Jean Baccou
IRSN, MIST
A probabilistic model for fast-to-evaluate 2D crack path prediction in heterogeneous materials
Jan 06, 2022

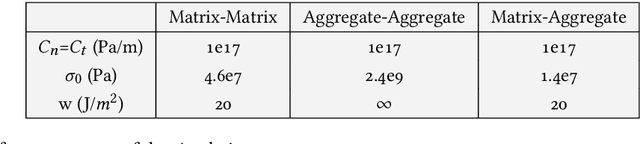

Abstract:This paper is devoted to the construction of a new fast-to-evaluate model for the prediction of 2D crack paths in concrete-like microstructures. The model generates piecewise linear cracks paths with segmentation points selected using a Markov chain model. The Markov chain kernel involves local indicators of mechanical interest and its parameters are learnt from numerical full-field 2D simulations of craking using a cohesive-volumetric finite element solver called XPER. The resulting model exhibits a drastic improvement of CPU time in comparison to simulations from XPER.
Numerical Sensitivity and Efficiency in the Treatment of Epistemic and Aleatory Uncertainty
Dec 13, 2007Abstract:The treatment of both aleatory and epistemic uncertainty by recent methods often requires an high computational effort. In this abstract, we propose a numerical sampling method allowing to lighten the computational burden of treating the information by means of so-called fuzzy random variables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge