Jingli Shi
Soft Prompt Guided Joint Learning for Cross-Domain Sentiment Analysis
Mar 01, 2023
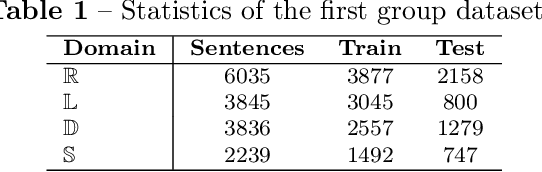

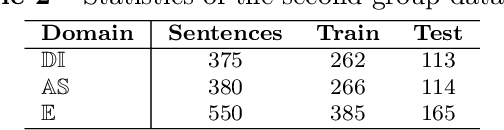
Abstract:Aspect term extraction is a fundamental task in fine-grained sentiment analysis, which aims at detecting customer's opinion targets from reviews on product or service. The traditional supervised models can achieve promising results with annotated datasets, however, the performance dramatically decreases when they are applied to the task of cross-domain aspect term extraction. Existing cross-domain transfer learning methods either directly inject linguistic features into Language models, making it difficult to transfer linguistic knowledge to target domain, or rely on the fixed predefined prompts, which is time-consuming to construct the prompts over all potential aspect term spans. To resolve the limitations, we propose a soft prompt-based joint learning method for cross domain aspect term extraction in this paper. Specifically, by incorporating external linguistic features, the proposed method learn domain-invariant representations between source and target domains via multiple objectives, which bridges the gap between domains with varied distributions of aspect terms. Further, the proposed method interpolates a set of transferable soft prompts consisted of multiple learnable vectors that are beneficial to detect aspect terms in target domain. Extensive experiments are conducted on the benchmark datasets and the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for cross-domain aspect terms extraction.
DOR: A Novel Dual-Observation-Based Approach for News Recommendation Systems
Feb 02, 2023
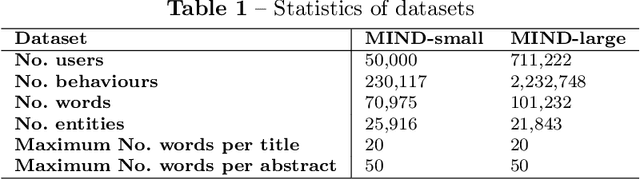
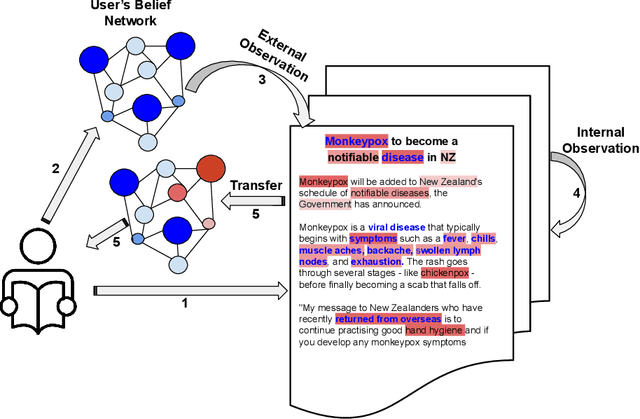
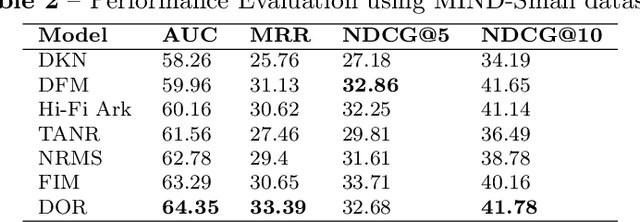
Abstract:Online social media platforms offer access to a vast amount of information, but sifting through the abundance of news can be overwhelming and tiring for readers. personalised recommendation algorithms can help users find information that interests them. However, most existing models rely solely on observations of user behaviour, such as viewing history, ignoring the connections between the news and a user's prior knowledge. This can result in a lack of diverse recommendations for individuals. In this paper, we propose a novel method to address the complex problem of news recommendation. Our approach is based on the idea of dual observation, which involves using a deep neural network with observation mechanisms to identify the main focus of a news article as well as the focus of the user on the article. This is achieved by taking into account the user's belief network, which reflects their personal interests and biases. By considering both the content of the news and the user's perspective, our approach is able to provide more personalised and accurate recommendations. We evaluate the performance of our model on real-world datasets and show that our proposed method outperforms several popular baselines.
Automatic Quantitative Analysis of Brain Organoids via Deep Learning
Nov 01, 2022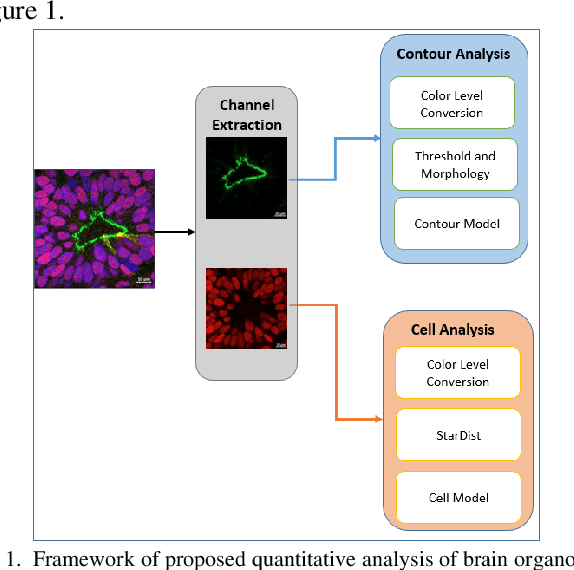
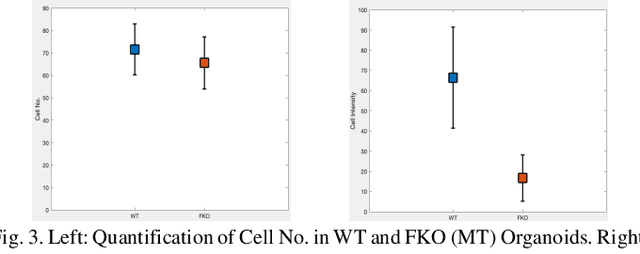
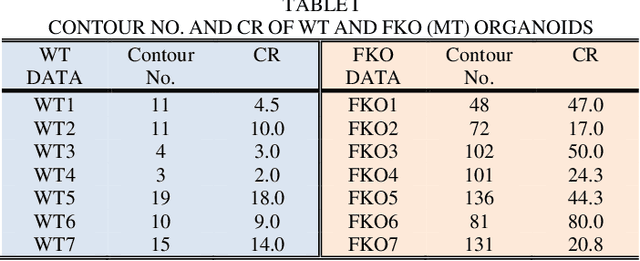
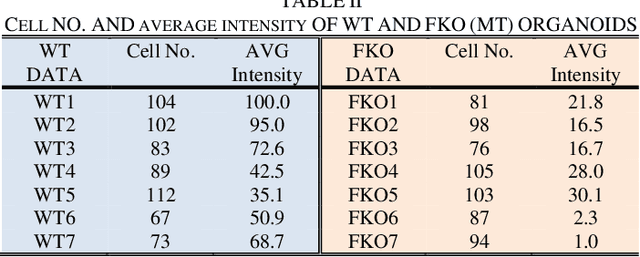
Abstract:Recent advances in brain organoid technology are exciting new ways, which have the potential to change the way how doctors and researchers understand and treat cerebral diseases. Despite the remarkable use of brain organoids derived from human stem cells in new drug testing, disease modeling, and scientific research, it is still heavily time-consuming work to observe and analyze the internal structure, cells, and neural inside the organoid by humans, specifically no standard quantitative analysis method combined growing AI technology for brain organoid. In this paper, an automated computer-assisted analysis method is proposed for brain organoid slice channels tagged with different fluorescent. We applied the method on two channels of two group microscopy images and the experiment result shows an obvious difference between Wild Type and Mutant Type cerebral organoids.
Graph-based Joint Pandemic Concern and Relation Extraction on Twitter
Jun 18, 2021
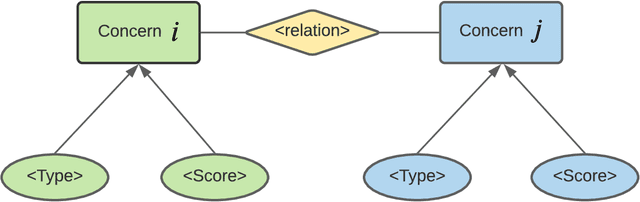
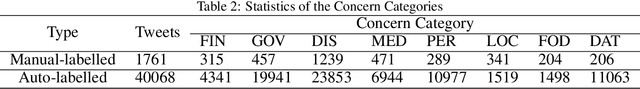
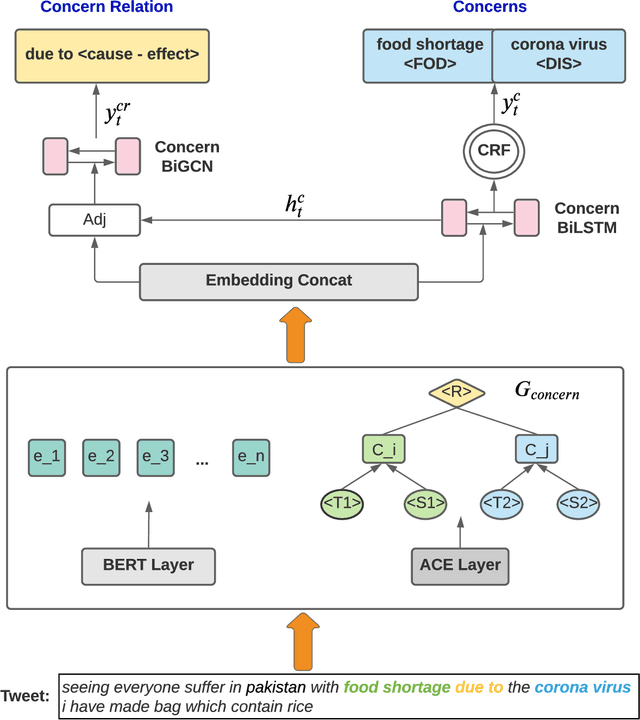
Abstract:Public concern detection provides potential guidance to the authorities for crisis management before or during a pandemic outbreak. Detecting people's concerns and attention from online social media platforms has been widely acknowledged as an effective approach to relieve public panic and prevent a social crisis. However, detecting concerns in time from massive information in social media turns out to be a big challenge, especially when sufficient manually labeled data is in the absence of public health emergencies, e.g., COVID-19. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end deep learning model to identify people's concerns and the corresponding relations based on Graph Convolutional Network and Bi-directional Long Short Term Memory integrated with Concern Graph. Except for the sequential features from BERT embeddings, the regional features of tweets can be extracted by the Concern Graph module, which not only benefits the concern detection but also enables our model to be high noise-tolerant. Thus, our model can address the issue of insufficient manually labeled data. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the proposed model by using both manually labeled tweets and automatically labeled tweets. The experimental results show that our model can outperform the state-of-art models on real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge