Jennifer LoCasale-Crouch
Automated Evaluation of Classroom Instructional Support with LLMs and BoWs: Connecting Global Predictions to Specific Feedback
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:With the aim to provide teachers with more specific, frequent, and actionable feedback about their teaching, we explore how Large Language Models (LLMs) can be used to estimate ``Instructional Support'' domain scores of the CLassroom Assessment Scoring System (CLASS), a widely used observation protocol. We design a machine learning architecture that uses either zero-shot prompting of Meta's Llama2, and/or a classic Bag of Words (BoW) model, to classify individual utterances of teachers' speech (transcribed automatically using OpenAI's Whisper) for the presence of 11 behavioral indicators of Instructional Support. Then, these utterance-level judgments are aggregated over an entire 15-min observation session to estimate a global CLASS score. Experiments on two CLASS-coded datasets of toddler and pre-kindergarten classrooms indicate that (1) automatic CLASS Instructional Support estimation accuracy using the proposed method (Pearson $R$ up to $0.46$) approaches human inter-rater reliability (up to $R=0.55$); (2) LLMs yield slightly greater accuracy than BoW for this task; and (3) the best models often combined features extracted from both LLM and BoW. Finally, (4) we illustrate how the model's outputs can be visualized at the utterance level to provide teachers with explainable feedback on which utterances were most positively or negatively correlated with specific CLASS dimensions.
Toward Automated Classroom Observation: Multimodal Machine Learning to Estimate CLASS Positive Climate and Negative Climate
May 19, 2020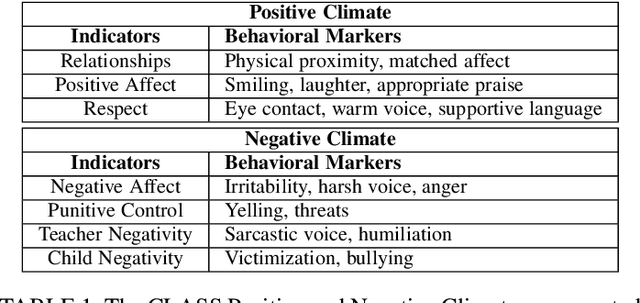
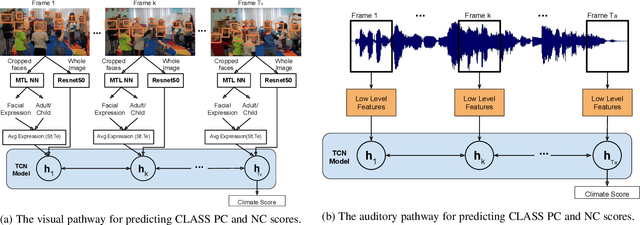
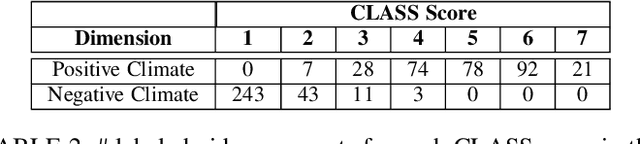

Abstract:In this work we present a multi-modal machine learning-based system, which we call ACORN, to analyze videos of school classrooms for the Positive Climate (PC) and Negative Climate (NC) dimensions of the CLASS observation protocol that is widely used in educational research. ACORN uses convolutional neural networks to analyze spectral audio features, the faces of teachers and students, and the pixels of each image frame, and then integrates this information over time using Temporal Convolutional Networks. The audiovisual ACORN's PC and NC predictions have Pearson correlations of $0.55$ and $0.63$ with ground-truth scores provided by expert CLASS coders on the UVA Toddler dataset (cross-validation on $n=300$ 15-min video segments), and a purely auditory ACORN predicts PC and NC with correlations of $0.36$ and $0.41$ on the MET dataset (test set of $n=2000$ videos segments). These numbers are similar to inter-coder reliability of human coders. Finally, using Graph Convolutional Networks we make early strides (AUC=$0.70$) toward predicting the specific moments (45-90sec clips) when the PC is particularly weak/strong. Our findings inform the design of automatic classroom observation and also more general video activity recognition and summary recognition systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge