Jan de Leeuw
Majorizing Stress Formula Two
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:Modifications of the smacof algorithm for multidimensional scaling are proposed that provide a convergent majorization algorithm for Kruskal's stress formula two.
Global Minima by Penalized Full-dimensional Scaling
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:The full-dimensional (metric, Euclidean, least squares) multidimensional scaling stress loss function is combined with a quadratic external penalty function term. The trajectory of minimizers of stress for increasing values of the penalty parameter is then used to find (tentative) global minima for low-dimensional multidimensional scaling. This is illustrated with several one-dimensional and two-dimensional examples.
Parcel loss prediction in last-mile delivery: deep and non-deep approaches with insights from Explainable AI
Oct 25, 2023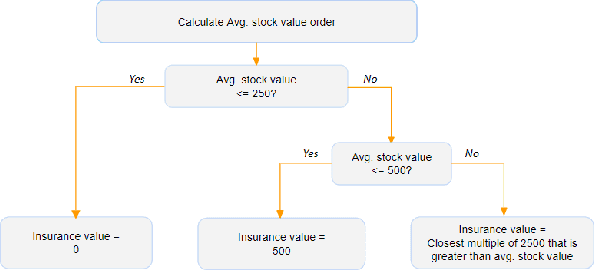
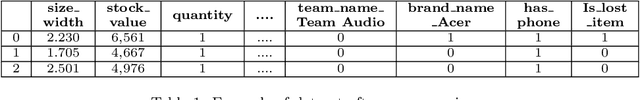
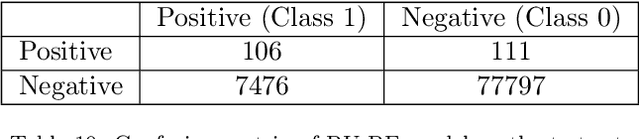
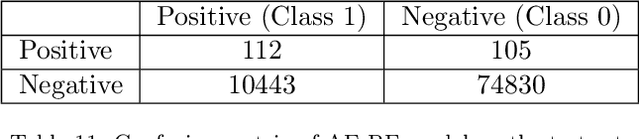
Abstract:Within the domain of e-commerce retail, an important objective is the reduction of parcel loss during the last-mile delivery phase. The ever-increasing availability of data, including product, customer, and order information, has made it possible for the application of machine learning in parcel loss prediction. However, a significant challenge arises from the inherent imbalance in the data, i.e., only a very low percentage of parcels are lost. In this paper, we propose two machine learning approaches, namely, Data Balance with Supervised Learning (DBSL) and Deep Hybrid Ensemble Learning (DHEL), to accurately predict parcel loss. The practical implication of such predictions is their value in aiding e-commerce retailers in optimizing insurance-related decision-making policies. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed machine learning models using one year data from Belgian shipments. The findings show that the DHEL model, which combines a feed-forward autoencoder with a random forest, achieves the highest classification performance. Furthermore, we use the techniques from Explainable AI (XAI) to illustrate how prediction models can be used in enhancing business processes and augmenting the overall value proposition for e-commerce retailers in the last mile delivery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge