Kai Gan
Boosting Consistency in Dual Training for Long-Tailed Semi-Supervised Learning
Jun 19, 2024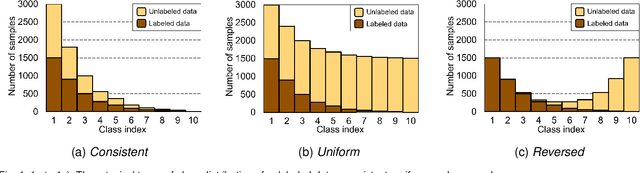
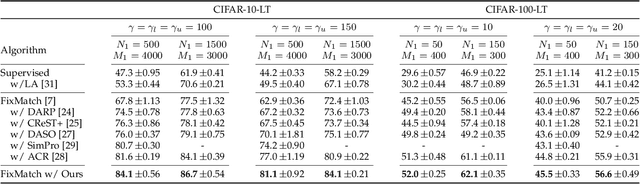
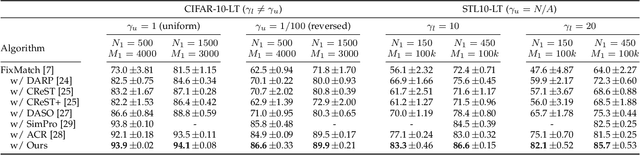
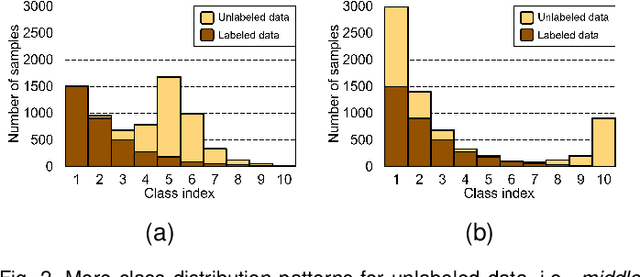
Abstract:While long-tailed semi-supervised learning (LTSSL) has received tremendous attention in many real-world classification problems, existing LTSSL algorithms typically assume that the class distributions of labeled and unlabeled data are almost identical. Those LTSSL algorithms built upon the assumption can severely suffer when the class distributions of labeled and unlabeled data are mismatched since they utilize biased pseudo-labels from the model. To alleviate this problem, we propose a new simple method that can effectively utilize unlabeled data from unknown class distributions through Boosting cOnsistency in duAl Training (BOAT). Specifically, we construct the standard and balanced branch to ensure the performance of the head and tail classes, respectively. Throughout the training process, the two branches incrementally converge and interact with each other, eventually resulting in commendable performance across all classes. Despite its simplicity, we show that BOAT achieves state-of-the-art performance on a variety of standard LTSSL benchmarks, e.g., an averaged 2.7% absolute increase in test accuracy against existing algorithms when the class distributions of labeled and unlabeled data are mismatched. Even when the class distributions are identical, BOAT consistently outperforms many sophisticated LTSSL algorithms. We carry out extensive ablation studies to tease apart the factors that are the most important to the success of BOAT. The source code is available at https://github.com/Gank0078/BOAT.
Erasing the Bias: Fine-Tuning Foundation Models for Semi-Supervised Learning
May 20, 2024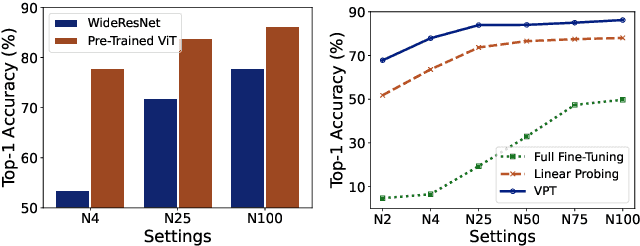
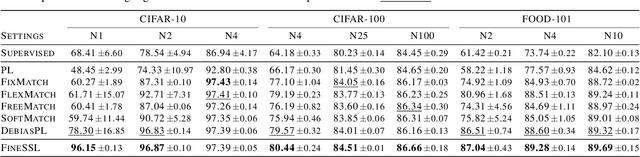
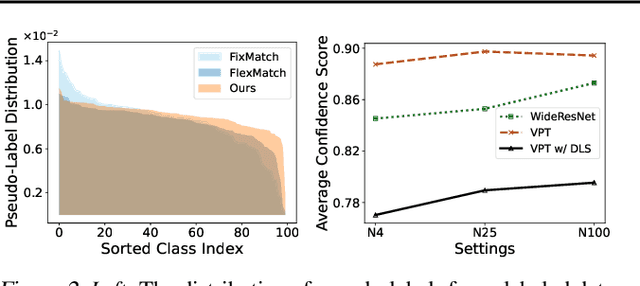
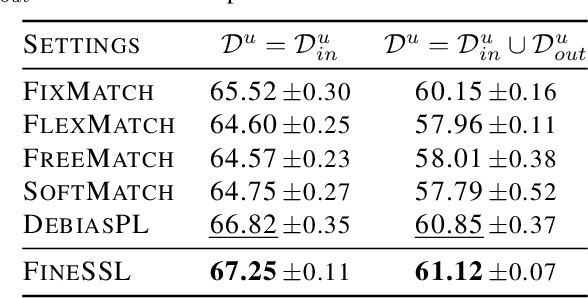
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has witnessed remarkable progress, resulting in the emergence of numerous method variations. However, practitioners often encounter challenges when attempting to deploy these methods due to their subpar performance. In this paper, we present a novel SSL approach named FineSSL that significantly addresses this limitation by adapting pre-trained foundation models. We identify the aggregated biases and cognitive deviation problems inherent in foundation models, and propose a simple yet effective solution by imposing balanced margin softmax and decoupled label smoothing. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that FineSSL sets a new state of the art for SSL on multiple benchmark datasets, reduces the training cost by over six times, and can seamlessly integrate various fine-tuning and modern SSL algorithms. The source code is available at https://github.com/Gank0078/FineSSL.
Bridging the Gap: Learning Pace Synchronization for Open-World Semi-Supervised Learning
Sep 21, 2023Abstract:In open-world semi-supervised learning, a machine learning model is tasked with uncovering novel categories from unlabeled data while maintaining performance on seen categories from labeled data. The central challenge is the substantial learning gap between seen and novel categories, as the model learns the former faster due to accurate supervisory information. To address this, we introduce 1) an adaptive margin loss based on estimated class distribution, which encourages a large negative margin for samples in seen classes, to synchronize learning paces, and 2) pseudo-label contrastive clustering, which pulls together samples which are likely from the same class in the output space, to enhance novel class discovery. Our extensive evaluations on multiple datasets demonstrate that existing models still hinder novel class learning, whereas our approach strikingly balances both seen and novel classes, achieving a remarkable 3% average accuracy increase on the ImageNet dataset compared to the prior state-of-the-art. Additionally, we find that fine-tuning the self-supervised pre-trained backbone significantly boosts performance over the default in prior literature. After our paper is accepted, we will release the code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge