Jina Kang
Can LLMs Reliably Simulate Human Learner Actions? A Simulation Authoring Framework for Open-Ended Learning Environments
Oct 03, 2024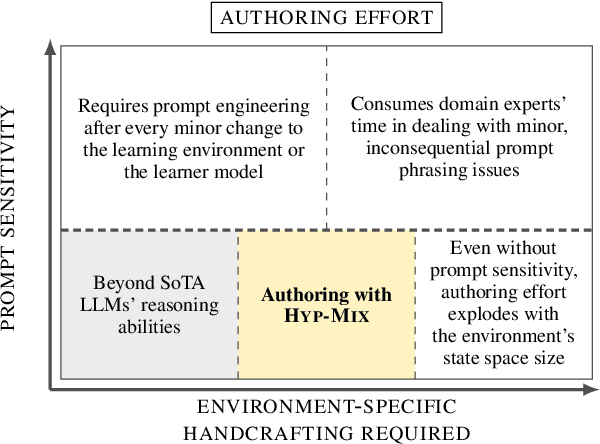

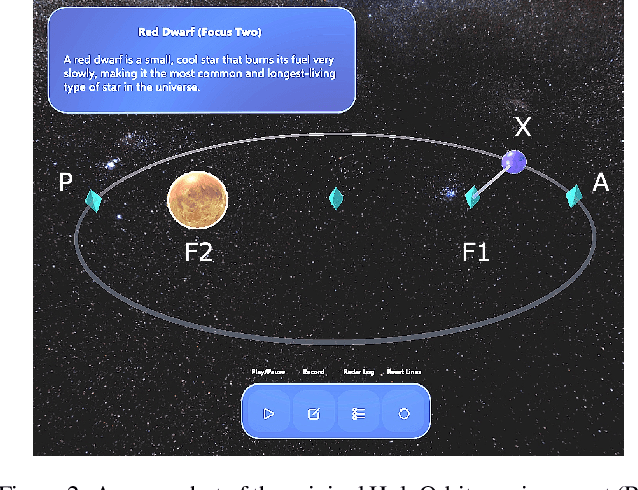
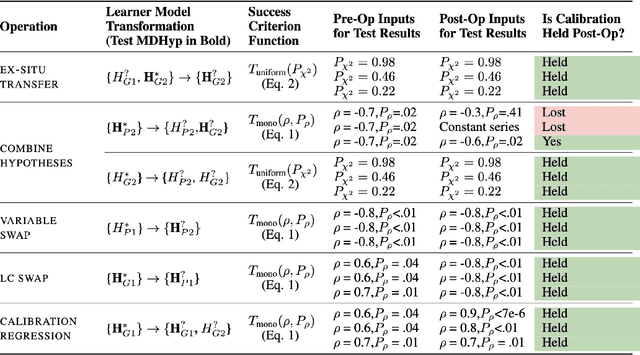
Abstract:Simulating learner actions helps stress-test open-ended interactive learning environments and prototype new adaptations before deployment. While recent studies show the promise of using large language models (LLMs) for simulating human behavior, such approaches have not gone beyond rudimentary proof-of-concept stages due to key limitations. First, LLMs are highly sensitive to minor prompt variations, raising doubts about their ability to generalize to new scenarios without extensive prompt engineering. Moreover, apparently successful outcomes can often be unreliable, either because domain experts unintentionally guide LLMs to produce expected results, leading to self-fulfilling prophecies; or because the LLM has encountered highly similar scenarios in its training data, meaning that models may not be simulating behavior so much as regurgitating memorized content. To address these challenges, we propose Hyp-Mix, a simulation authoring framework that allows experts to develop and evaluate simulations by combining testable hypotheses about learner behavior. Testing this framework in a physics learning environment, we found that GPT-4 Turbo maintains calibrated behavior even as the underlying learner model changes, providing the first evidence that LLMs can be used to simulate realistic behaviors in open-ended interactive learning environments, a necessary prerequisite for useful LLM behavioral simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge