Jiang Biao
Robotic Inspection and 3D GPR-based Reconstruction for Underground Utilities
Jun 03, 2021
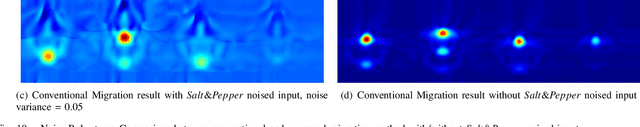
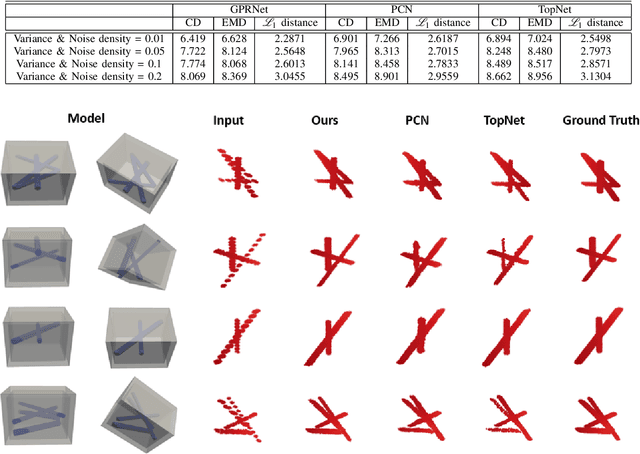
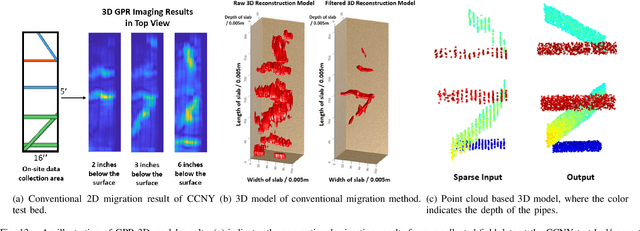
Abstract:Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is an effective non-destructive evaluation (NDE) device for inspecting and surveying subsurface objects (i.e., rebars, utility pipes) in complex environments. However, the current practice for GPR data collection requires a human inspector to move a GPR cart along pre-marked grid lines and record the GPR data in both X and Y directions for post-processing by 3D GPR imaging software. It is time-consuming and tedious work to survey a large area. Furthermore, identifying the subsurface targets depends on the knowledge of an experienced engineer, who has to make manual and subjective interpretation that limits the GPR applications, especially in large-scale scenarios. In addition, the current GPR imaging technology is not intuitive, and not for normal users to understand, and not friendly to visualize. To address the above challenges, this paper presents a novel robotic system to collect GPR data, interpret GPR data, localize the underground utilities, reconstruct and visualize the underground objects' dense point cloud model in a user-friendly manner. This system is composed of three modules: 1) a vision-aided Omni-directional robotic data collection platform, which enables the GPR antenna to scan the target area freely with an arbitrary trajectory while using a visual-inertial-based positioning module tags the GPR measurements with positioning information; 2) a deep neural network (DNN) migration module to interpret the raw GPR B-scan image into a cross-section of object model; 3) a DNN-based 3D reconstruction method, i.e., GPRNet, to generate underground utility model represented as fine 3D point cloud. Comparative studies on synthetic and field GPR raw data with various incompleteness and noise are performed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge