Kartik Krishna
Finite Time Lyapunov Exponent Analysis of Model Predictive Control and Reinforcement Learning
Apr 14, 2023



Abstract:Finite-time Lyapunov exponents (FTLEs) provide a powerful approach to compute time-varying analogs of invariant manifolds in unsteady fluid flow fields. These manifolds are useful to visualize the transport mechanisms of passive tracers advecting with the flow. However, many vehicles and mobile sensors are not passive, but are instead actuated according to some intelligent trajectory planning or control law; for example, model predictive control and reinforcement learning are often used to design energy-efficient trajectories in a dynamically changing background flow. In this work, we investigate the use of FTLE on such controlled agents to gain insight into optimal transport routes for navigation in known unsteady flows. We find that these controlled FTLE (cFTLE) coherent structures separate the flow field into different regions with similar costs of transport to the goal location. These separatrices are functions of the planning algorithm's hyper-parameters, such as the optimization time horizon and the cost of actuation. Computing the invariant sets and manifolds of active agent dynamics in dynamic flow fields is useful in the context of robust motion control, hyperparameter tuning, and determining safe and collision-free trajectories for autonomous systems. Moreover, these cFTLE structures provide insight into effective deployment locations for mobile agents with actuation and energy constraints to traverse the ocean or atmosphere.
Finite-Horizon, Energy-Optimal Trajectories in Unsteady Flows
Mar 18, 2021
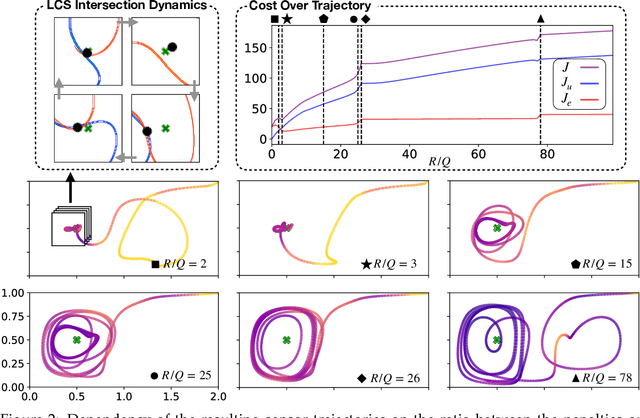
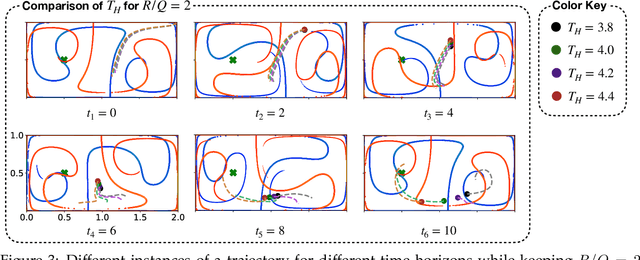
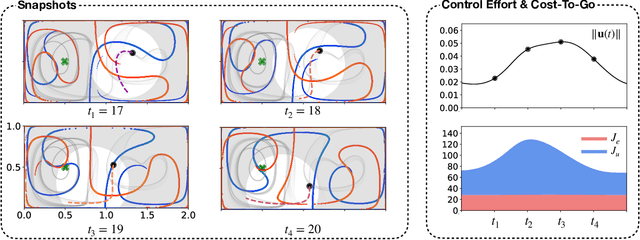
Abstract:Intelligent mobile sensors, such as uninhabited aerial or underwater vehicles, are becoming prevalent in environmental sensing and monitoring applications. These active sensing platforms operate in unsteady fluid flows, including windy urban environments, hurricanes, and ocean currents. Often constrained in their actuation capabilities, the dynamics of these mobile sensors depend strongly on the background flow, making their deployment and control particularly challenging. Therefore, efficient trajectory planning with partial knowledge about the background flow is essential for teams of mobile sensors to adaptively sense and monitor their environments. In this work, we investigate the use of finite-horizon model predictive control (MPC) for the energy-efficient trajectory planning of an active mobile sensor in an unsteady fluid flow field. We uncover connections between the finite-time optimal trajectories and finite-time Lyapunov exponents (FTLE) of the background flow, confirming that energy-efficient trajectories exploit invariant coherent structures in the flow. We demonstrate our findings on the unsteady double gyre vector field, which is a canonical model for chaotic mixing in the ocean. We present an exhaustive search through critical MPC parameters including the prediction horizon, maximum sensor actuation, and relative penalty on the accumulated state error and actuation effort. We find that even relatively short prediction horizons can often yield nearly energy-optimal trajectories. These results are promising for the adaptive planning of energy-efficient trajectories for swarms of mobile sensors in distributed sensing and monitoring.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge