Jack Nikodem
A Realistic Simulation Framework for Learning with Label Noise
Jul 23, 2021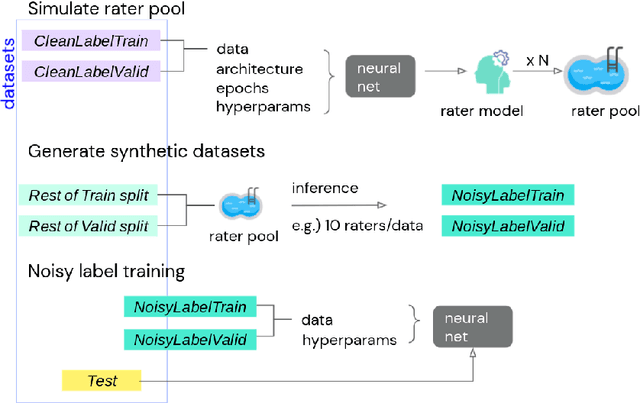
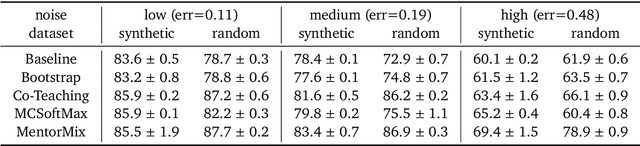
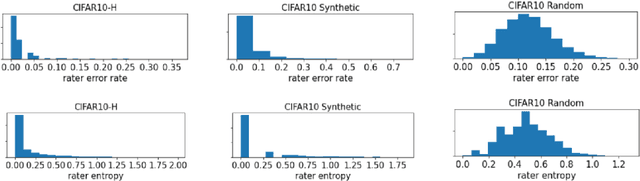
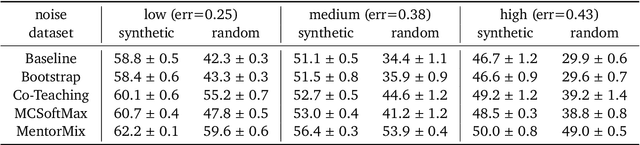
Abstract:We propose a simulation framework for generating realistic instance-dependent noisy labels via a pseudo-labeling paradigm. We show that this framework generates synthetic noisy labels that exhibit important characteristics of the label noise in practical settings via comparison with the CIFAR10-H dataset. Equipped with controllable label noise, we study the negative impact of noisy labels across a few realistic settings to understand when label noise is more problematic. We also benchmark several existing algorithms for learning with noisy labels and compare their behavior on our synthetic datasets and on the datasets with independent random label noise. Additionally, with the availability of annotator information from our simulation framework, we propose a new technique, Label Quality Model (LQM), that leverages annotator features to predict and correct against noisy labels. We show that by adding LQM as a label correction step before applying existing noisy label techniques, we can further improve the models' performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge