Jen Hong Tan
How Lightweight Can A Vision Transformer Be
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we explore a strategy that uses Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to streamline, rather than augment, vision transformers. Each expert in an MoE layer is a SwiGLU feedforward network, where V and W2 are shared across the layer. No complex attention or convolutional mechanisms are employed. Depth-wise scaling is applied to progressively reduce the size of the hidden layer and the number of experts is increased in stages. Grouped query attention is used. We studied the proposed approach with and without pre-training on small datasets and investigated whether transfer learning works at this scale. We found that the architecture is competitive even at a size of 0.67M parameters.
Pre-training of Lightweight Vision Transformers on Small Datasets with Minimally Scaled Images
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Can a lightweight Vision Transformer (ViT) match or exceed the performance of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) like ResNet on small datasets with small image resolutions? This report demonstrates that a pure ViT can indeed achieve superior performance through pre-training, using a masked auto-encoder technique with minimal image scaling. Our experiments on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets involved ViT models with fewer than 3.65 million parameters and a multiply-accumulate (MAC) count below 0.27G, qualifying them as 'lightweight' models. Unlike previous approaches, our method attains state-of-the-art performance among similar lightweight transformer-based architectures without significantly scaling up images from CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100. This achievement underscores the efficiency of our model, not only in handling small datasets but also in effectively processing images close to their original scale.
Segmentation of optic disc, fovea and retinal vasculature using a single convolutional neural network
Feb 02, 2017
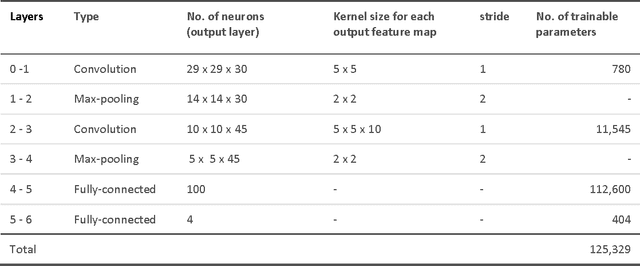
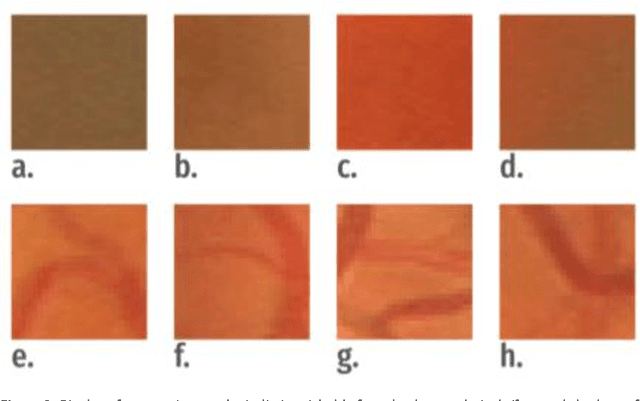
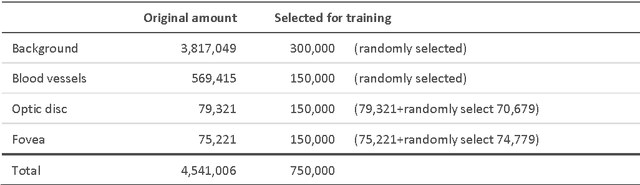
Abstract:We have developed and trained a convolutional neural network to automatically and simultaneously segment optic disc, fovea and blood vessels. Fundus images were normalised before segmentation was performed to enforce consistency in background lighting and contrast. For every effective point in the fundus image, our algorithm extracted three channels of input from the neighbourhood of the point and forward the response across the 7 layer network. In average, our segmentation achieved an accuracy of 92.68 percent on the testing set from Drive database.
Active spline model: A shape based model-interactive segmentation
Feb 26, 2014



Abstract:Rarely in literature a method of segmentation cares for the edit after the algorithm delivers. They provide no solution when segmentation goes wrong. We propose to formulate point distribution model in terms of centripetal-parameterized Catmull-Rom spline. Such fusion brings interactivity to model-based segmentation, so that edit is better handled. When the delivered segment is unsatisfactory, user simply shifts points to vary the curve. We ran the method on three disparate imaging modalities and achieved an average overlap of 0.879 for automated lung segmentation on chest radiographs. The edit afterward improved the average overlap to 0.945, with a minimum of 0.925. The source code and the demo video are available at http://wp.me/p3vCKy-2S
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge