Jaewon Jang
Can Consumer Chatbots Reason? A Student-Led Field Experiment Embedded in an "AI-for-All" Undergraduate Course
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Claims about whether large language model (LLM) chatbots "reason" are typically debated using curated benchmarks and laboratory-style evaluation protocols. This paper offers a complementary perspective: a student-led field experiment embedded as a midterm project in UNIV 182 (AI4All) at George Mason University, a Mason Core course designed for undergraduates across disciplines with no expected prior STEM exposure. Student teams designed their own reasoning tasks, ran them on widely used consumer chatbots representative of current capabilities, and evaluated both (i) answer correctness and (ii) the validity of the chatbot's stated reasoning (for example, cases where an answer is correct but the explanation is not, or vice versa). Across eight teams that reported standardized scores, students contributed 80 original reasoning prompts spanning six categories: pattern completion, transformation rules, spatial/visual reasoning, quantitative reasoning, relational/logic reasoning, and analogical reasoning. These prompts yielded 320 model responses plus follow-up explanations. Aggregating team-level results, OpenAI GPT-5 and Claude 4.5 achieved the highest mean answer accuracy (86.2% and 83.8%), followed by Grok 4 (82.5%) and Perplexity (73.1%); explanation validity showed a similar ordering (81.2%, 80.0%, 77.5%, 66.2%). Qualitatively, teams converged on a consistent error signature: strong performance on short, structured math and pattern items but reduced reliability on spatial/visual reasoning and multi-step transformations, with frequent "sound right but reason wrong" explanations. The assignment's primary contribution is pedagogical: it operationalizes AI literacy as experimental practice (prompt design, measurement, rater disagreement, and interpretability/grounding) while producing a reusable, student-generated corpus of reasoning probes grounded in authentic end-user interaction.
Employing Genetic Algorithm as an Efficient Alternative to Parameter Sweep Based Multi-Layer Thickness Optimization in Solar Cells
Sep 26, 2019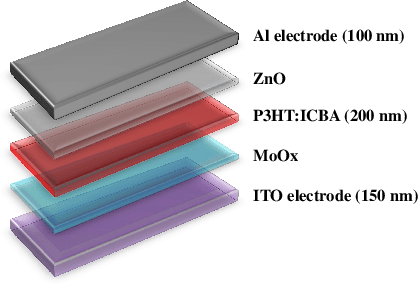
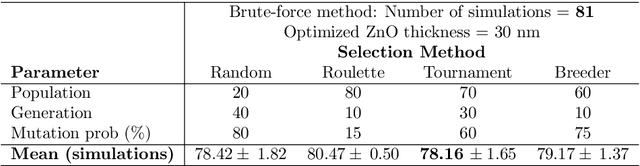
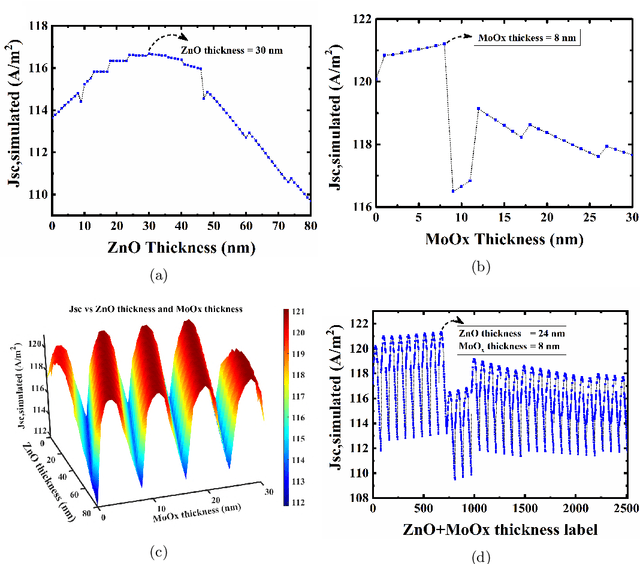
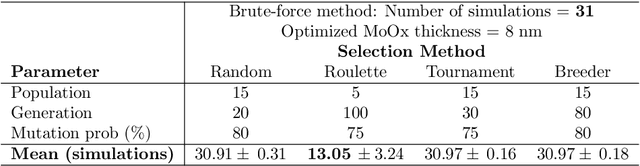
Abstract:Conventional solar cells are predominately designed similar to a stacked structure. Optimizing the layer thicknesses in this stack structure is crucial to extract the best efficiency of the solar cell. The commonplace method used in optimization simulations, such as for optimizing the optical spacer layers' thicknesses, is the parameter sweep. Our experiments show that the introduction of genetic algorithm based method results in a significantly faster and accurate search method when compared to brute-force parameter sweep method in both single and multi-layer optimization. While other sweep methods can also outperform the brute-force method, they do not consistently exhibit $100\%$ accuracy in the optimized results like our genetic algorithm. Our best case scenario was observed to utilize 57.9% less simulations than brute-force method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge