Jackson Kaunismaa
Eliciting Harmful Capabilities by Fine-Tuning On Safeguarded Outputs
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Model developers implement safeguards in frontier models to prevent misuse, for example, by employing classifiers to filter dangerous outputs. In this work, we demonstrate that even robustly safeguarded models can be used to elicit harmful capabilities in open-source models through elicitation attacks. Our elicitation attacks consist of three stages: (i) constructing prompts in adjacent domains to a target harmful task that do not request dangerous information; (ii) obtaining responses to these prompts from safeguarded frontier models; (iii) fine-tuning open-source models on these prompt-output pairs. Since the requested prompts cannot be used to directly cause harm, they are not refused by frontier model safeguards. We evaluate these elicitation attacks within the domain of hazardous chemical synthesis and processing, and demonstrate that our attacks recover approximately 40% of the capability gap between the base open-source model and an unrestricted frontier model. We then show that the efficacy of elicitation attacks scales with the capability of the frontier model and the amount of generated fine-tuning data. Our work demonstrates the challenge of mitigating ecosystem level risks with output-level safeguards.
How Do ConvNets Understand Image Intensity?
Jun 01, 2023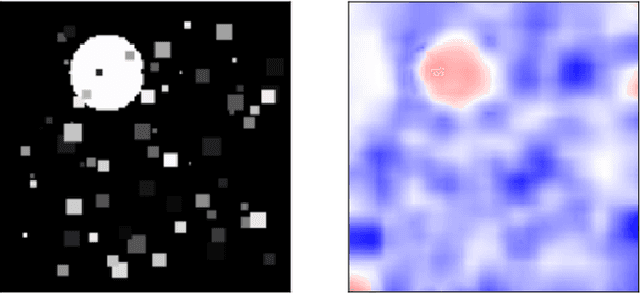
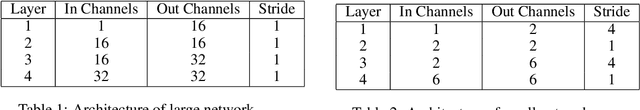

Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (ConvNets) usually rely on edge/shape information to classify images. Visualization methods developed over the last decade confirm that ConvNets rely on edge information. We investigate situations where the ConvNet needs to rely on image intensity in addition to shape. We show that the ConvNet relies on image intensity information using visualization.
cMelGAN: An Efficient Conditional Generative Model Based on Mel Spectrograms
May 15, 2022



Abstract:Analysing music in the field of machine learning is a very difficult problem with numerous constraints to consider. The nature of audio data, with its very high dimensionality and widely varying scales of structure, is one of the primary reasons why it is so difficult to model. There are many applications of machine learning in music, like the classifying the mood of a piece of music, conditional music generation, or popularity prediction. The goal for this project was to develop a genre-conditional generative model of music based on Mel spectrograms and evaluate its performance by comparing it to existing generative music models that use note-based representations. We initially implemented an autoregressive, RNN-based generative model called MelNet . However, due to its slow speed and low fidelity output, we decided to create a new, fully convolutional architecture that is based on the MelGAN [4] and conditional GAN architectures, called cMelGAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge