Kai-Yueh Chang
Compatibility Family Learning for Item Recommendation and Generation
Dec 02, 2017
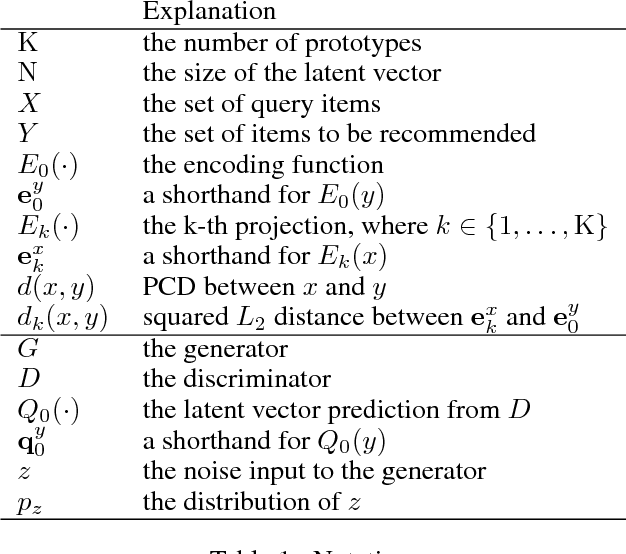
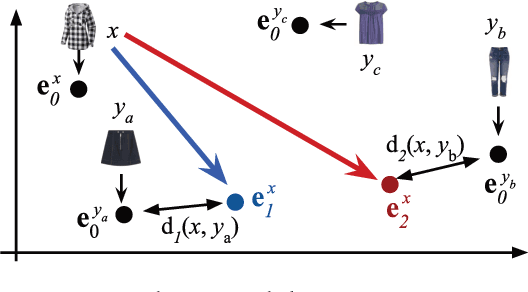
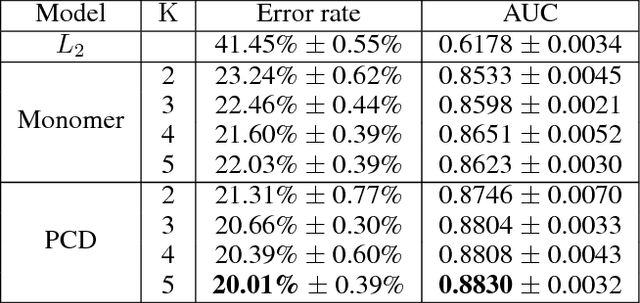
Abstract:Compatibility between items, such as clothes and shoes, is a major factor among customer's purchasing decisions. However, learning "compatibility" is challenging due to (1) broader notions of compatibility than those of similarity, (2) the asymmetric nature of compatibility, and (3) only a small set of compatible and incompatible items are observed. We propose an end-to-end trainable system to embed each item into a latent vector and project a query item into K compatible prototypes in the same space. These prototypes reflect the broad notions of compatibility. We refer to both the embedding and prototypes as "Compatibility Family". In our learned space, we introduce a novel Projected Compatibility Distance (PCD) function which is differentiable and ensures diversity by aiming for at least one prototype to be close to a compatible item, whereas none of the prototypes are close to an incompatible item. We evaluate our system on a toy dataset, two Amazon product datasets, and Polyvore outfit dataset. Our method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance. Finally, we show that we can visualize the candidate compatible prototypes using a Metric-regularized Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (MrCGAN), where the input is a projected prototype and the output is a generated image of a compatible item. We ask human evaluators to judge the relative compatibility between our generated images and images generated by CGANs conditioned directly on query items. Our generated images are significantly preferred, with roughly twice the number of votes as others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge