Jae-Hun Lee
Rethinking Evaluation Protocols of Visual Representations Learned via Self-supervised Learning
Apr 07, 2023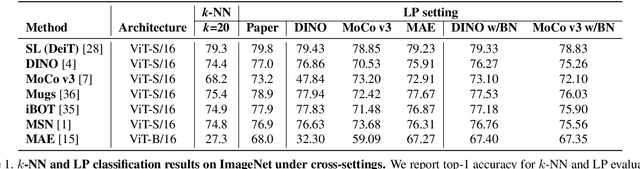
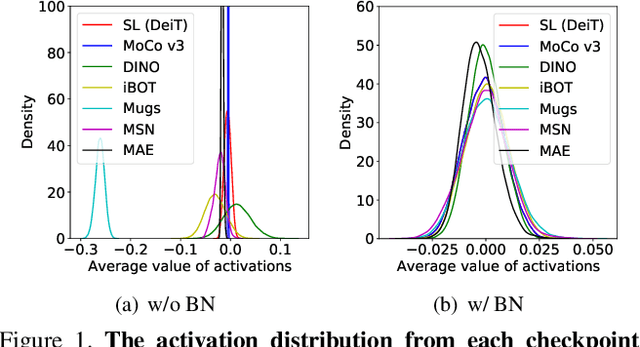
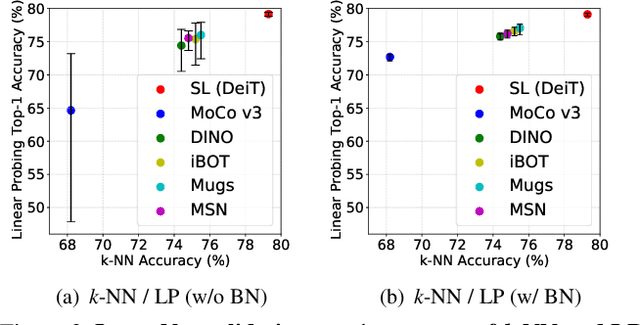

Abstract:Linear probing (LP) (and $k$-NN) on the upstream dataset with labels (e.g., ImageNet) and transfer learning (TL) to various downstream datasets are commonly employed to evaluate the quality of visual representations learned via self-supervised learning (SSL). Although existing SSL methods have shown good performances under those evaluation protocols, we observe that the performances are very sensitive to the hyperparameters involved in LP and TL. We argue that this is an undesirable behavior since truly generic representations should be easily adapted to any other visual recognition task, i.e., the learned representations should be robust to the settings of LP and TL hyperparameters. In this work, we try to figure out the cause of performance sensitivity by conducting extensive experiments with state-of-the-art SSL methods. First, we find that input normalization for LP is crucial to eliminate performance variations according to the hyperparameters. Specifically, batch normalization before feeding inputs to a linear classifier considerably improves the stability of evaluation, and also resolves inconsistency of $k$-NN and LP metrics. Second, for TL, we demonstrate that a weight decay parameter in SSL significantly affects the transferability of learned representations, which cannot be identified by LP or $k$-NN evaluations on the upstream dataset. We believe that the findings of this study will be beneficial for the community by drawing attention to the shortcomings in the current SSL evaluation schemes and underscoring the need to reconsider them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge