Jan-Peter Kucklick
A Comparison of Multi-View Learning Strategies for Satellite Image-Based Real Estate Appraisal
May 11, 2021
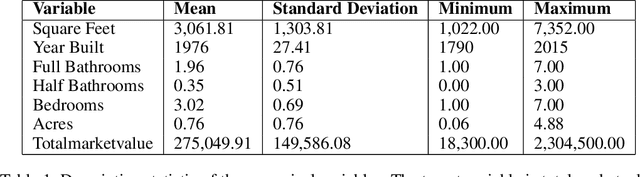
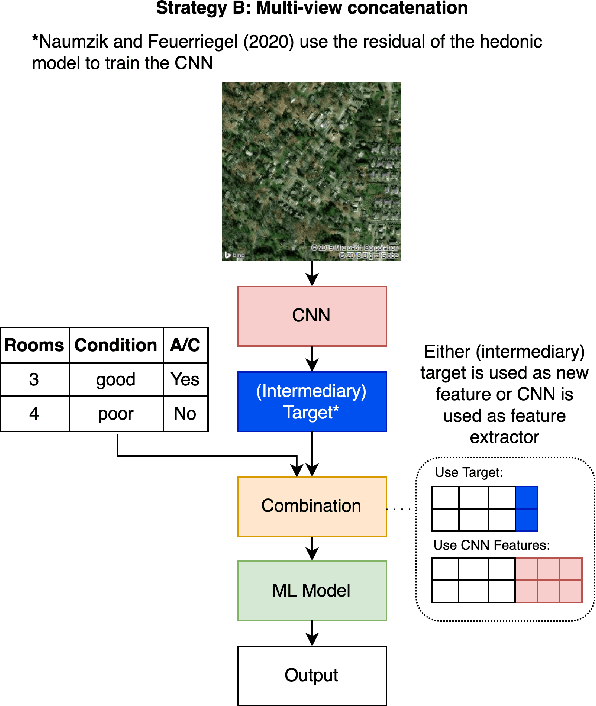

Abstract:In the house credit process, banks and lenders rely on a fast and accurate estimation of a real estate price to determine the maximum loan value. Real estate appraisal is often based on relational data, capturing the hard facts of the property. Yet, models benefit strongly from including image data, capturing additional soft factors. The combination of the different data types requires a multi-view learning method. Therefore, the question arises which strengths and weaknesses different multi-view learning strategies have. In our study, we test multi-kernel learning, multi-view concatenation and multi-view neural networks on real estate data and satellite images from Asheville, NC. Our results suggest that multi-view learning increases the predictive performance up to 13% in MAE. Multi-view neural networks perform best, however result in intransparent black-box models. For users seeking interpretability, hybrid multi-view neural networks or a boosting strategy are a suitable alternative.
Location, location, location: Satellite image-based real-estate appraisal
Jun 04, 2020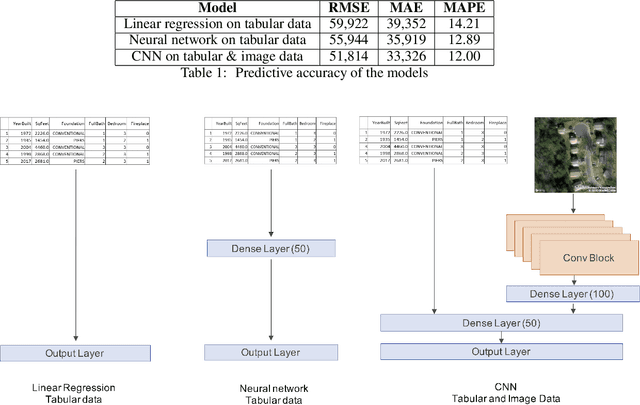
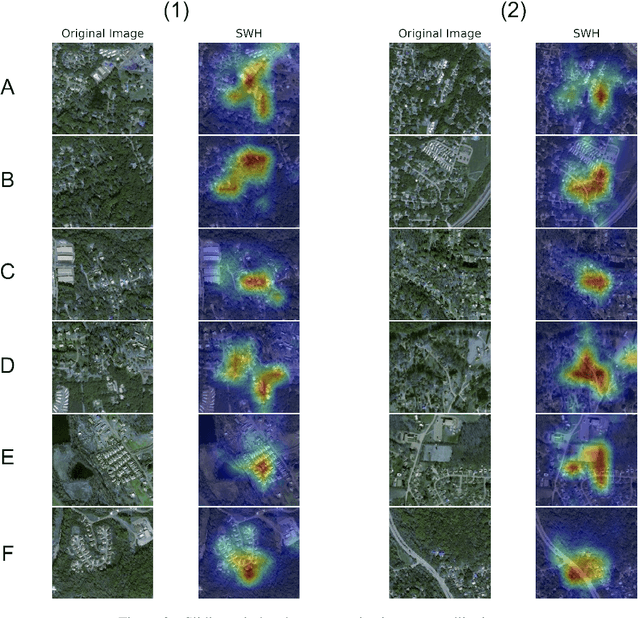
Abstract:Buying a home is one of the most important buying decisions people have to make in their life. The latest research on real-estate appraisal focuses on incorporating image data in addition to structured data into the modeling process. This research measures the prediction performance of satellite images and structured data by using convolutional neural networks. The resulting CNN model trained performs 7% better in MAE than the advanced baseline of a neural network trained on structured data. Moreover, sliding-window heatmap provides visual interpretability of satellite images, revealing that neighborhood structures are essential in the price estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge