Jordi Sabater-Mir
Instilling Organisational Values in Firefighters through Simulation-Based Training
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:In firefighting and other emergency operations, decisions made under pressure carry profound ethical weight and can significantly impact incident outcomes and firefighter safety. Traditional training methods, while foundational, often fall short in adequately preparing firefighters for the complex ethical dilemmas and value conflicts inherent in chaotic emergency environments. This paper proposes a conceptual framework for enhancing firefighter training by systematically integrating departmental values into simulation-based training. This approach fosters deeper value internalisation and improves value-driven decision-making under pressure. Furthermore, the underlying tools can also be leveraged to evaluate and refine departmental operational protocols for better alignment with preferred values.
Teaching AI to Feel: A Collaborative, Full-Body Exploration of Emotive Communication
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Commonaiverse is an interactive installation exploring human emotions through full-body motion tracking and real-time AI feedback. Participants engage in three phases: Teaching, Exploration and the Cosmos Phase, collaboratively expressing and interpreting emotions with the system. The installation integrates MoveNet for precise motion tracking and a multi-recommender AI system to analyze emotional states dynamically, responding with adaptive audiovisual outputs. By shifting from top-down emotion classification to participant-driven, culturally diverse definitions, we highlight new pathways for inclusive, ethical affective computing. We discuss how this collaborative, out-of-the-box approach pushes multimedia research beyond single-user facial analysis toward a more embodied, co-created paradigm of emotional AI. Furthermore, we reflect on how this reimagined framework fosters user agency, reduces bias, and opens avenues for advanced interactive applications.
LLM Reasoner and Automated Planner: A new NPC approach
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:In domains requiring intelligent agents to emulate plausible human-like behaviour, such as formative simulations, traditional techniques like behaviour trees encounter significant challenges. Large Language Models (LLMs), despite not always yielding optimal solutions, usually offer plausible and human-like responses to a given problem. In this paper, we exploit this capability and propose a novel architecture that integrates an LLM for decision-making with a classical automated planner that can generate sound plans for that decision. The combination aims to equip an agent with the ability to make decisions in various situations, even if they were not anticipated during the design phase.
uHelp: intelligent volunteer search for mutual help communities
Jan 26, 2023



Abstract:When people need help with their day-to-day activities, they turn to family, friends or neighbours. But despite an increasingly networked world, technology falls short in finding suitable volunteers. In this paper, we propose uHelp, a platform for building a community of helpful people and supporting community members find the appropriate help within their social network. Lately, applications that focus on finding volunteers have started to appear, such as Helpin or Facebook's Community Help. However, what distinguishes uHelp from existing applications is its trust-based intelligent search for volunteers. Although trust is crucial to these innovative social applications, none of them have seriously achieved yet a trust-building solution such as that of uHelp. uHelp's intelligent search for volunteers is based on a number of AI technologies: (1) a novel trust-based flooding algorithm that navigates one's social network looking for appropriate trustworthy volunteers; (2) a novel trust model that maintains the trustworthiness of peers by learning from their similar past experiences; and (3) a semantic similarity model that assesses the similarity of experiences. This article presents the uHelp application, describes the underlying AI technologies that allow uHelp find trustworthy volunteers efficiently, and illustrates the implementation details. uHelp's initial prototype has been tested with a community of single parents in Barcelona, and the app is available online at both Apple Store and Google Play.
Value alignment: a formal approach
Oct 18, 2021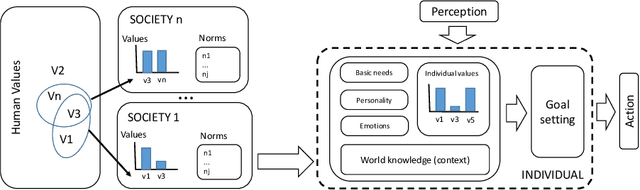
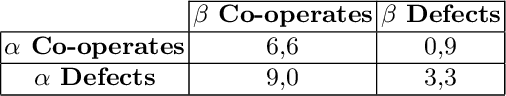
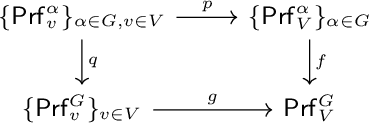
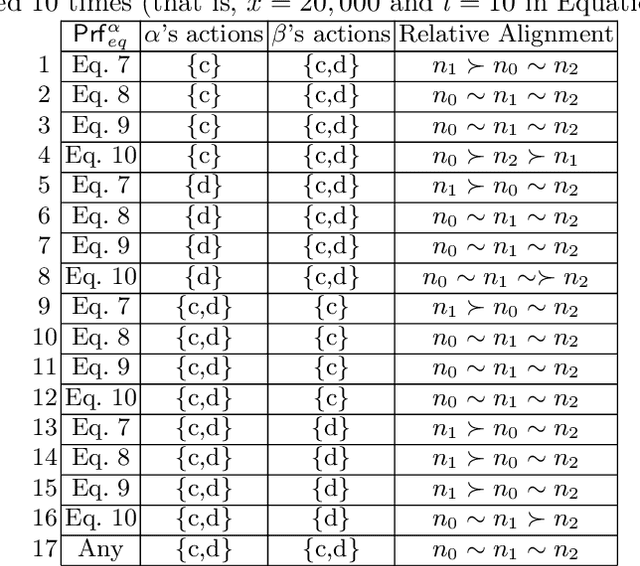
Abstract:principles that should govern autonomous AI systems. It essentially states that a system's goals and behaviour should be aligned with human values. But how to ensure value alignment? In this paper we first provide a formal model to represent values through preferences and ways to compute value aggregations; i.e. preferences with respect to a group of agents and/or preferences with respect to sets of values. Value alignment is then defined, and computed, for a given norm with respect to a given value through the increase/decrease that it results in the preferences of future states of the world. We focus on norms as it is norms that govern behaviour, and as such, the alignment of a given system with a given value will be dictated by the norms the system follows.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge