Conditional Optimal Filter Selection for Multispectral Object Classification
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2024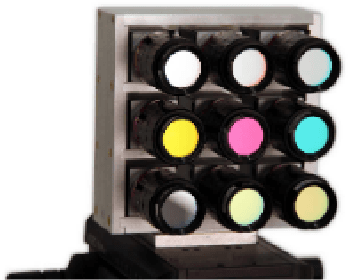
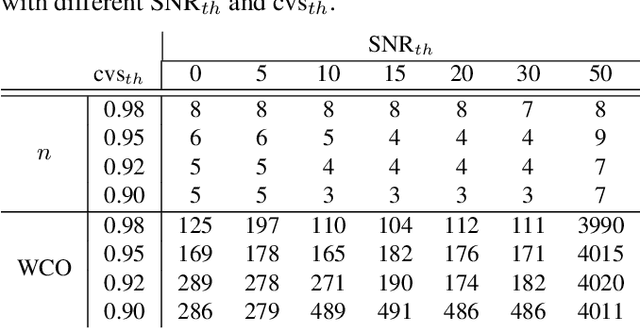
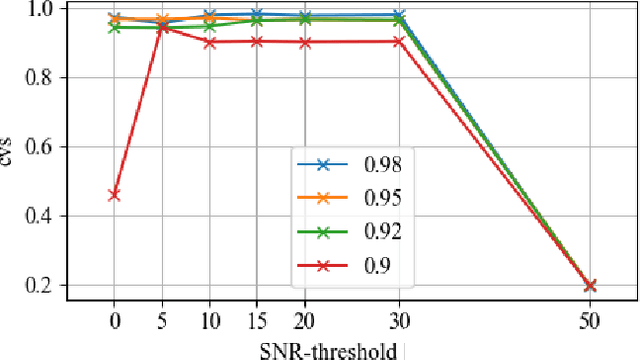
Capturing images using multispectral camera arrays has gained importance in medical, agricultural and environmental processes. However, using all available spectral bands is infeasible and produces much data, while only a fraction is needed for a given task. Nearby bands may contain similar information, therefore redundant spectral bands should not be considered in the evaluation process to keep complexity and the data load low. In current methods, a restricted and pre-determined number of spectral bands is selected. Our approach improves this procedure by including preset conditions such as noise or the bandwidth of available filters, minimizing spectral redundancy. Furthermore, a minimal filter selection can be conducted, keeping the hardware setup at low costs, while still obtaining all important spectral information. In comparison to the fast binary search filter band selection method, we managed to reduce the amount of misclassified objects of the SMM dataset from 318 to 124 using a random forest classifier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge