Joyce Xu
Understanding Adversarial Robustness Through Loss Landscape Geometries
Jul 22, 2019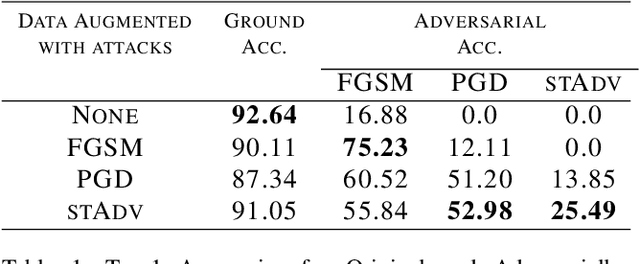
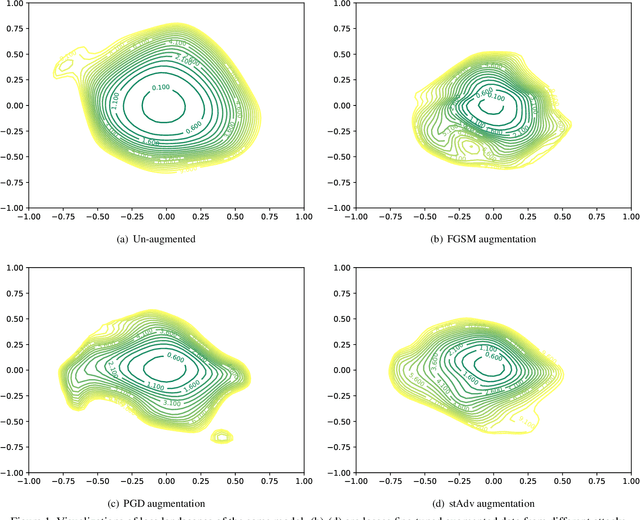

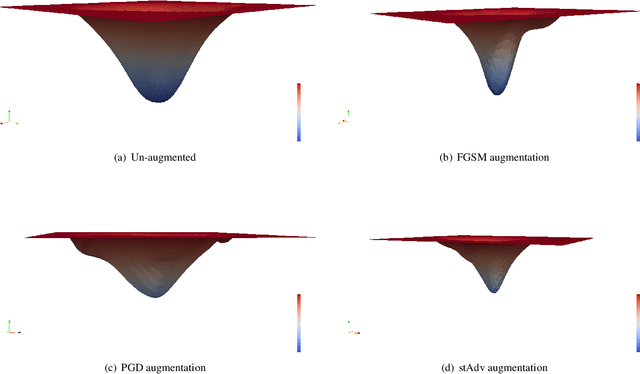
Abstract:The pursuit of explaining and improving generalization in deep learning has elicited efforts both in regularization techniques as well as visualization techniques of the loss surface geometry. The latter is related to the intuition prevalent in the community that flatter local optima leads to lower generalization error. In this paper, we harness the state-of-the-art "filter normalization" technique of loss-surface visualization to qualitatively understand the consequences of using adversarial training data augmentation as the explicit regularization technique of choice. Much to our surprise, we discover that this oft deployed adversarial augmentation technique does not actually result in "flatter" loss-landscapes, which requires rethinking adversarial training generalization, and the relationship between generalization and loss landscapes geometries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge