Jacob Hartzer
Online Multi-IMU Calibration Using Visual-Inertial Odometry
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:This work presents a centralized multi-IMU filter framework with online intrinsic and extrinsic calibration for unsynchronized inertial measurement units that is robust against changes in calibration parameters. The novel EKF-based method estimates the positional and rotational offsets of the system of sensors as well as their intrinsic biases without the use of rigid body geometric constraints. Additionally, the filter is flexible in the total number of sensors used while leveraging the commonly used MSCKF framework for camera measurements. The filter framework has been validated using Monte Carlo simulation as well as experimentally. In both simulations and experiments, using multiple IMU measurement streams within the proposed filter framework outperforms the use of a single IMU in a filter prediction step while also producing consistent and accurate estimates of initial calibration errors. Compared to current state-of-the-art optimizers, the filter produces similar intrinsic and extrinsic calibration parameters for each sensor. Finally, an open source repository has been provided at https://github.com/unmannedlab/ekf-cal containing both the online estimator and the simulation used for testing and evaluation.
Online Multi Camera-IMU Calibration
Sep 28, 2022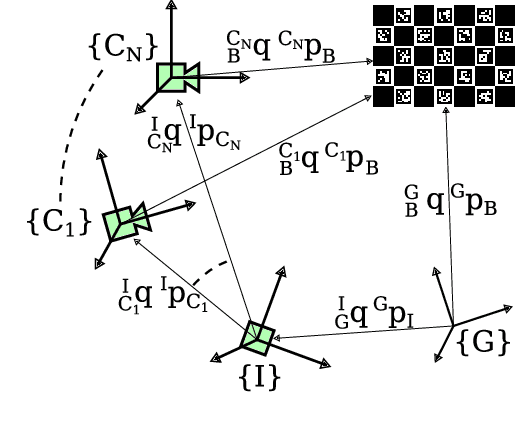

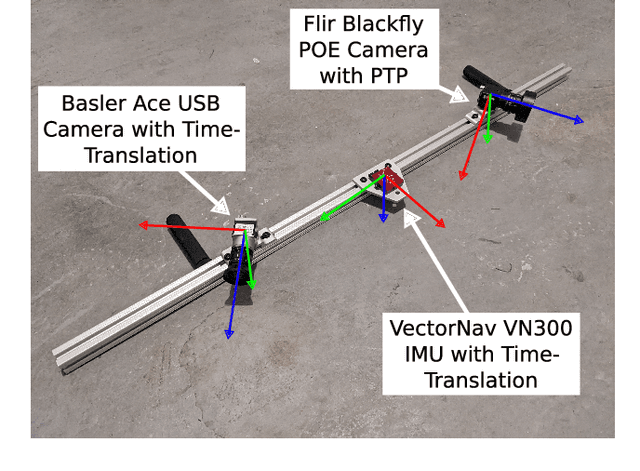
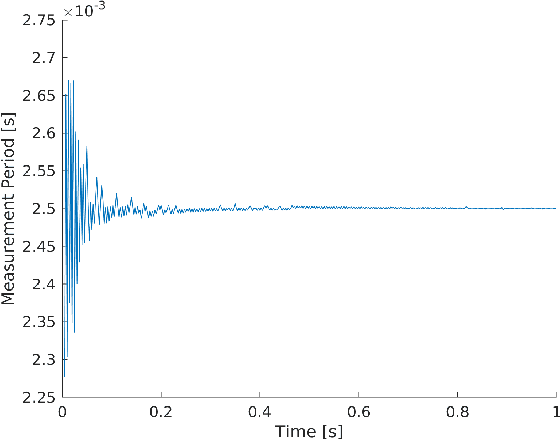
Abstract:Visual-inertial navigation systems are powerful in their ability to accurately estimate localization of mobile systems within complex environments that preclude the use of global navigation satellite systems. However, these navigation systems are reliant on accurate and up-to-date temporospatial calibrations of the sensors being used. As such, online estimators for these parameters are useful in resilient systems. This paper presents an extension to existing Kalman Filter based frameworks for estimating and calibrating the extrinsic parameters of multi-camera IMU systems. In addition to extending the filter framework to include multiple camera sensors, the measurement model was reformulated to make use of measurement data that is typically made available in fiducial detection software. A secondary filter layer was used to estimate time translation parameters without closed-loop feedback of sensor data. Experimental calibration results, including the use of cameras with non-overlapping fields of view, were used to validate the stability and accuracy of the filter formulation when compared to offline methods. Finally the generalized filter code has been open-sourced and is available online.
Vehicular Teamwork: Collaborative localization of Autonomous Vehicles
Apr 29, 2021



Abstract:This paper develops a distributed collaborative localization algorithm based on an extended kalman filter. This algorithm incorporates Ultra-Wideband (UWB) measurements for vehicle to vehicle ranging, and shows improvements in localization accuracy where GPS typically falls short. The algorithm was first tested in a newly created open-source simulation environment that emulates various numbers of vehicles and sensors while simultaneously testing multiple localization algorithms. Predicted error distributions for various algorithms are quickly producible using the Monte-Carlo method and optimization techniques within MatLab. The simulation results were validated experimentally in an outdoor, urban environment. Improvements of localization accuracy over a typical extended kalman filter ranged from 2.9% to 9.3% over 180 meter test runs. When GPS was denied, these improvements increased up to 83.3% over a standard kalman filter. In both simulation and experimentally, the DCL algorithm was shown to be a good approximation of a full state filter, while reducing required communication between vehicles. These results are promising in showing the efficacy of adding UWB ranging sensors to cars for collaborative and landmark localization, especially in GPS-denied environments. In the future, additional moving vehicles with additional tags will be tested in other challenging GPS denied environments.
AutoCone: An OmniDirectional Robot for Lane-Level Cone Placement
Apr 29, 2021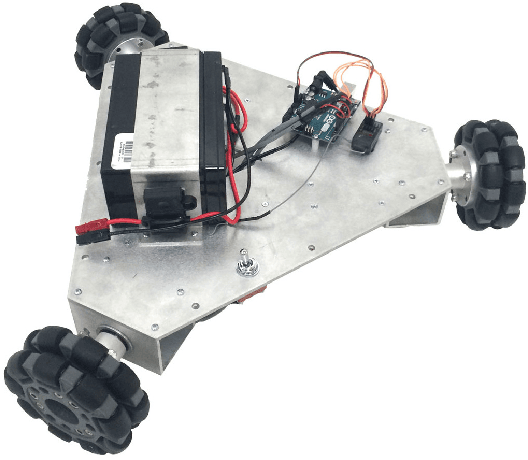
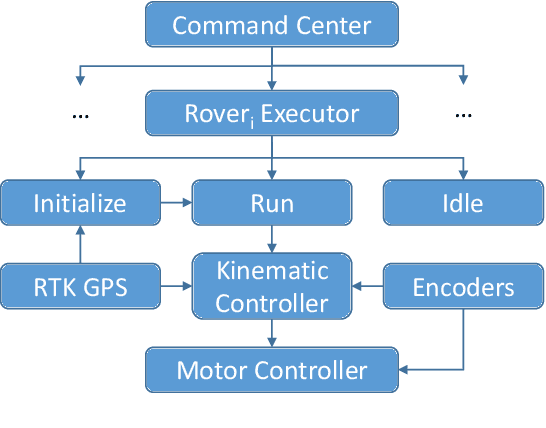
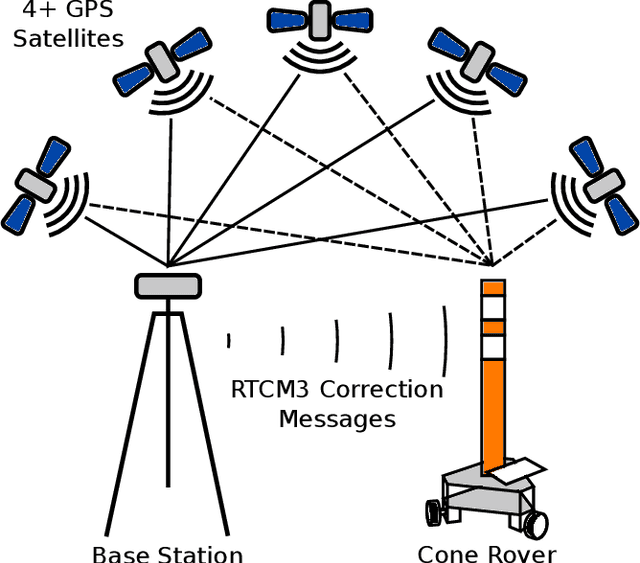

Abstract:This paper summarizes the progress in developing a rugged, low-cost, automated ground cone robot network capable of traffic delineation at lane-level precision. A holonomic omnidirectional base with a traffic delineator was developed to allow flexibility in initialization. RTK GPS was utilized to reduce minimum position error to 2 centimeters. Due to recent developments, the cost of the platform is now less than $1,600. To minimize the effects of GPS-denied environments, wheel encoders and an Extended Kalman Filter were implemented to maintain lane-level accuracy during operation and a maximum error of 1.97 meters through 50 meters with little to no GPS signal. Future work includes increasing the operational speed of the platforms, incorporating lanelet information for path planning, and cross-platform estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge