Jason D. Hales
General multi-fidelity surrogate models: Framework and active learning strategies for efficient rare event simulation
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:Estimating the probability of failure for complex real-world systems using high-fidelity computational models is often prohibitively expensive, especially when the probability is small. Exploiting low-fidelity models can make this process more feasible, but merging information from multiple low-fidelity and high-fidelity models poses several challenges. This paper presents a robust multi-fidelity surrogate modeling strategy in which the multi-fidelity surrogate is assembled using an active learning strategy using an on-the-fly model adequacy assessment set within a subset simulation framework for efficient reliability analysis. The multi-fidelity surrogate is assembled by first applying a Gaussian process correction to each low-fidelity model and assigning a model probability based on the model's local predictive accuracy and cost. Three strategies are proposed to fuse these individual surrogates into an overall surrogate model based on model averaging and deterministic/stochastic model selection. The strategies also dictate which model evaluations are necessary. No assumptions are made about the relationships between low-fidelity models, while the high-fidelity model is assumed to be the most accurate and most computationally expensive model. Through two analytical and two numerical case studies, including a case study evaluating the failure probability of Tristructural isotropic-coated (TRISO) nuclear fuels, the algorithm is shown to be highly accurate while drastically reducing the number of high-fidelity model calls (and hence computational cost).
Reliability Estimation of an Advanced Nuclear Fuel using Coupled Active Learning, Multifidelity Modeling, and Subset Simulation
Jan 06, 2022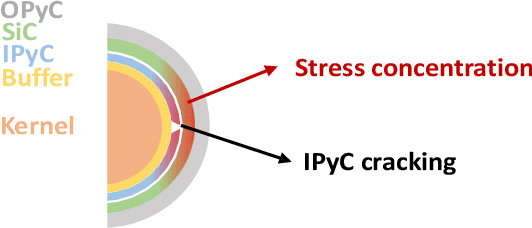
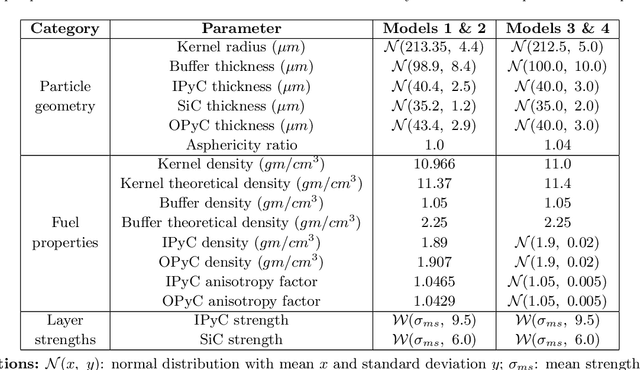
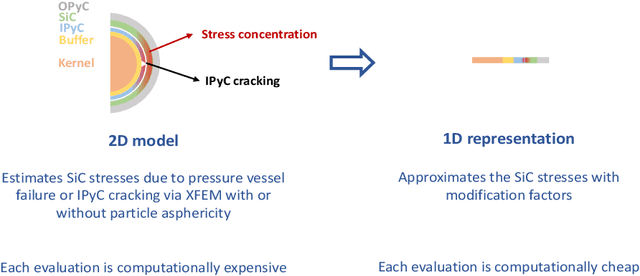
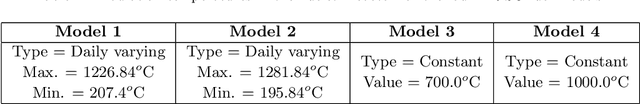
Abstract:Tristructural isotropic (TRISO)-coated particle fuel is a robust nuclear fuel and determining its reliability is critical for the success of advanced nuclear technologies. However, TRISO failure probabilities are small and the associated computational models are expensive. We used coupled active learning, multifidelity modeling, and subset simulation to estimate the failure probabilities of TRISO fuels using several 1D and 2D models. With multifidelity modeling, we replaced expensive high-fidelity (HF) model evaluations with information fusion from two low-fidelity (LF) models. For the 1D TRISO models, we considered three multifidelity modeling strategies: only Kriging, Kriging LF prediction plus Kriging correction, and deep neural network (DNN) LF prediction plus Kriging correction. While the results across these multifidelity modeling strategies compared satisfactorily, strategies employing information fusion from two LF models consistently called the HF model least often. Next, for the 2D TRISO model, we considered two multifidelity modeling strategies: DNN LF prediction plus Kriging correction (data-driven) and 1D TRISO LF prediction plus Kriging correction (physics-based). The physics-based strategy, as expected, consistently required the fewest calls to the HF model. However, the data-driven strategy had a lower overall simulation time since the DNN predictions are instantaneous, and the 1D TRISO model requires a non-negligible simulation time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge