Jacob Carse
Calibrating Where It Matters: Constrained Temperature Scaling
Jun 17, 2024


Abstract:We consider calibration of convolutional classifiers for diagnostic decision making. Clinical decision makers can use calibrated classifiers to minimise expected costs given their own cost function. Such functions are usually unknown at training time. If minimising expected costs is the primary aim, algorithms should focus on tuning calibration in regions of probability simplex likely to effect decisions. We give an example, modifying temperature scaling calibration, and demonstrate improved calibration where it matters using convnets trained to classify dermoscopy images.
Unsupervised Representation Learning from Pathology Images with Multi-directional Contrastive Predictive Coding
May 11, 2021



Abstract:Digital pathology tasks have benefited greatly from modern deep learning algorithms. However, their need for large quantities of annotated data has been identified as a key challenge. This need for data can be countered by using unsupervised learning in situations where data are abundant but access to annotations is limited. Feature representations learned from unannotated data using contrastive predictive coding (CPC) have been shown to enable classifiers to obtain state of the art performance from relatively small amounts of annotated computer vision data. We present a modification to the CPC framework for use with digital pathology patches. This is achieved by introducing an alternative mask for building the latent context and using a multi-directional PixelCNN autoregressor. To demonstrate our proposed method we learn feature representations from the Patch Camelyon histology dataset. We show that our proposed modification can yield improved deep classification of histology patches.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Domain Dialogue Systems
Nov 26, 2016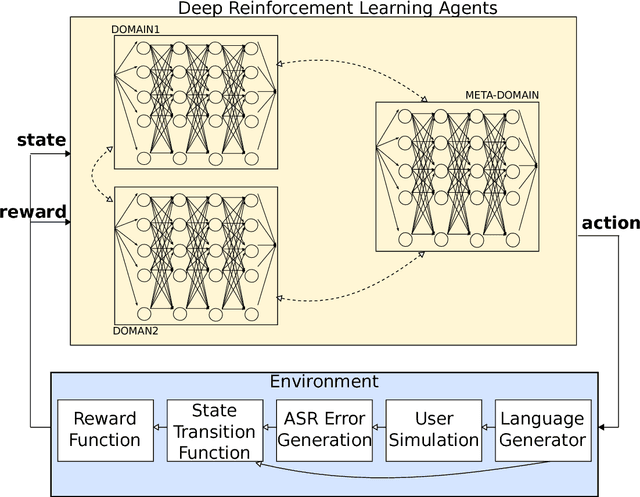
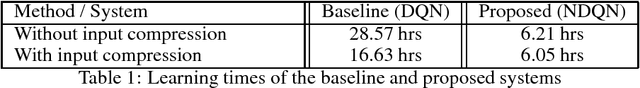
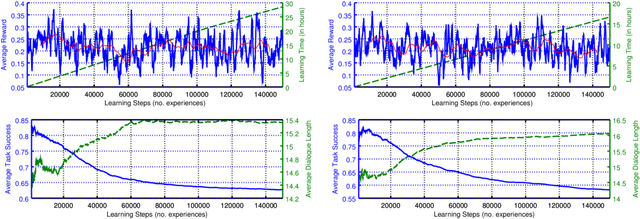
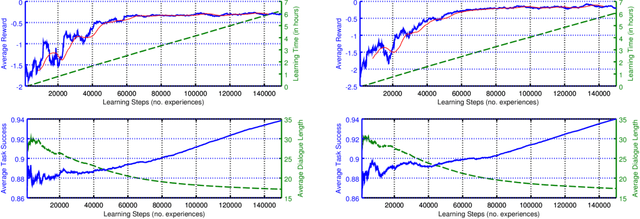
Abstract:Standard deep reinforcement learning methods such as Deep Q-Networks (DQN) for multiple tasks (domains) face scalability problems. We propose a method for multi-domain dialogue policy learning---termed NDQN, and apply it to an information-seeking spoken dialogue system in the domains of restaurants and hotels. Experimental results comparing DQN (baseline) versus NDQN (proposed) using simulations report that our proposed method exhibits better scalability and is promising for optimising the behaviour of multi-domain dialogue systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge