José-Luis Blanco-Claraco
MultiVehicle Simulator (MVSim): lightweight dynamics simulator for multiagents and mobile robotics research
Feb 21, 2023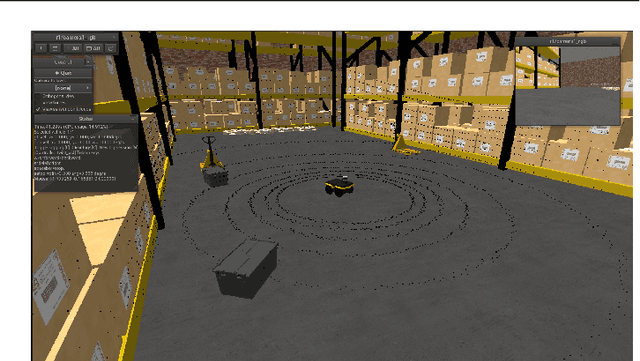
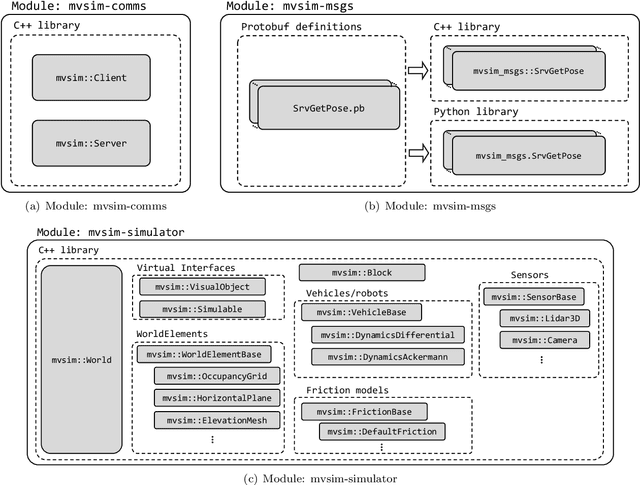
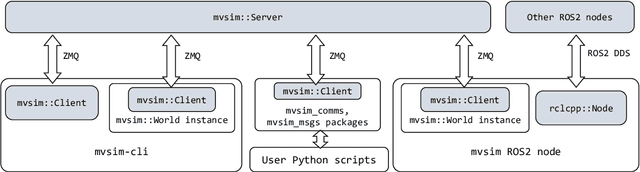
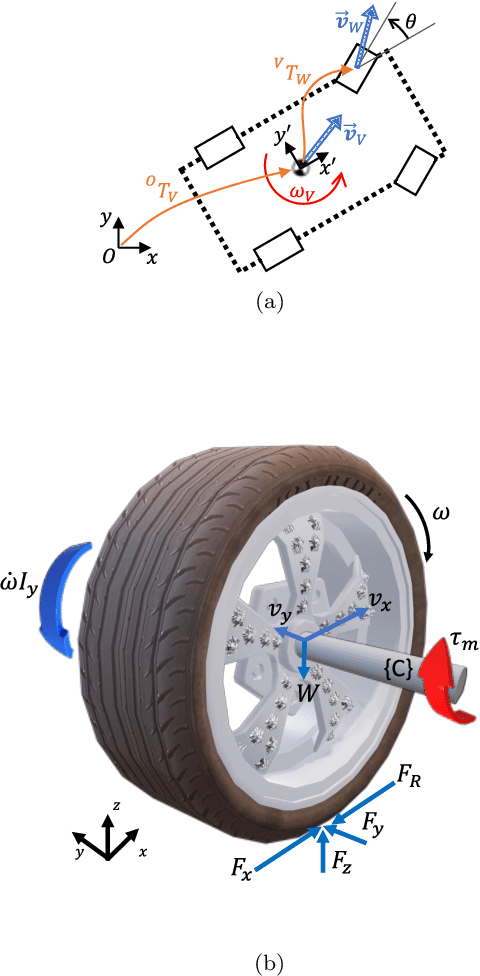
Abstract:Development of applications related to closed-loop control requires either testing on the field or on a realistic simulator, with the latter being more convenient, inexpensive, safe, and leading to shorter development cycles. To address that need, the present work introduces MVSim, a simulator for multiple vehicles or robots capable of running dozens of agents in simple scenarios, or a handful of them in complex scenarios. MVSim employs realistic physics-grounded friction models for tire-ground interaction, and aims at accurate and GPU-accelerated simulation of most common modern sensors employed in mobile robotics and autonomous vehicle research, such as depth and RGB cameras, or 2D and 3D LiDAR scanners. All depth-related sensors are able to accurately measure distances to 3D models provided by the user to define custom world elements. Efficient simulation is achieved by means of focusing on ground vehicles, which allows the use of a simplified 2D physics engine for body collisions while solving wheel-ground interaction forces separately. The core parts of the system are written in C++ for maximum efficiency, while Python, ROS 1, and ROS 2 wrappers are also offered for easy integration into user systems. A custom publish/subscribe protocol based on ZeroMQ (ZMQ) is defined to allow for multiprocess applications to access or modify a running simulation. This simulator enables and makes easier to do research and development on vehicular dynamics, autonomous navigation algorithms, and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) methods.
A general framework for modeling and dynamic simulation of multibody systems using factor graphs
Jan 08, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel general framework grounded in the factor graph theory to solve kinematic and dynamic problems for multi-body systems. Although the motion of multi-body systems is considered to be a well-studied problem and various methods have been proposed for its solution, a unified approach providing an intuitive interpretation is still pursued. We describe how to build factor graphs to model and simulate multibody systems using both, independent and dependent coordinates. Then, batch optimization or a fixed-lag-smoother can be applied to solve the underlying optimization problem that results in a highly-sparse nonlinear minimization problem. The proposed framework has been tested in extensive simulations and validated against a commercial multibody software. We release a reference implementation as an open-source C++ library, based on the GTSAM framework, a well-known estimation library. Simulations of forward and inverse dynamics are presented, showing comparable accuracy with classical approaches. The proposed factor graph-based framework has the potential to be integrated into applications related with motion estimation and parameter identification of complex mechanical systems, ranging from mechanisms to vehicles, or robot manipulators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge