Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Javier Sánchez-Junquera
Unmasking Bias in News
Jun 11, 2019Figures and Tables:
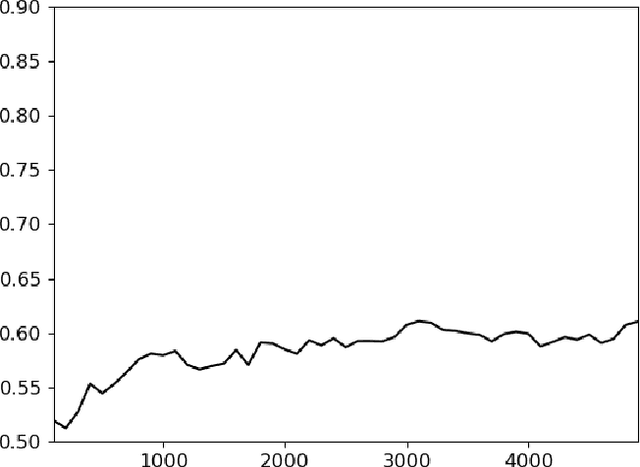
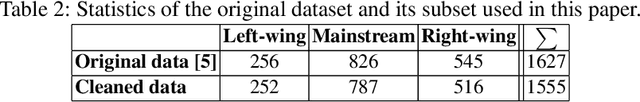





Abstract:We present experiments on detecting hyperpartisanship in news using a 'masking' method that allows us to assess the role of style vs. content for the task at hand. Our results corroborate previous research on this task in that topic related features yield better results than stylistic ones. We additionally show that competitive results can be achieved by simply including higher-length n-grams, which suggests the need to develop more challenging datasets and tasks that address implicit and more subtle forms of bias.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge