Kang He
Kling-Omni Technical Report
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:We present Kling-Omni, a generalist generative framework designed to synthesize high-fidelity videos directly from multimodal visual language inputs. Adopting an end-to-end perspective, Kling-Omni bridges the functional separation among diverse video generation, editing, and intelligent reasoning tasks, integrating them into a holistic system. Unlike disjointed pipeline approaches, Kling-Omni supports a diverse range of user inputs, including text instructions, reference images, and video contexts, processing them into a unified multimodal representation to deliver cinematic-quality and highly-intelligent video content creation. To support these capabilities, we constructed a comprehensive data system that serves as the foundation for multimodal video creation. The framework is further empowered by efficient large-scale pre-training strategies and infrastructure optimizations for inference. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that Kling-Omni demonstrates exceptional capabilities in in-context generation, reasoning-based editing, and multimodal instruction following. Moving beyond a content creation tool, we believe Kling-Omni is a pivotal advancement toward multimodal world simulators capable of perceiving, reasoning, generating and interacting with the dynamic and complex worlds.
KlingAvatar 2.0 Technical Report
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Avatar video generation models have achieved remarkable progress in recent years. However, prior work exhibits limited efficiency in generating long-duration high-resolution videos, suffering from temporal drifting, quality degradation, and weak prompt following as video length increases. To address these challenges, we propose KlingAvatar 2.0, a spatio-temporal cascade framework that performs upscaling in both spatial resolution and temporal dimension. The framework first generates low-resolution blueprint video keyframes that capture global semantics and motion, and then refines them into high-resolution, temporally coherent sub-clips using a first-last frame strategy, while retaining smooth temporal transitions in long-form videos. To enhance cross-modal instruction fusion and alignment in extended videos, we introduce a Co-Reasoning Director composed of three modality-specific large language model (LLM) experts. These experts reason about modality priorities and infer underlying user intent, converting inputs into detailed storylines through multi-turn dialogue. A Negative Director further refines negative prompts to improve instruction alignment. Building on these components, we extend the framework to support ID-specific multi-character control. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model effectively addresses the challenges of efficient, multimodally aligned long-form high-resolution video generation, delivering enhanced visual clarity, realistic lip-teeth rendering with accurate lip synchronization, strong identity preservation, and coherent multimodal instruction following.
LogicTree: Structured Proof Exploration for Coherent and Rigorous Logical Reasoning with Large Language Models
Apr 18, 2025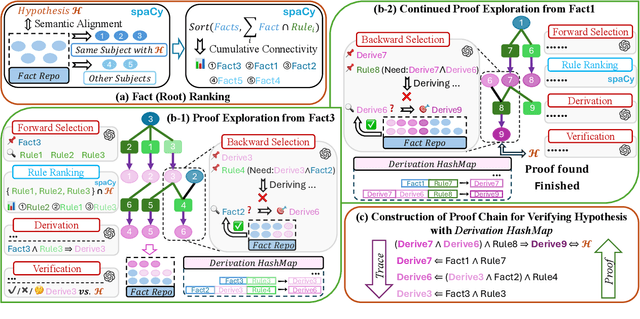
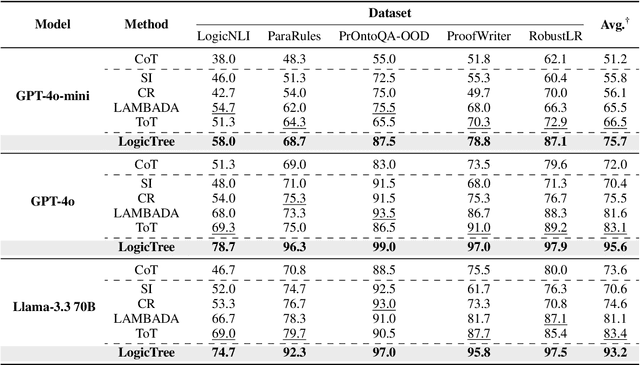
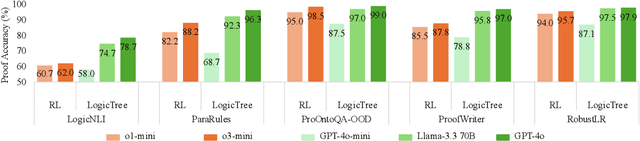
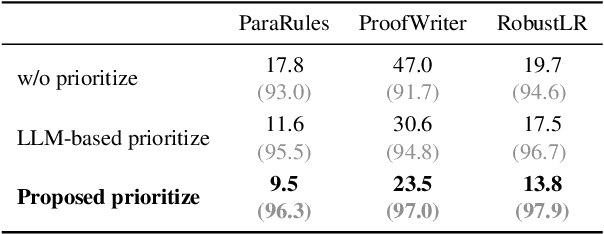
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable multi-step reasoning capabilities across various domains. However, LLMs still face distinct challenges in complex logical reasoning, as (1) proof-finding requires systematic exploration and the maintenance of logical coherence and (2) searching the right combination of premises at each reasoning step is inherently challenging in tasks with large premise space. To address this, we propose LogicTree, an inference-time modular framework employing algorithm-guided search to automate structured proof exploration and ensure logical coherence. Advancing beyond tree-of-thought (ToT), we incorporate caching mechanism into LogicTree to enable effective utilization of historical knowledge, preventing reasoning stagnation and minimizing redundancy. Furthermore, we address the combinatorial complexity of premise search by decomposing it into a linear process. The refined premise selection restricts subsequent inference to at most one derivation per step, enhancing reasoning granularity and enforcing strict step-by-step reasoning. Additionally, we introduce two LLM-free heuristics for premise prioritization, enabling strategic proof search. Experimental results on five datasets demonstrate that LogicTree optimally scales inference-time computation to achieve higher proof accuracy, surpassing chain-of-thought (CoT) and ToT with average gains of 23.6% and 12.5%, respectively, on GPT-4o. Moreover, within LogicTree, GPT-4o outperforms o3-mini by 7.6% on average.
Prompt-Based Bias Calibration for Better Zero/Few-Shot Learning of Language Models
Feb 15, 2024Abstract:Prompt learning is susceptible to intrinsic bias present in pre-trained language models (LMs), resulting in sub-optimal performance of prompt-based zero/few-shot learning. In this work, we propose a null-input prompting method to calibrate intrinsic bias encoded in pre-trained LMs. Different from prior efforts that address intrinsic bias primarily for social fairness and often involve excessive computational cost, our objective is to explore enhancing LMs' performance in downstream zero/few-shot learning while emphasizing the efficiency of intrinsic bias calibration. Specifically, we leverage a diverse set of auto-selected null-meaning inputs generated from GPT-4 to prompt pre-trained LMs for intrinsic bias probing. Utilizing the bias-reflected probability distribution, we formulate a distribution disparity loss for bias calibration, where we exclusively update bias parameters ($0.1\%$ of total parameters) of LMs towards equal probability distribution. Experimental results show that the calibration promotes an equitable starting point for LMs while preserving language modeling abilities. Across a wide range of datasets, including sentiment analysis and topic classification, our method significantly improves zero/few-shot learning performance of LMs for both in-context learning and prompt-based fine-tuning (on average $9\%$ and $2\%$, respectively).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge