Jiajing Wan
Longer Fixations, More Computation: Gaze-Guided Recurrent Neural Networks
Oct 31, 2023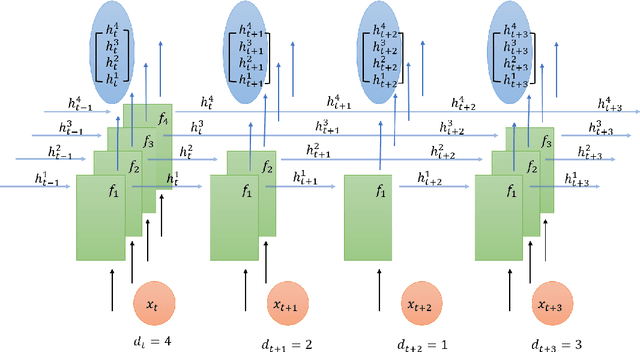
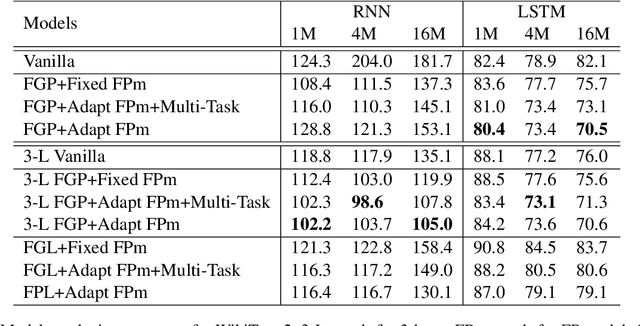
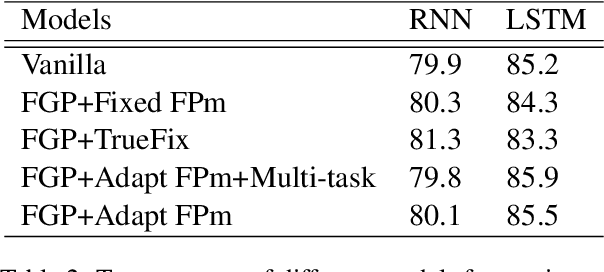

Abstract:Humans read texts at a varying pace, while machine learning models treat each token in the same way in terms of a computational process. Therefore, we ask, does it help to make models act more like humans? In this paper, we convert this intuition into a set of novel models with fixation-guided parallel RNNs or layers and conduct various experiments on language modeling and sentiment analysis tasks to test their effectiveness, thus providing empirical validation for this intuition. Our proposed models achieve good performance on the language modeling task, considerably surpassing the baseline model. In addition, we find that, interestingly, the fixation duration predicted by neural networks bears some resemblance to humans' fixation. Without any explicit guidance, the model makes similar choices to humans. We also investigate the reasons for the differences between them, which explain why "model fixations" are often more suitable than human fixations, when used to guide language models.
KaLM at SemEval-2020 Task 4: Knowledge-aware Language Models for Comprehension And Generation
May 24, 2020



Abstract:This paper presents our strategies in SemEval 2020 Task 4: Commonsense Validation and Explanation. We propose a novel way to search for evidence and choose the different large-scale pre-trained models as the backbone for three subtasks. The results show that our evidence-searching approach improves model performance on commonsense explanation task. Our team ranks 2nd in subtask C according to human evaluation score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge