Jack Naylor
dLITE: Differentiable Lighting-Informed Trajectory Evaluation for On-Orbit Inspection
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Visual inspection of space-borne assets is of increasing interest to spacecraft operators looking to plan maintenance, characterise damage, and extend the life of high-value satellites in orbit. The environment of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) presents unique challenges when planning inspection operations that maximise visibility, information, and data quality. Specular reflection of sunlight from spacecraft bodies, self-shadowing, and dynamic lighting in LEO significantly impact the quality of data captured throughout an orbit. This is exacerbated by the relative motion between spacecraft, which introduces variable imaging distances and attitudes during inspection. Planning inspection trajectories with the aide of simulation is a common approach. However, the ability to design and optimise an inspection trajectory specifically to improve the resulting image quality in proximity operations remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present $\partial$LITE, an end-to-end differentiable simulation pipeline for on-orbit inspection operations. We leverage state-of-the-art differentiable rendering tools and a custom orbit propagator to enable end-to-end optimisation of orbital parameters based on visual sensor data. $\partial$LITE enables us to automatically design non-obvious trajectories, vastly improving the quality and usefulness of attained data. To our knowledge, our differentiable inspection-planning pipeline is the first of its kind and provides new insights into modern computational approaches to spacecraft mission planning. Project page: https://appearance-aware.github.io/dlite/
Surf-NeRF: Surface Regularised Neural Radiance Fields
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) provide a high fidelity, continuous scene representation that can realistically represent complex behaviour of light. Despite recent works like Ref-NeRF improving geometry through physics-inspired models, the ability for a NeRF to overcome shape-radiance ambiguity and converge to a representation consistent with real geometry remains limited. We demonstrate how curriculum learning of a surface light field model helps a NeRF converge towards a more geometrically accurate scene representation. We introduce four additional regularisation terms to impose geometric smoothness, consistency of normals and a separation of Lambertian and specular appearance at geometry in the scene, conforming to physical models. Our approach yields improvements of 14.4% to normals on positionally encoded NeRFs and 9.2% on grid-based models compared to current reflection-based NeRF variants. This includes a separated view-dependent appearance, conditioning a NeRF to have a geometric representation consistent with the captured scene. We demonstrate compatibility of our method with existing NeRF variants, as a key step in enabling radiance-based representations for geometry critical applications.
NOCaL: Calibration-Free Semi-Supervised Learning of Odometry and Camera Intrinsics
Oct 18, 2022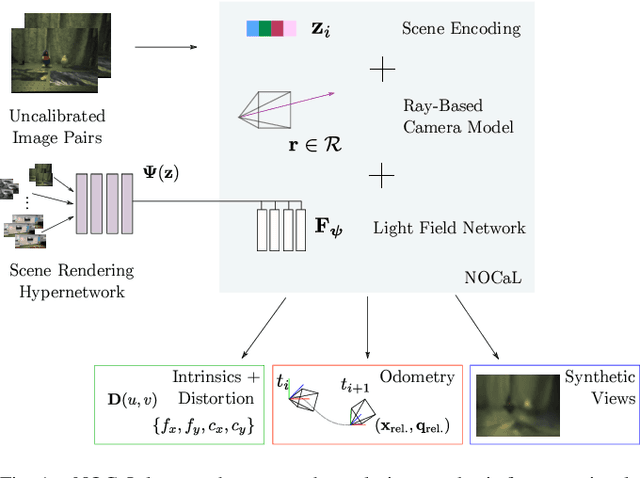
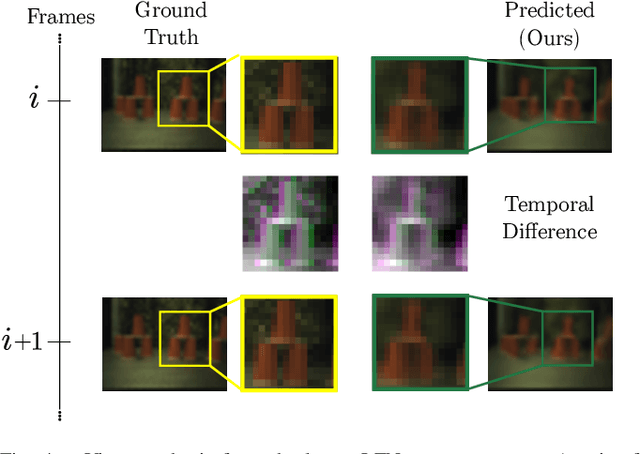
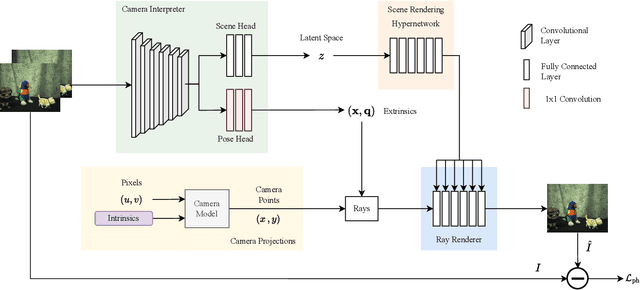
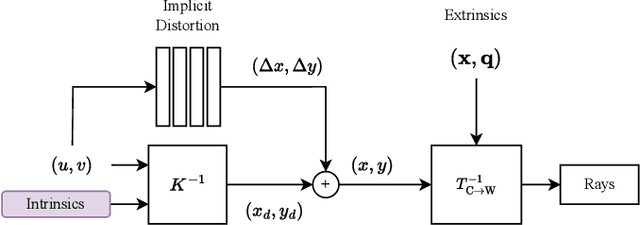

Abstract:There are a multitude of emerging imaging technologies that could benefit robotics. However the need for bespoke models, calibration and low-level processing represents a key barrier to their adoption. In this work we present NOCaL, Neural odometry and Calibration using Light fields, a semi-supervised learning architecture capable of interpreting previously unseen cameras without calibration. NOCaL learns to estimate camera parameters, relative pose, and scene appearance. It employs a scene-rendering hypernetwork pretrained on a large number of existing cameras and scenes, and adapts to previously unseen cameras using a small supervised training set to enforce metric scale. We demonstrate NOCaL on rendered and captured imagery using conventional cameras, demonstrating calibration-free odometry and novel view synthesis. This work represents a key step toward automating the interpretation of general camera geometries and emerging imaging technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge