Kathy Baxter
The Risks of Machine Learning Systems
Apr 21, 2022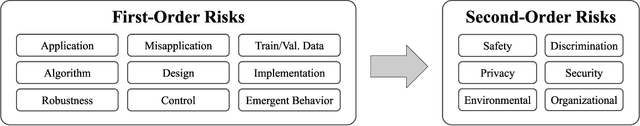
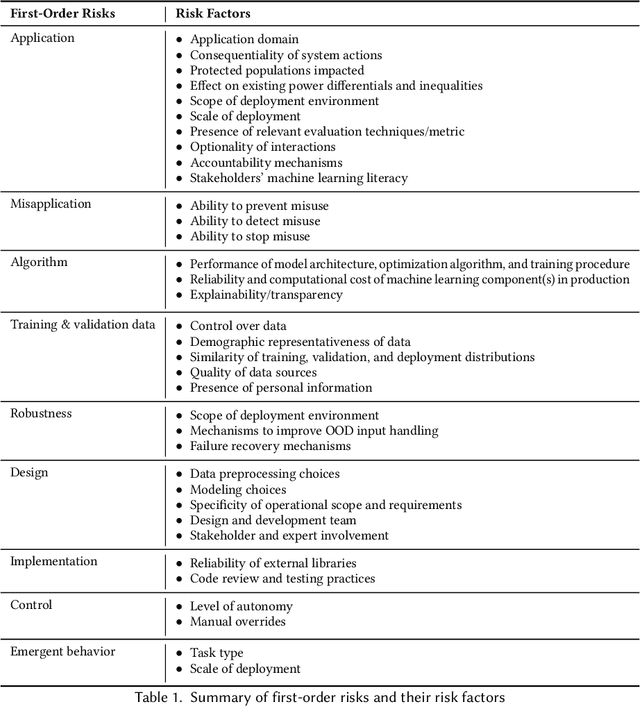
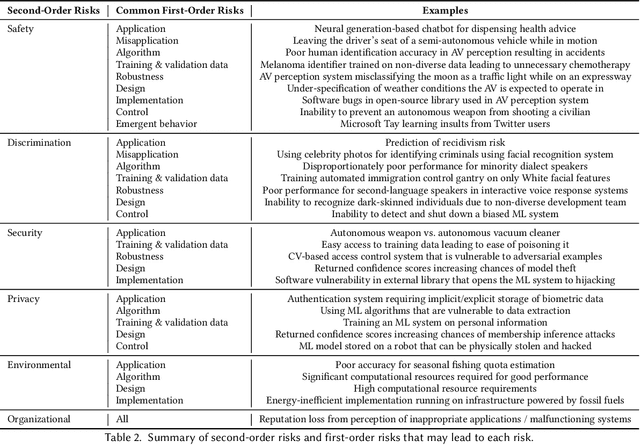
Abstract:The speed and scale at which machine learning (ML) systems are deployed are accelerating even as an increasing number of studies highlight their potential for negative impact. There is a clear need for companies and regulators to manage the risk from proposed ML systems before they harm people. To achieve this, private and public sector actors first need to identify the risks posed by a proposed ML system. A system's overall risk is influenced by its direct and indirect effects. However, existing frameworks for ML risk/impact assessment often address an abstract notion of risk or do not concretize this dependence. We propose to address this gap with a context-sensitive framework for identifying ML system risks comprising two components: a taxonomy of the first- and second-order risks posed by ML systems, and their contributing factors. First-order risks stem from aspects of the ML system, while second-order risks stem from the consequences of first-order risks. These consequences are system failures that result from design and development choices. We explore how different risks may manifest in various types of ML systems, the factors that affect each risk, and how first-order risks may lead to second-order effects when the system interacts with the real world. Throughout the paper, we show how real events and prior research fit into our Machine Learning System Risk framework (MLSR). MLSR operates on ML systems rather than technologies or domains, recognizing that a system's design, implementation, and use case all contribute to its risk. In doing so, it unifies the risks that are commonly discussed in the ethical AI community (e.g., ethical/human rights risks) with system-level risks (e.g., application, design, control risks), paving the way for holistic risk assessments of ML systems.
Reliability Testing for Natural Language Processing Systems
Jun 01, 2021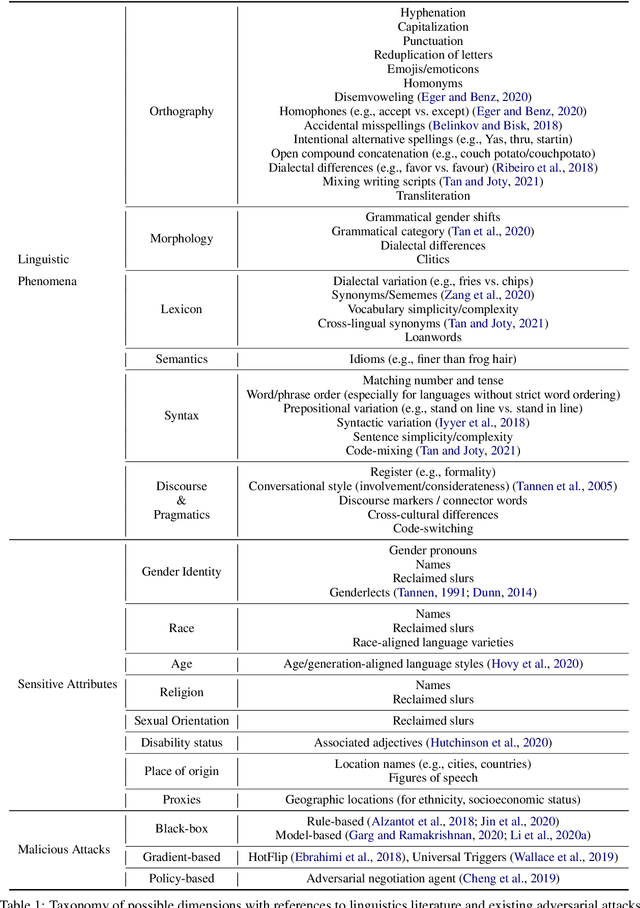
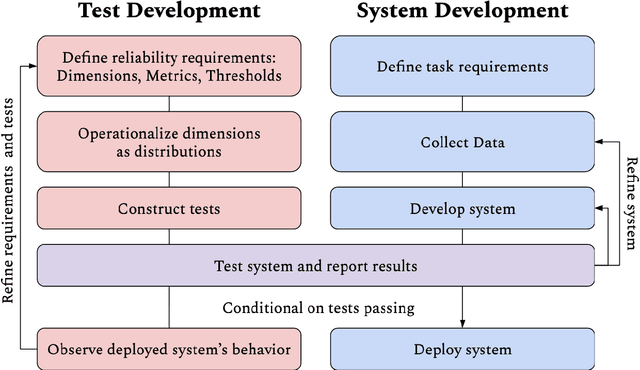
Abstract:Questions of fairness, robustness, and transparency are paramount to address before deploying NLP systems. Central to these concerns is the question of reliability: Can NLP systems reliably treat different demographics fairly and function correctly in diverse and noisy environments? To address this, we argue for the need for reliability testing and contextualize it among existing work on improving accountability. We show how adversarial attacks can be reframed for this goal, via a framework for developing reliability tests. We argue that reliability testing -- with an emphasis on interdisciplinary collaboration -- will enable rigorous and targeted testing, and aid in the enactment and enforcement of industry standards.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge