Jean-Philippe Cointet
SPOT: An Annotated French Corpus and Benchmark for Detecting Critical Interventions in Online Conversations
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce SPOT (Stopping Points in Online Threads), the first annotated corpus translating the sociological concept of stopping point into a reproducible NLP task. Stopping points are ordinary critical interventions that pause or redirect online discussions through a range of forms (irony, subtle doubt or fragmentary arguments) that frameworks like counterspeech or social correction often overlook. We operationalize this concept as a binary classification task and provide reliable annotation guidelines. The corpus contains 43,305 manually annotated French Facebook comments linked to URLs flagged as false information by social media users, enriched with contextual metadata (article, post, parent comment, page or group, and source). We benchmark fine-tuned encoder models (CamemBERT) and instruction-tuned LLMs under various prompting strategies. Results show that fine-tuned encoders outperform prompted LLMs in F1 score by more than 10 percentage points, confirming the importance of supervised learning for emerging non-English social media tasks. Incorporating contextual metadata further improves encoder models F1 scores from 0.75 to 0.78. We release the anonymized dataset, along with the annotation guidelines and code in our code repository, to foster transparency and reproducible research.
Graphically Speaking: Unmasking Abuse in Social Media with Conversation Insights
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Detecting abusive language in social media conversations poses significant challenges, as identifying abusiveness often depends on the conversational context, characterized by the content and topology of preceding comments. Traditional Abusive Language Detection (ALD) models often overlook this context, which can lead to unreliable performance metrics. Recent Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods that integrate conversational context often depend on limited and simplified representations, and report inconsistent results. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that utilize graph neural networks (GNNs) to model social media conversations as graphs, where nodes represent comments, and edges capture reply structures. We systematically investigate various graph representations and context windows to identify the optimal configuration for ALD. Our GNN model outperform both context-agnostic baselines and linear context-aware methods, achieving significant improvements in F1 scores. These findings demonstrate the critical role of structured conversational context and establish GNNs as a robust framework for advancing context-aware abusive language detection.
Your most telling friends: Propagating latent ideological features on Twitter using neighborhood coherence
Mar 12, 2021
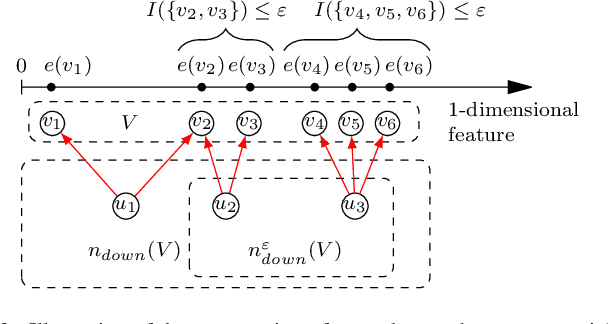
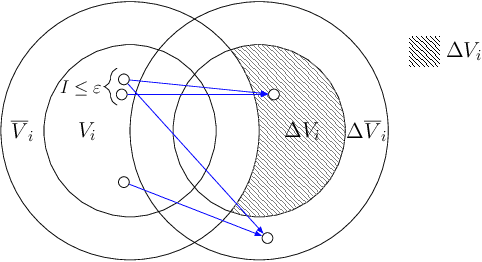
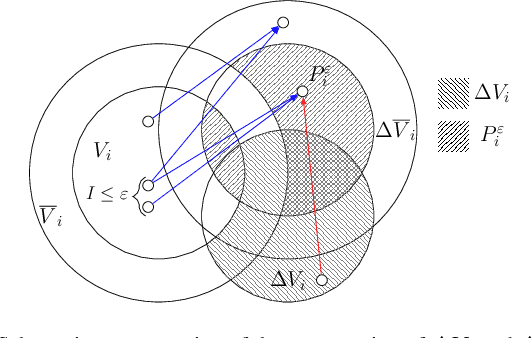
Abstract:Multidimensional scaling in networks allows for the discovery of latent information about their structure by embedding nodes in some feature space. Ideological scaling for users in social networks such as Twitter is an example, but similar settings can include diverse applications in other networks and even media platforms or e-commerce. A growing literature of ideology scaling methods in social networks restricts the scaling procedure to nodes that provide interpretability of the feature space: on Twitter, it is common to consider the sub-network of parliamentarians and their followers. This allows to interpret inferred latent features as indices for ideology-related concepts inspecting the position of members of parliament. While effective in inferring meaningful features, this is generally restrained to these sub-networks, limiting interesting applications such as country-wide measurement of polarization and its evolution. We propose two methods to propagate ideological features beyond these sub-networks: one based on homophily (linked users have similar ideology), and the other on structural similarity (nodes with similar neighborhoods have similar ideologies). In our methods, we leverage the concept of neighborhood ideological coherence as a parameter for propagation. Using Twitter data, we produce an ideological scaling for 370K users, and analyze the two families of propagation methods on a population of 6.5M users. We find that, when coherence is considered, the ideology of a user is better estimated from those with similar neighborhoods, than from their immediate neighbors.
Multi-Level Modeling of Quotation Families Morphogenesis
Jan 04, 2013



Abstract:This paper investigates cultural dynamics in social media by examining the proliferation and diversification of clearly-cut pieces of content: quoted texts. In line with the pioneering work of Leskovec et al. and Simmons et al. on memes dynamics we investigate in deep the transformations that quotations published online undergo during their diffusion. We deliberately put aside the structure of the social network as well as the dynamical patterns pertaining to the diffusion process to focus on the way quotations are changed, how often they are modified and how these changes shape more or less diverse families and sub-families of quotations. Following a biological metaphor, we try to understand in which way mutations can transform quotations at different scales and how mutation rates depend on various properties of the quotations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge