Karl Åström
The Impact of Semi-Supervised Learning on Line Segment Detection
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we present a method for line segment detection in images, based on a semi-supervised framework. Leveraging the use of a consistency loss based on differently augmented and perturbed unlabeled images with a small amount of labeled data, we show comparable results to fully supervised methods. This opens up application scenarios where annotation is difficult or expensive, and for domain specific adaptation of models. We are specifically interested in real-time and online applications, and investigate small and efficient learning backbones. Our method is to our knowledge the first to target line detection using modern state-of-the-art methodologies for semi-supervised learning. We test the method on both standard benchmarks and domain specific scenarios for forestry applications, showing the tractability of the proposed method.
Learning Multi-Target TDOA Features for Sound Event Localization and Detection
Aug 30, 2024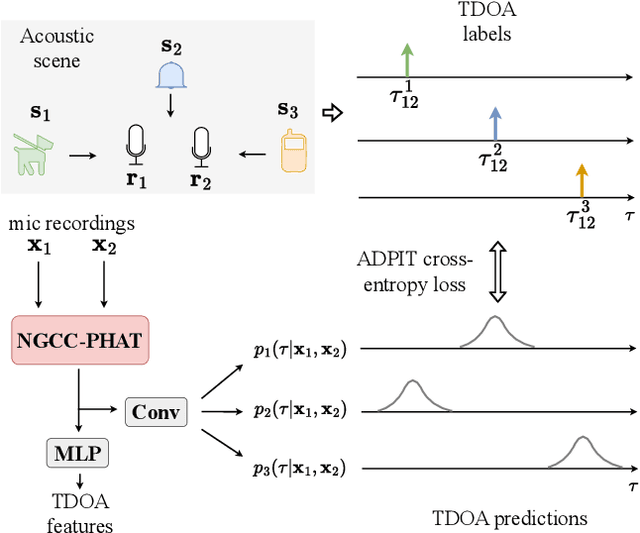
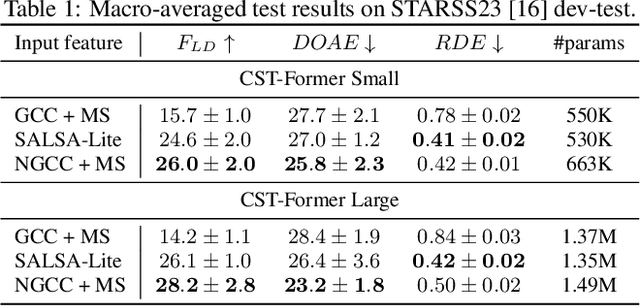
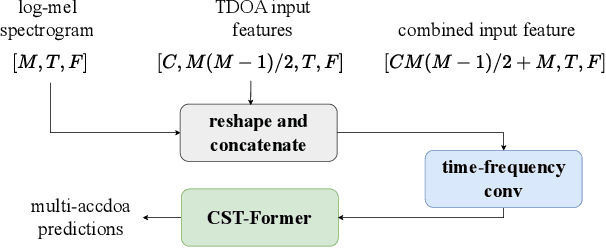
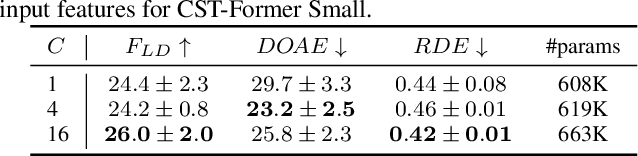
Abstract:Sound event localization and detection (SELD) systems using audio recordings from a microphone array rely on spatial cues for determining the location of sound events. As a consequence, the localization performance of such systems is to a large extent determined by the quality of the audio features that are used as inputs to the system. We propose a new feature, based on neural generalized cross-correlations with phase-transform (NGCC-PHAT), that learns audio representations suitable for localization. Using permutation invariant training for the time-difference of arrival (TDOA) estimation problem enables NGCC-PHAT to learn TDOA features for multiple overlapping sound events. These features can be used as a drop-in replacement for GCC-PHAT inputs to a SELD-network. We test our method on the STARSS23 dataset and demonstrate improved localization performance compared to using standard GCC-PHAT or SALSA-Lite input features.
wav2pos: Sound Source Localization using Masked Autoencoders
Aug 28, 2024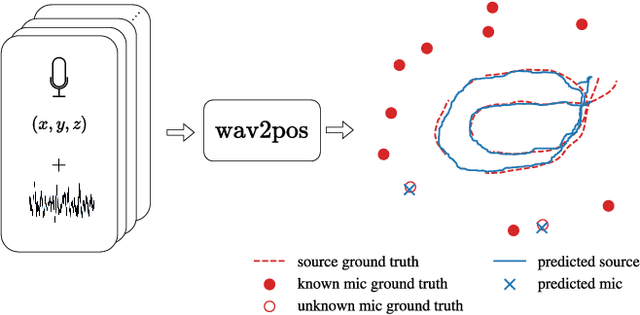
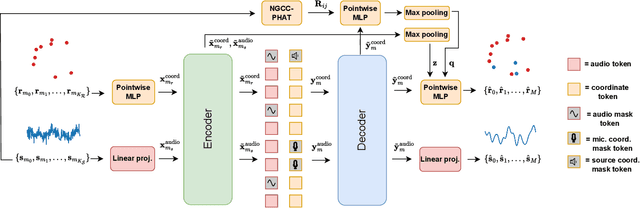
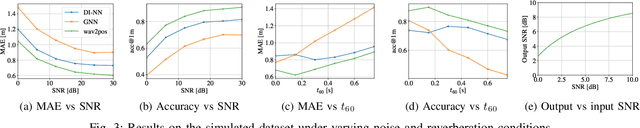

Abstract:We present a novel approach to the 3D sound source localization task for distributed ad-hoc microphone arrays by formulating it as a set-to-set regression problem. By training a multi-modal masked autoencoder model that operates on audio recordings and microphone coordinates, we show that such a formulation allows for accurate localization of the sound source, by reconstructing coordinates masked in the input. Our approach is flexible in the sense that a single model can be used with an arbitrary number of microphones, even when a subset of audio recordings and microphone coordinates are missing. We test our method on simulated and real-world recordings of music and speech in indoor environments, and demonstrate competitive performance compared to both classical and other learning based localization methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge