Jeff Shrager
ELIZA Reanimated: The world's first chatbot restored on the world's first time sharing system
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:ELIZA, created by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT in the early 1960s, is usually considered the world's first chatbot. It was developed in MAD-SLIP on MIT's CTSS, the world's first time-sharing system, on an IBM 7094. We discovered an original ELIZA printout in Prof. Weizenbaum's archives at MIT, including an early version of the famous DOCTOR script, a nearly complete version of the MAD-SLIP code, and various support functions in MAD and FAP. Here we describe the reanimation of this original ELIZA on a restored CTSS, itself running on an emulated IBM 7094. The entire stack is open source, so that any user of a unix-like OS can run the world's first chatbot on the world's first time-sharing system.
ELIZA Reinterpreted: The world's first chatbot was not intended as a chatbot at all
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:ELIZA, often considered the world's first chatbot, was written by Joseph Weizenbaum in the early 1960s. Weizenbaum did not intend to invent the chatbot, but rather to build a platform for research into human-machine conversation and the important cognitive processes of interpretation and misinterpretation. His purpose was obscured by ELIZA's fame, resulting in large part from the fortuitous timing of it's creation, and it's escape into the wild. In this paper I provide a rich historical context for ELIZA's creation, demonstrating that ELIZA arose from the intersection of some of the central threads in the technical history of AI. I also briefly discuss how ELIZA escaped into the world, and how its accidental escape, along with several coincidental turns of the programming language screws, led both to the misapprehension that ELIZA was intended as a chatbot, and to the loss of the original ELIZA to history for over 50 years.
Weight Set Decomposition for Weighted Rank Aggregation: An interpretable and visual decision support tool
May 31, 2022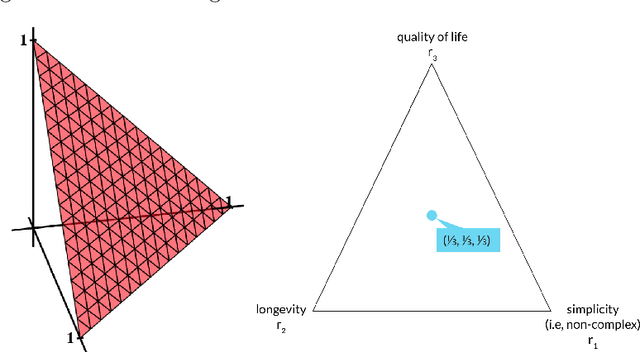
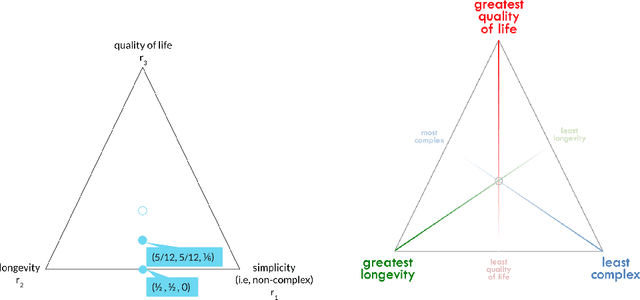
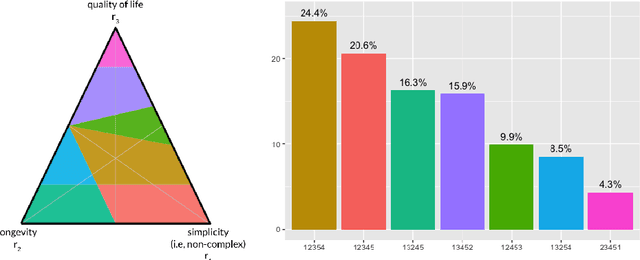
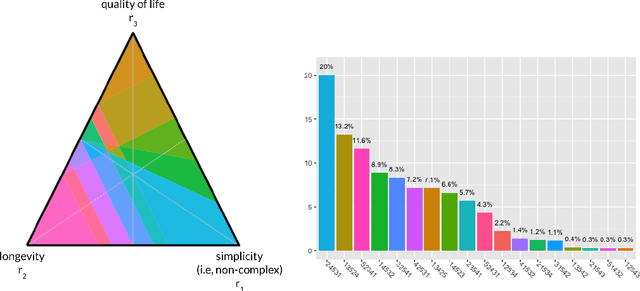
Abstract:The problem of interpreting or aggregating multiple rankings is common to many real-world applications. Perhaps the simplest and most common approach is a weighted rank aggregation, wherein a (convex) weight is applied to each input ranking and then ordered. This paper describes a new tool for visualizing and displaying ranking information for the weighted rank aggregation method. Traditionally, the aim of rank aggregation is to summarize the information from the input rankings and provide one final ranking that hopefully represents a more accurate or truthful result than any one input ranking. While such an aggregated ranking is, and clearly has been, useful to many applications, it also obscures information. In this paper, we show the wealth of information that is available for the weighted rank aggregation problem due to its structure. We apply weight set decomposition to the set of convex multipliers, study the properties useful for understanding this decomposition, and visualize the indifference regions. This methodology reveals information--that is otherwise collapsed by the aggregated ranking--into a useful, interpretable, and intuitive decision support tool. Included are multiple illustrative examples, along with heuristic and exact algorithms for computing the weight set decomposition.
Theoretical Issues for Global Cumulative Treatment Analysis (GCTA)
Aug 05, 2013Abstract:Adaptive trials are now mainstream science. Recently, researchers have taken the adaptive trial concept to its natural conclusion, proposing what we call "Global Cumulative Treatment Analysis" (GCTA). Similar to the adaptive trial, decision making and data collection and analysis in the GCTA are continuous and integrated, and treatments are ranked in accord with the statistics of this information, combined with what offers the most information gain. Where GCTA differs from an adaptive trial, or, for that matter, from any trial design, is that all patients are implicitly participants in the GCTA process, regardless of whether they are formally enrolled in a trial. This paper discusses some of the theoretical and practical issues that arise in the design of a GCTA, along with some preliminary thoughts on how they might be approached.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge