Jagat Sesh Challa
Trust Regions Sell, But Who's Buying? Overlap Geometry as an Alternative Trust Region for Policy Optimization
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Standard trust-region methods constrain policy updates via Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence. However, KL controls only an average divergence and does not directly prevent rare, large likelihood-ratio excursions that destabilize training--precisely the failure mode that motivates heuristics such as PPO's clipping. We propose overlap geometry as an alternative trust region, constraining distributional overlap via the Bhattacharyya coefficient (closely related to the Hellinger/Renyi-1/2 geometry). This objective penalizes separation in the ratio tails, yielding tighter control over likelihood-ratio excursions without relying on total variation bounds that can be loose in tail regimes. We derive Bhattacharyya-TRPO (BTRPO) and Bhattacharyya-PPO (BPPO), enforcing overlap constraints via square-root ratio updates: BPPO clips the square-root ratio q = sqrt(r), and BTRPO applies a quadratic Hellinger/Bhattacharyya penalty. Empirically, overlap-based updates improve robustness and aggregate performance as measured by RLiable under matched training budgets, suggesting overlap constraints as a practical, principled alternative to KL for stable policy optimization.
Beyond Single Bugs: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Multi-Vulnerability Detection
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in automated software security, particularly in vulnerability detection. However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on isolated, single-vulnerability samples or function-level classification, failing to reflect the complexity of real-world software where multiple interacting vulnerabilities often coexist within large files. Recent studies indicate that LLMs suffer from "count bias" and "selection bias" in multi-label tasks, yet this has not been rigorously quantified in the domain of code security. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark for Multi-Vulnerability Detection across four major languages: C, C++, Python, and JavaScript. We construct a dataset of 40,000 files by systematically injecting controlled counts of vulnerabilities (1, 3, 5, and 9) into long-context code samples (7.5k-10k tokens) sourced from CodeParrot. We evaluate five state-of-the-art LLMs, including GPT-4o-mini, Llama-3.3-70B, and the Qwen-2.5 series. Our results reveal a sharp degradation in performance as vulnerability density increases. While Llama-3.3-70B achieves near-perfect F1 scores (approximately 0.97) on single-vulnerability C tasks, performance drops by up to 40% in high-density settings. Notably, Python and JavaScript show distinct failure modes compared to C/C++, with models exhibiting severe "under-counting" (Recall dropping to less than 0.30) in complex Python files.
CricBench: A Multilingual Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs in Cricket Analytics
Dec 26, 2025



Abstract:Cricket is the second most popular sport globally, commanding a massive following of over 2.5 billion fans globally. Enthusiasts and analysts frequently seek advanced statistical insights, such as long-term historical performance trends or complex player comparisons, that are often unavailable through standard web searches. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have advanced significantly in Text-to-SQL tasks, their capability to handle the domain-specific nuances, complex schema variations, and multilingual requirements inherent to sports analytics remains under-explored. To investigate this potential capability gap, we present CricBench, a comprehensive benchmark suite for evaluating LLMs on specialized cricket data. To curate a "Gold Standard" dataset, we collaborate with domain experts in cricket and SQL to manually author complex queries, ensuring logical correctness. Recognizing linguistic diversity, we construct the benchmark in both English and Hindi, establishing a framework that is open for further extension to other regional languages. We evaluate six state-of-the-art models, including GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and open-source models, using a strict evaluation protocol. Our results reveal that high performance on general benchmarks does not guarantee success in specialized domains. While the open-weights reasoning model DeepSeek R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance (50.6%), surpassing proprietary giants like Claude 3.7 Sonnet (47.7%) and GPT-4o (33.7%), it still exhibits a significant accuracy drop when moving from general benchmarks (BIRD) to CricBench. Furthermore, we observe that code-mixed Hindi queries frequently yield parity or higher accuracy compared to English, challenging the assumption that English is the optimal prompt language for specialized SQL tasks.
Exposing DeepFakes via Hyperspectral Domain Mapping
Nov 13, 2025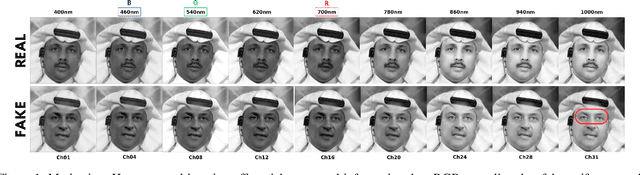
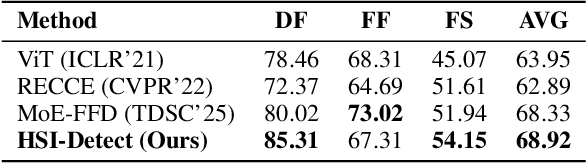
Abstract:Modern generative and diffusion models produce highly realistic images that can mislead human perception and even sophisticated automated detection systems. Most detection methods operate in RGB space and thus analyze only three spectral channels. We propose HSI-Detect, a two-stage pipeline that reconstructs a 31-channel hyperspectral image from a standard RGB input and performs detection in the hyperspectral domain. Expanding the input representation into denser spectral bands amplifies manipulation artifacts that are often weak or invisible in the RGB domain, particularly in specific frequency bands. We evaluate HSI-Detect across FaceForensics++ dataset and show the consistent improvements over RGB-only baselines, illustrating the promise of spectral-domain mapping for Deepfake detection.
Talking with Oompa Loompas: A novel framework for evaluating linguistic acquisition of LLM agents
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Existing evaluation studies on linguistic competence of large language models (LLM agents) have focused primarily on vocabulary learning, morphological rule induction, syntactic generalization, pragmatic inference, and cross-linguistic transfer. However, none assess whether LLM agents can acquire a language through pattern recognition and interactive feedback, a central feature of human language acquisition. We propose a novel experimental framework in which an LLM agent is evaluated on its ability to acquire and use a newly constructed language (Tinkatongue) in conversation with a bot that understands only Tinkatongue. Our findings show that LLM agents fail to establish a conversation within 100 responses, yet they adopt distinct strategies that mirror human approaches to language learning. The results suggest a new direction for evaluation benchmarks and open pathways to model designs that learn more effectively from interactive feedback.
HAEPO: History-Aggregated Exploratory Policy Optimization
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Exploration is essential in modern learning, from reinforcement learning environments with small neural policies to large language models (LLMs). Existing work, such as DPO, leverages full sequence log-likelihoods to capture an entire trajectory of the model's decisions, while methods like GRPO aggregate per-token ratios into a trajectory-level update. However, both often limit exploration on long-horizon tasks. We introduce History-Aggregated Exploratory Policy Optimization (HAEPO), a history-aware exploratory loss to combat these shortcomings. HAEPO compresses each trajectory into the sum of its logarithmic probabilities (a cumulative logarithmic likelihood), and applies a Plackett-Luce softmax across trajectories to obtain normalized weights proportional to their returns, thus encouraging broader exploration. We add entropy regularization to stabilize the aggressive updates to prevent premature collapse and a soft KL penalty relative to a frozen copy of the previous (reference) policy. Empirically, HAEPO converges fast, explores thoroughly, aligns closely with true rewards, and demonstrates robust learning behavior better or at par with PPO, GRPO, and DPO across diverse tasks. Thus, HAEPO provides a stable and interpretable framework by explicitly leveraging full-trajectory history while balancing exploration and stability.
SAC: A Framework for Measuring and Inducing Personality Traits in LLMs with Dynamic Intensity Control
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have gained significant traction across a wide range of fields in recent years. There is also a growing expectation for them to display human-like personalities during interactions. To meet this expectation, numerous studies have proposed methods for modelling LLM personalities through psychometric evaluations. However, most existing models face two major limitations: they rely on the Big Five (OCEAN) framework, which only provides coarse personality dimensions, and they lack mechanisms for controlling trait intensity. In this paper, we address this gap by extending the Machine Personality Inventory (MPI), which originally used the Big Five model, to incorporate the 16 Personality Factor (16PF) model, allowing expressive control over sixteen distinct traits. We also developed a structured framework known as Specific Attribute Control (SAC) for evaluating and dynamically inducing trait intensity in LLMs. Our method introduces adjective-based semantic anchoring to guide trait intensity expression and leverages behavioural questions across five intensity factors: \textit{Frequency}, \textit{Depth}, \textit{Threshold}, \textit{Effort}, and \textit{Willingness}. Through experimentation, we find that modelling intensity as a continuous spectrum yields substantially more consistent and controllable personality expression compared to binary trait toggling. Moreover, we observe that changes in target trait intensity systematically influence closely related traits in psychologically coherent directions, suggesting that LLMs internalize multi-dimensional personality structures rather than treating traits in isolation. Our work opens new pathways for controlled and nuanced human-machine interactions in domains such as healthcare, education, and interviewing processes, bringing us one step closer to truly human-like social machines.
Rubric Is All You Need: Enhancing LLM-based Code Evaluation With Question-Specific Rubrics
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Since the disruption in LLM technology brought about by the release of GPT-3 and ChatGPT, LLMs have shown remarkable promise in programming-related tasks. While code generation remains a popular field of research, code evaluation using LLMs remains a problem with no conclusive solution. In this paper, we focus on LLM-based code evaluation and attempt to fill in the existing gaps. We propose multi-agentic novel approaches using question-specific rubrics tailored to the problem statement, arguing that these perform better for logical assessment than the existing approaches that use question-agnostic rubrics. To address the lack of suitable evaluation datasets, we introduce two datasets: a Data Structures and Algorithms dataset containing 150 student submissions from a popular Data Structures and Algorithms practice website, and an Object Oriented Programming dataset comprising 80 student submissions from undergraduate computer science courses. In addition to using standard metrics (Spearman Correlation, Cohen's Kappa), we additionally propose a new metric called as Leniency, which quantifies evaluation strictness relative to expert assessment. Our comprehensive analysis demonstrates that question-specific rubrics significantly enhance logical assessment of code in educational settings, providing better feedback aligned with instructional goals beyond mere syntactic correctness.
"It's not like Jarvis, but it's pretty close!" -- Examining ChatGPT's Usage among Undergraduate Students in Computer Science
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Google Bard have garnered significant attention in the academic community. Previous research has evaluated these LLMs for various applications such as generating programming exercises and solutions. However, these evaluations have predominantly been conducted by instructors and researchers, not considering the actual usage of LLMs by students. This study adopts a student-first approach to comprehensively understand how undergraduate computer science students utilize ChatGPT, a popular LLM, released by OpenAI. We employ a combination of student surveys and interviews to obtain valuable insights into the benefits, challenges, and suggested improvements related to ChatGPT. Our findings suggest that a majority of students (over 57%) have a convincingly positive outlook towards adopting ChatGPT as an aid in coursework-related tasks. However, our research also highlights various challenges that must be resolved for long-term acceptance of ChatGPT amongst students. The findings from this investigation have broader implications and may be applicable to other LLMs and their role in computing education.
InFER: A Multi-Ethnic Indian Facial Expression Recognition Dataset
Sep 30, 2023
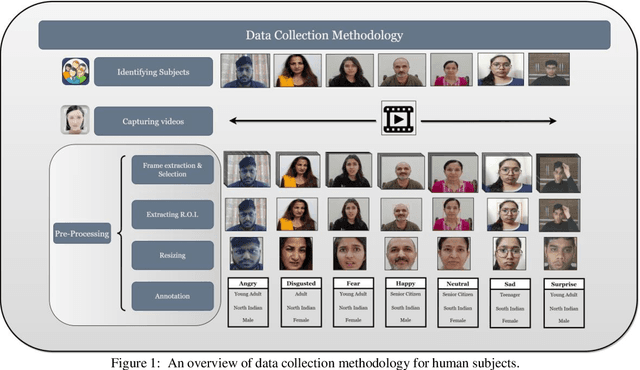


Abstract:The rapid advancement in deep learning over the past decade has transformed Facial Expression Recognition (FER) systems, as newer methods have been proposed that outperform the existing traditional handcrafted techniques. However, such a supervised learning approach requires a sufficiently large training dataset covering all the possible scenarios. And since most people exhibit facial expressions based upon their age group, gender, and ethnicity, a diverse facial expression dataset is needed. This becomes even more crucial while developing a FER system for the Indian subcontinent, which comprises of a diverse multi-ethnic population. In this work, we present InFER, a real-world multi-ethnic Indian Facial Expression Recognition dataset consisting of 10,200 images and 4,200 short videos of seven basic facial expressions. The dataset has posed expressions of 600 human subjects, and spontaneous/acted expressions of 6000 images crowd-sourced from the internet. To the best of our knowledge InFER is the first of its kind consisting of images from 600 subjects from very diverse ethnicity of the Indian Subcontinent. We also present the experimental results of baseline & deep FER methods on our dataset to substantiate its usability in real-world practical applications.
* In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence Volume 3: ICAART; ISBN 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN 2184-433X, SciTePress, pages 550-557. DOI: 10.5220/0011699400003393
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge