J. Jothi Balaji
Automated Detection and Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Comprehensive Survey
Jun 30, 2021
Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of vision loss in the world,. In the past few Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of vision loss in the world. In the past few years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) based approaches have been used to detect and grade DR. Early detection enables appropriate treatment and thus prevents vision loss, Both fundus and optical coherence tomography (OCT) images are used to image the retina. With deep learning/machine learning apprroaches it is possible to extract features from the images and detect the presence of DR. Multiple strategies are implemented to detect and grade the presence of DR using classification, segmentation, and hybrid techniques. This review covers the literature dealing with AI approaches to DR that have been published in the open literature over a five year span (2016-2021). In addition a comprehensive list of available DR datasets is reported. Both the PICO (P-patient, I-intervention, C-control O-outcome) and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA)2009 search strategies were employed. We summarize a total of 114 published articles which conformed to the scope of the review. In addition a list of 43 major datasets is presented.
Quantitative and Qualitative Evaluation of Explainable Deep Learning Methods for Ophthalmic Diagnosis
Sep 26, 2020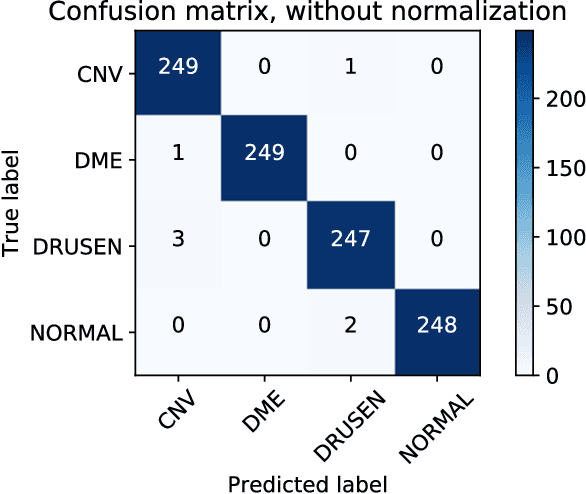
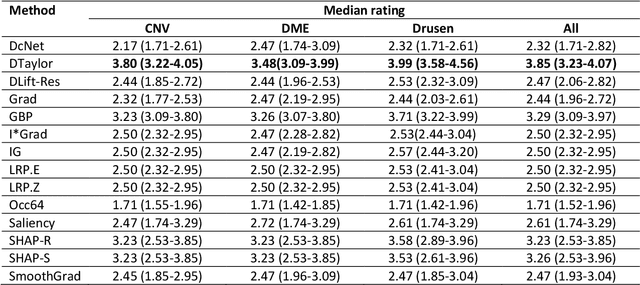
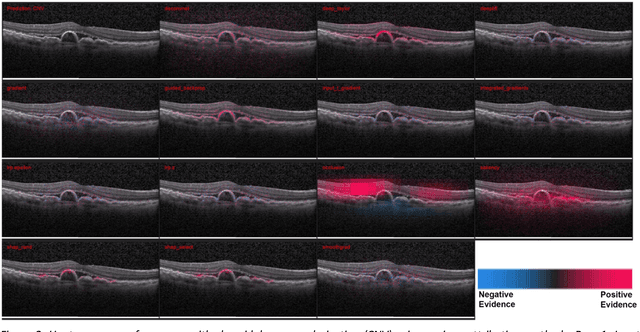
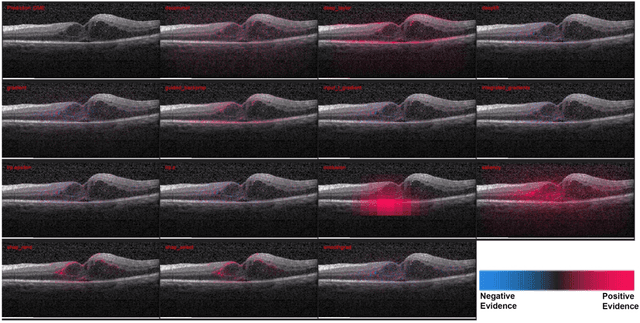
Abstract:Background: The lack of explanations for the decisions made by algorithms such as deep learning has hampered their acceptance by the clinical community despite highly accurate results on multiple problems. Recently, attribution methods have emerged for explaining deep learning models, and they have been tested on medical imaging problems. The performance of attribution methods is compared on standard machine learning datasets and not on medical images. In this study, we perform a comparative analysis to determine the most suitable explainability method for retinal OCT diagnosis. Methods: A commonly used deep learning model known as Inception v3 was trained to diagnose 3 retinal diseases - choroidal neovascularization (CNV), diabetic macular edema (DME), and drusen. The explanations from 13 different attribution methods were rated by a panel of 14 clinicians for clinical significance. Feedback was obtained from the clinicians regarding the current and future scope of such methods. Results: An attribution method based on a Taylor series expansion, called Deep Taylor was rated the highest by clinicians with a median rating of 3.85/5. It was followed by two other attribution methods, Guided backpropagation and SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations). Conclusion: Explanations of deep learning models can make them more transparent for clinical diagnosis. This study compared different explanations methods in the context of retinal OCT diagnosis and found that the best performing method may not be the one considered best for other deep learning tasks. Overall, there was a high degree of acceptance from the clinicians surveyed in the study. Keywords: explainable AI, deep learning, machine learning, image processing, Optical coherence tomography, retina, Diabetic macular edema, Choroidal Neovascularization, Drusen
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge