral bands is infeasible and produces much data, while only a fraction is needed for a given task. Nearby bands may contain similar information, therefore redundant spectral bands should not be considered in the evaluation process to keep complexity and the data load low. In current methods, a restricted and pre-determined number of spectral bands is selected. Our approach improves this procedure by including preset conditions such as noise or the bandwidth of available filters, minimizing spectral redundancy. Furthermore, a minimal filter selection can be conducted, keeping the hardware setup at low costs, while still obtaining all important spectral information. In comparison to the fast binary search filter band selection method, we managed to reduce the amount of misclassified objects of the SMM dataset from 318 to 124 using a random forest classifier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge