Jake Rap
ON-Traffic: An Operator Learning Framework for Online Traffic Flow Estimation and Uncertainty Quantification from Lagrangian Sensors
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate traffic flow estimation and prediction are critical for the efficient management of transportation systems, particularly under increasing urbanization. Traditional methods relying on static sensors often suffer from limited spatial coverage, while probe vehicles provide richer, albeit sparse and irregular data. This work introduces ON-Traffic, a novel deep operator Network and a receding horizon learning-based framework tailored for online estimation of spatio-temporal traffic state along with quantified uncertainty by using measurements from moving probe vehicles and downstream boundary inputs. Our framework is evaluated in both numerical and simulation datasets, showcasing its ability to handle irregular, sparse input data, adapt to time-shifted scenarios, and provide well-calibrated uncertainty estimates. The results demonstrate that the model captures complex traffic phenomena, including shockwaves and congestion propagation, while maintaining robustness to noise and sensor dropout. These advancements present a significant step toward online, adaptive traffic management systems.
Merging Tasks for Video Panoptic Segmentation
Jul 10, 2021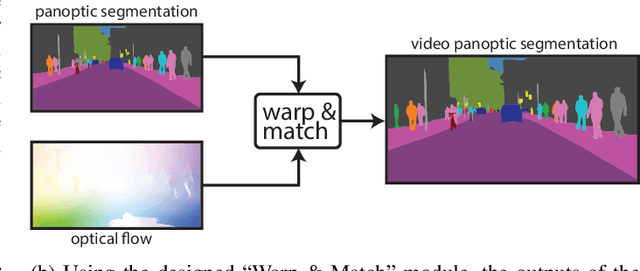
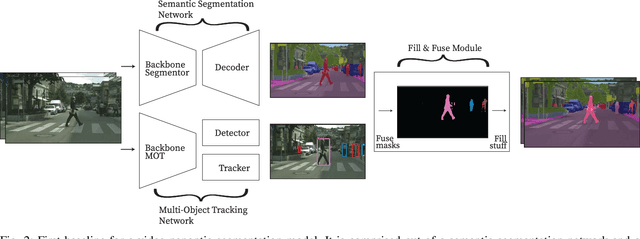


Abstract:In this paper, the task of video panoptic segmentation is studied and two different methods to solve the task will be proposed. Video panoptic segmentation (VPS) is a recently introduced computer vision task that requires classifying and tracking every pixel in a given video. The nature of this task makes the cost of annotating datasets for it prohibiting. To understand video panoptic segmentation, first, earlier introduced constituent tasks that focus on semantics and tracking separately will be researched. Thereafter, two data-driven approaches which do not require training on a tailored VPS dataset will be selected to solve it. The first approach will show how a model for video panoptic segmentation can be built by heuristically fusing the outputs of a pre-trained semantic segmentation model and a pre-trained multi-object tracking model. This can be desired if one wants to easily extend the capabilities of either model. The second approach will counter some of the shortcomings of the first approach by building on top of a shared neural network backbone with task-specific heads. This network is designed for panoptic segmentation and will be extended by a mask propagation module to link instance masks across time, yielding the video panoptic segmentation format.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge