Jianchang Liu
Conformal Navigation Transformations with Application to Robot Navigation in Complex Workspaces
Aug 22, 2022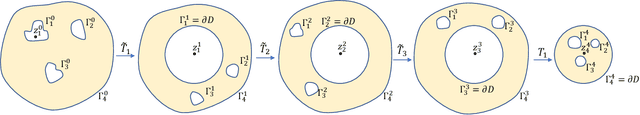
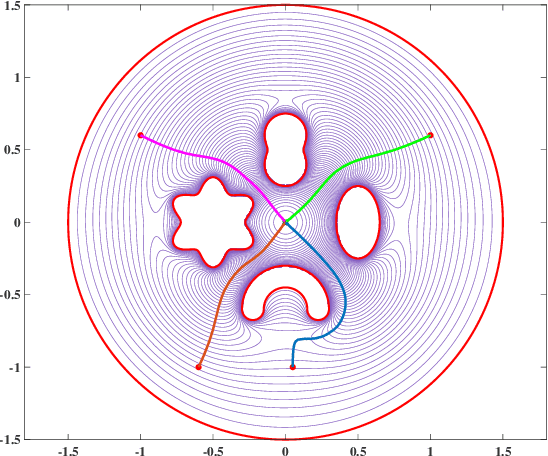
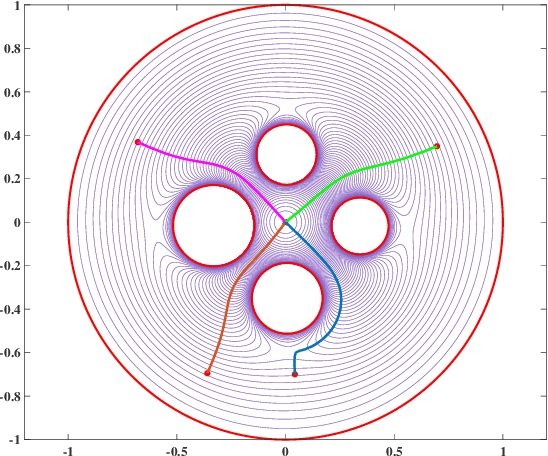
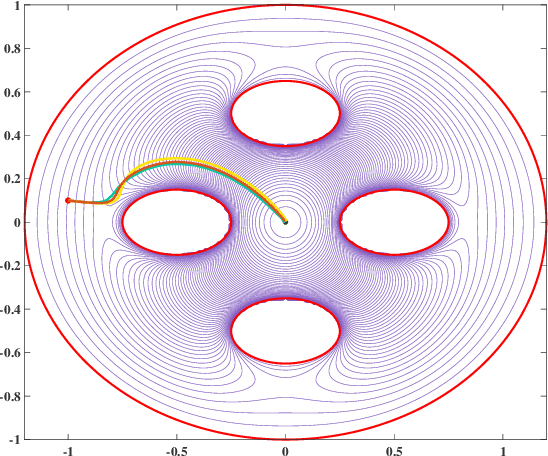
Abstract:Navigation functions provide both path and motion planning, which can be used to ensure obstacle avoidance and convergence in the sphere world. When dealing with complex and realistic scenarios, constructing a transformation to the sphere world is essential and, at the same time, challenging. This work proposes a novel transformation termed the conformal navigation transformation to achieve collision-free navigation of a robot in a workspace populated with obstacles of arbitrary shapes. The properties of the conformal navigation transformation, including uniqueness, invariance of navigation properties, and no angular deformation, are investigated, which contribute to the solution of the robot navigation problem in complex environments. Based on navigation functions and the proposed transformation, feedback controllers are derived for the automatic guidance and motion control of kinematic and dynamic mobile robots. Moreover, an iterative method is proposed to construct the conformal navigation transformation in a multiply-connected workspace, which transforms the multiply-connected problem into multiple simply-connected problems to achieve fast convergence. In addition to the analytic guarantees, simulation studies verify the effectiveness of the proposed methodology in workspaces with non-trivial obstacles.
Mobile Robot Navigation in Complex Polygonal Workspaces Using Conformal Navigation Transformations
Aug 20, 2022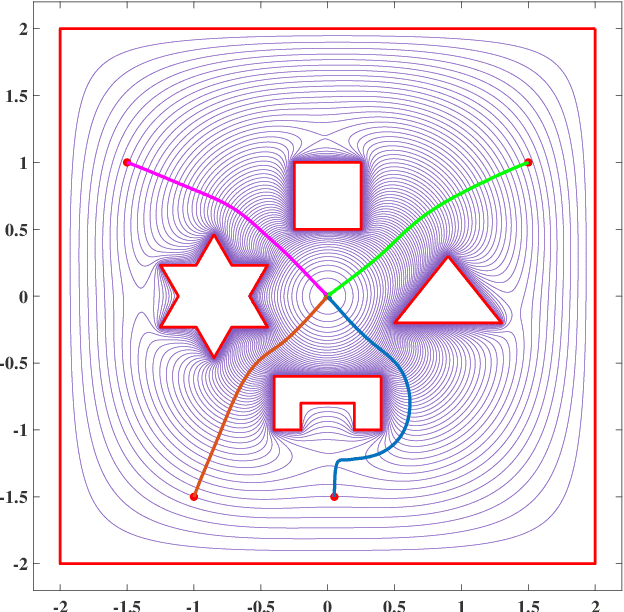
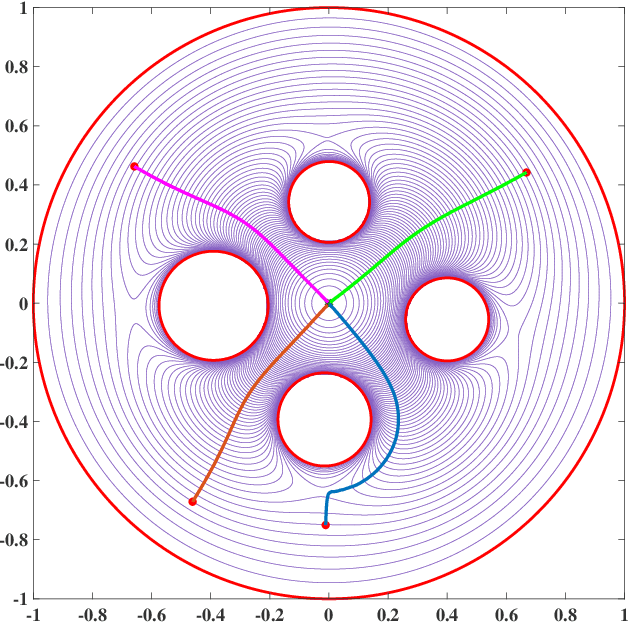
Abstract:This work proposes a novel transformation termed the conformal navigation transformation to achieve collision-free navigation of a robot in a workspace populated with arbitrary polygonal obstacles. The properties of the conformal navigation transformation in the polygonal workspace are investigated in this work as well as its capability to provide a solution to the navigation problem. %The properties of the conformal navigation transformation are investigated, which contribute to the solution of the robot navigation problem in complex polygonal environments. %which facilitates the navigation of robots in complex environments. The definition of the navigation function is generalized to accommodate non-smooth obstacle boundaries. Based on the proposed transformation and the generalized navigation function, a provably correct feedback controller is derived for the automatic guidance and motion control of the kinematic mobile robot. Moreover, an iterative method is proposed to construct the conformal navigation transformation in a multi-connected polygonal workspace, which transforms the multi-connected problem into multiple single-connected problems to achieve fast convergence.In addition to the analytic guarantees, the simulation study verifies the effectiveness of the proposed methodology in a workspace with non-trivial polygonal obstacles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge