Jinghe Zhang
Sparse Longitudinal Representations of Electronic Health Record Data for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients
Nov 09, 2020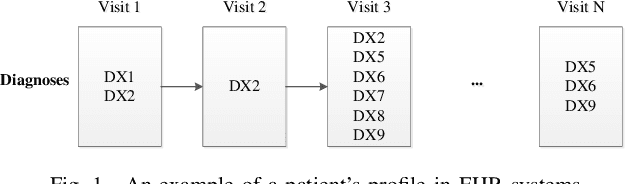
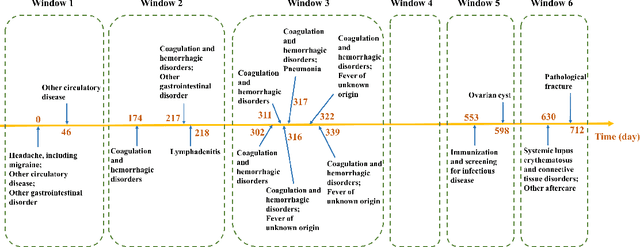
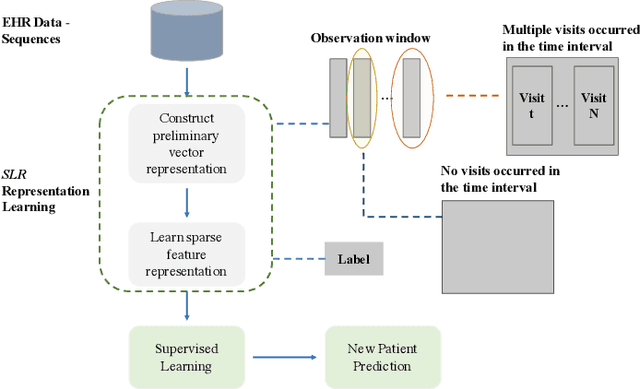
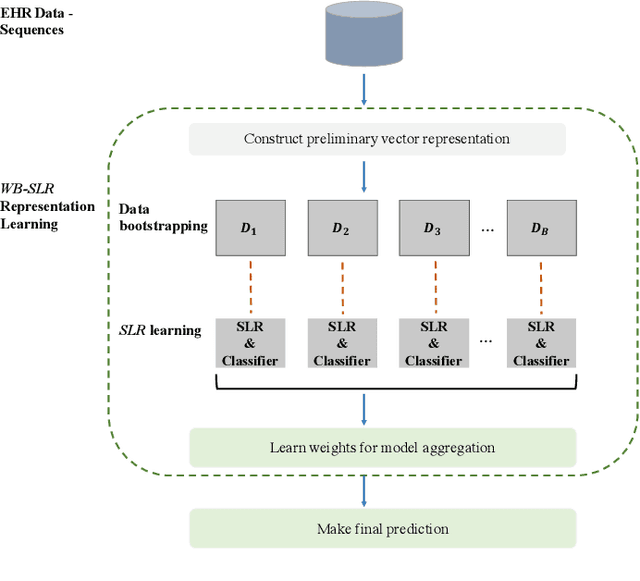
Abstract:Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a gradual loss of renal function over time, and it increases the risk of mortality, decreased quality of life, as well as serious complications. The prevalence of CKD has been increasing in the last couple of decades, which is partly due to the increased prevalence of diabetes and hypertension. To accurately detect CKD in diabetic patients, we propose a novel framework to learn sparse longitudinal representations of patients' medical records. The proposed method is also compared with widely used baselines such as Aggregated Frequency Vector and Bag-of-Pattern in Sequences on real EHR data, and the experimental results indicate that the proposed model achieves higher predictive performance. Additionally, the learned representations are interpreted and visualized to bring clinical insights.
Patient2Vec: A Personalized Interpretable Deep Representation of the Longitudinal Electronic Health Record
Oct 25, 2018



Abstract:The wide implementation of electronic health record (EHR) systems facilitates the collection of large-scale health data from real clinical settings. Despite the significant increase in adoption of EHR systems, this data remains largely unexplored, but presents a rich data source for knowledge discovery from patient health histories in tasks such as understanding disease correlations and predicting health outcomes. However, the heterogeneity, sparsity, noise, and bias in this data present many complex challenges. This complexity makes it difficult to translate potentially relevant information into machine learning algorithms. In this paper, we propose a computational framework, Patient2Vec, to learn an interpretable deep representation of longitudinal EHR data which is personalized for each patient. To evaluate this approach, we apply it to the prediction of future hospitalizations using real EHR data and compare its predictive performance with baseline methods. Patient2Vec produces a vector space with meaningful structure and it achieves an AUC around 0.799 outperforming baseline methods. In the end, the learned feature importance can be visualized and interpreted at both the individual and population levels to bring clinical insights.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge