Jasmine A. Berry
Agent Assessment of Others Through the Lens of Self
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:The maturation of cognition, from introspection to understanding others, has long been a hallmark of human development. This position paper posits that for AI systems to truly emulate or approach human-like interactions, especially within multifaceted environments populated with diverse agents, they must first achieve an in-depth and nuanced understanding of self. Drawing parallels with the human developmental trajectory from self-awareness to mentalizing (also called theory of mind), the paper argues that the quality of an autonomous agent's introspective capabilities of self are crucial in mirroring quality human-like understandings of other agents. While counterarguments emphasize practicality, computational efficiency, and ethical concerns, this position proposes a development approach, blending algorithmic considerations of self-referential processing. Ultimately, the vision set forth is not merely of machines that compute but of entities that introspect, empathize, and understand, harmonizing with the complex compositions of human cognition.
Counter-Hypothetical Particle Filters for Single Object Pose Tracking
May 28, 2023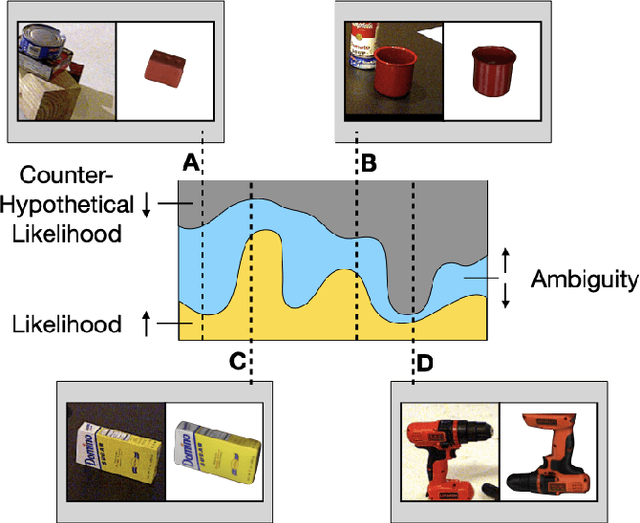
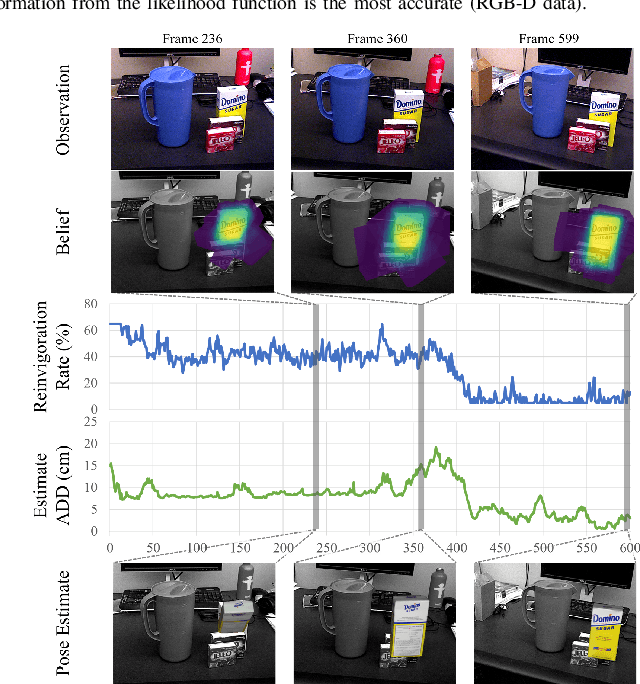
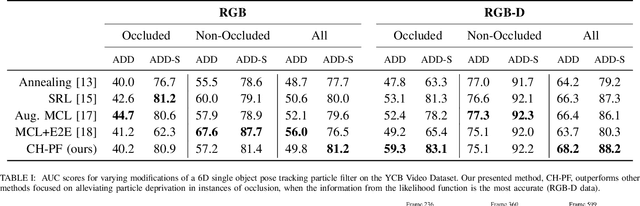
Abstract:Particle filtering is a common technique for six degree of freedom (6D) pose estimation due to its ability to tractably represent belief over object pose. However, the particle filter is prone to particle deprivation due to the high-dimensional nature of 6D pose. When particle deprivation occurs, it can cause mode collapse of the underlying belief distribution during importance sampling. If the region surrounding the true state suffers from mode collapse, recovering its belief is challenging since the area is no longer represented in the probability mass formed by the particles. Previous methods mitigate this problem by randomizing and resetting particles in the belief distribution, but determining the frequency of reinvigoration has relied on hand-tuning abstract heuristics. In this paper, we estimate the necessary reinvigoration rate at each time step by introducing a Counter-Hypothetical likelihood function, which is used alongside the standard likelihood. Inspired by the notions of plausibility and implausibility from Evidential Reasoning, the addition of our Counter-Hypothetical likelihood function assigns a level of doubt to each particle. The competing cumulative values of confidence and doubt across the particle set are used to estimate the level of failure within the filter, in order to determine the portion of particles to be reinvigorated. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on the rigid body object 6D pose tracking task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge