João Gonçalves
Combining Autoregressive and Autoencoder Language Models for Text Classification
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:This paper presents CAALM-TC (Combining Autoregressive and Autoencoder Language Models for Text Classification), a novel method that enhances text classification by integrating autoregressive and autoencoder language models. Autoregressive large language models such as Open AI's GPT, Meta's Llama or Microsoft's Phi offer promising prospects for content analysis practitioners, but they generally underperform supervised BERT based models for text classification. CAALM leverages autoregressive models to generate contextual information based on input texts, which is then combined with the original text and fed into an autoencoder model for classification. This hybrid approach capitalizes on the extensive contextual knowledge of autoregressive models and the efficient classification capabilities of autoencoders. Experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that CAALM consistently outperforms existing methods, particularly in tasks with smaller datasets and more abstract classification objectives. The findings indicate that CAALM offers a scalable and effective solution for automated content analysis in social science research that minimizes sample size requirements.
The advantages of context specific language models: the case of the Erasmian Language Model
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:The current trend to improve language model performance seems to be based on scaling up with the number of parameters (e.g. the state of the art GPT4 model has approximately 1.7 trillion parameters) or the amount of training data fed into the model. However this comes at significant costs in terms of computational resources and energy costs that compromise the sustainability of AI solutions, as well as risk relating to privacy and misuse. In this paper we present the Erasmian Language Model (ELM) a small context specific, 900 million parameter model, pre-trained and fine-tuned by and for Erasmus University Rotterdam. We show how the model performs adequately in a classroom context for essay writing, and how it achieves superior performance in subjects that are part of its context. This has implications for a wide range of institutions and organizations, showing that context specific language models may be a viable alternative for resource constrained, privacy sensitive use cases.
A Pig, an Angel and a Cactus Walk Into a Blender: A Descriptive Approach to Visual Blending
Nov 30, 2017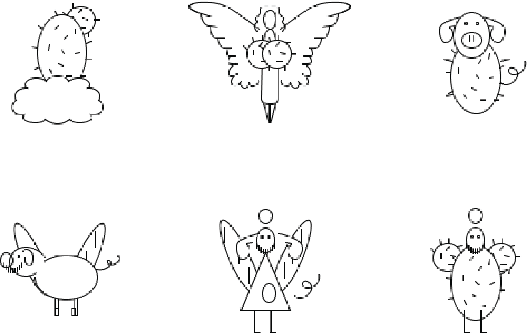
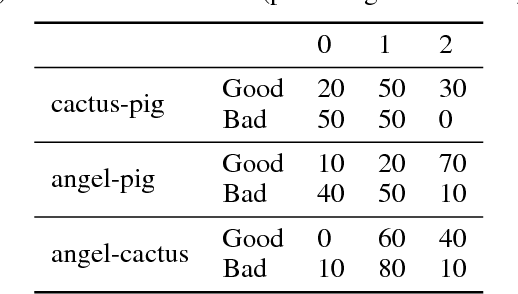
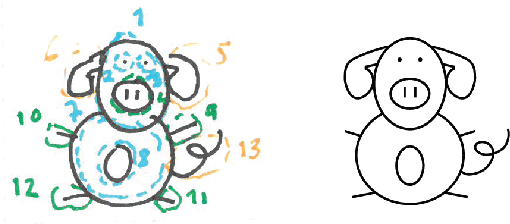
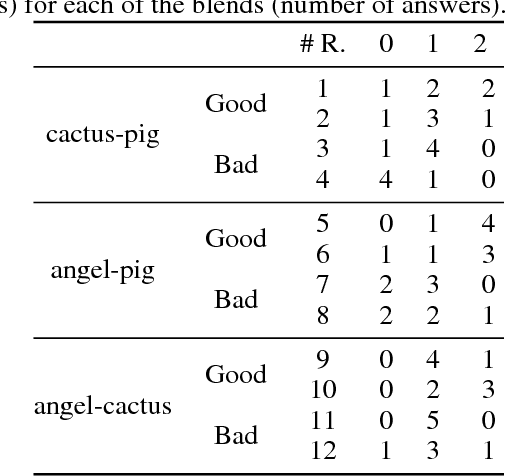
Abstract:A descriptive approach for automatic generation of visual blends is presented. The implemented system, the Blender, is composed of two components: the Mapper and the Visual Blender. The approach uses structured visual representations along with sets of visual relations which describe how the elements (in which the visual representation can be decomposed) relate among each other. Our system is a hybrid blender, as the blending process starts at the Mapper (conceptual level) and ends at the Visual Blender (visual representation level). The experimental results show that the Blender is able to create analogies from input mental spaces and produce well-composed blends, which follow the rules imposed by its base-analogy and its relations. The resulting blends are visually interesting and some can be considered as unexpected.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge