Jayadev Billa
Improving Low-Resource Speech Recognition with Pretrained Speech Models: Continued Pretraining vs. Semi-Supervised Training
Jul 01, 2022
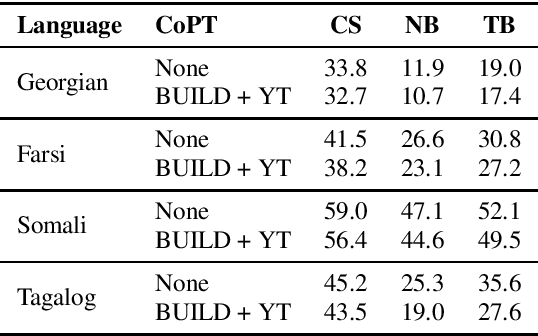

Abstract:Self-supervised Transformer based models, such as wav2vec 2.0 and HuBERT, have produced significant improvements over existing approaches to automatic speech recognition (ASR). This is evident in the performance of the wav2vec 2.0 based pretrained XLSR-53 model across many languages when fine-tuned with available labeled data. However, the performance from finetuning these models can be dependent on the amount of in-language or similar-to-in-language data included in the pretraining dataset. In this paper we investigate continued pretraining (CoPT) with unlabeled in-language audio data on the XLSR-53 pretrained model in several low-resource languages. CoPT is more computationally efficient than semi-supervised training (SST), the standard approach of utilizing unlabeled data in ASR, since it omits the need for pseudo-labeling of the unlabeled data. We show CoPT results in word error rates (WERs), equal to or slightly better than using SST. In addition, we show that using the CoPT model for pseudo-labeling, and using these labels in SST, results in further improvements in WER.
Improving low-resource ASR performance with untranscribed out-of-domain data
Jun 02, 2021


Abstract:Semi-supervised training (SST) is a common approach to leverage untranscribed/unlabeled speech data to improve automatic speech recognition performance in low-resource languages. However, if the available unlabeled speech is mismatched to the target domain, SST is not as effective, and in many cases performs worse than the original system. In this paper, we address the issue of low-resource ASR when only untranscribed out-of-domain speech data is readily available in the target language. Specifically, we look to improve performance on conversational/telephony speech (target domain) using web resources, in particular YouTube data, which more closely resembles news/topical broadcast data. Leveraging SST, we show that while in some cases simply pooling the out-of-domain data with the training data lowers word error rate (WER), in all cases, we see improvements if we train first with the out-of-domain data and then fine-tune the resulting model with the original training data. Using 2000 hours of speed perturbed YouTube audio in each target language, with semi-supervised transcripts, we show improvements on multiple languages/data sets, of up to 16.3% relative improvement in WER over the baseline systems and up to 7.4% relative improvement in WER over a system that simply pools the out-of-domain data with the training data.
Improving LSTM-CTC based ASR performance in domains with limited training data
May 23, 2018



Abstract:This paper addresses the observed performance gap between automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems based on Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks trained with the connectionist temporal classification (CTC) loss function and systems based on hybrid Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) trained with the cross entropy (CE) loss function on domains with limited data. We step through a number of experiments that show incremental improvements on a baseline EESEN toolkit based LSTM-CTC ASR system trained on the Librispeech 100hr (train-clean-100) corpus. Our results show that with effective combination of data augmentation and regularization, a LSTM-CTC based system can exceed the performance of a strong Kaldi based baseline trained on the same data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge