Jacob W. Bartel
GE2E-KWS: Generalized End-to-End Training and Evaluation for Zero-shot Keyword Spotting
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:We propose GE2E-KWS -- a generalized end-to-end training and evaluation framework for customized keyword spotting. Specifically, enrollment utterances are separated and grouped by keywords from the training batch and their embedding centroids are compared to all other test utterance embeddings to compute the loss. This simulates runtime enrollment and verification stages, and improves convergence stability and training speed by optimizing matrix operations compared to SOTA triplet loss approaches. To benchmark different models reliably, we propose an evaluation process that mimics the production environment and compute metrics that directly measure keyword matching accuracy. Trained with GE2E loss, our 419KB quantized conformer model beats a 7.5GB ASR encoder by 23.6% relative AUC, and beats a same size triplet loss model by 60.7% AUC. Our KWS models are natively streamable with low memory footprints, and designed to continuously run on-device with no retraining needed for new keywords (zero-shot).
Synth4Kws: Synthesized Speech for User Defined Keyword Spotting in Low Resource Environments
Jul 23, 2024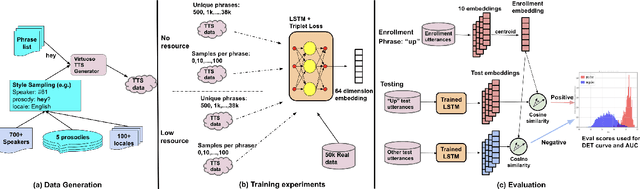
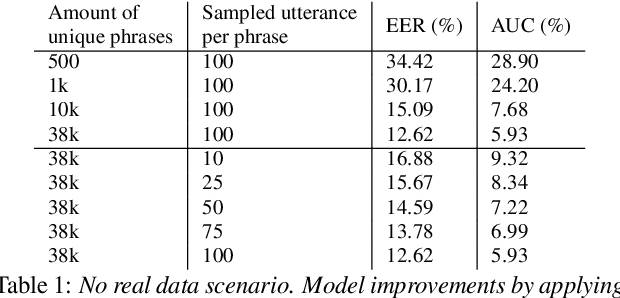
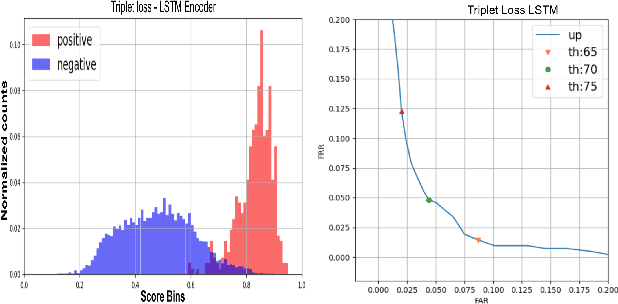
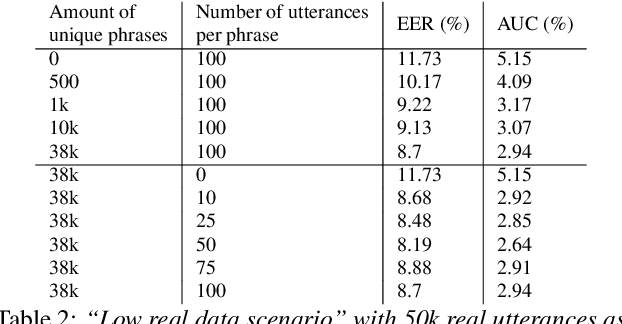
Abstract:One of the challenges in developing a high quality custom keyword spotting (KWS) model is the lengthy and expensive process of collecting training data covering a wide range of languages, phrases and speaking styles. We introduce Synth4Kws - a framework to leverage Text to Speech (TTS) synthesized data for custom KWS in different resource settings. With no real data, we found increasing TTS phrase diversity and utterance sampling monotonically improves model performance, as evaluated by EER and AUC metrics over 11k utterances of the speech command dataset. In low resource settings, with 50k real utterances as a baseline, we found using optimal amounts of TTS data can improve EER by 30.1% and AUC by 46.7%. Furthermore, we mix TTS data with varying amounts of real data and interpolate the real data needed to achieve various quality targets. Our experiments are based on English and single word utterances but the findings generalize to i18n languages and other keyword types.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge